复杂库实现了复杂类,以包含笛卡尔形式的复数以及用于对其进行操作的若干函数和重载。 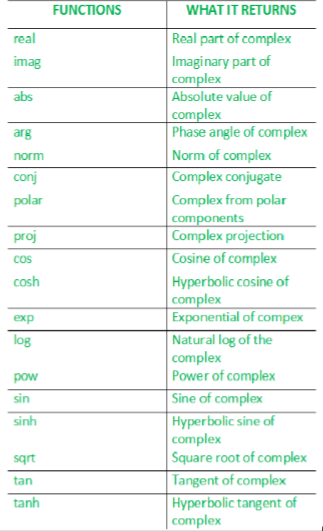
- real() –返回复数的实数部分。
- imag() –返回复数的虚部。
// Program illustrating the use of real() and // imag() function #include// for std::complex, std::real, std::imag #include using namespace std; // driver function int main() { // defines the complex number: (10 + 2i) std::complex mycomplex(10.0, 2.0); // prints the real part using the real function cout << "Real part: " << real(mycomplex) << endl; cout << "Imaginary part: " << imag(mycomplex) << endl; return 0; } 输出:
Real part: 10 Imaginary part: 2 - abs() –返回复数的绝对值。
- arg() –返回复数的参数。
// Program illustrating the use of arg() and abs() #include// for std::complex, std::abs, std::atg #include using namespace std; // driver function int main () { // defines the complex number: (3.0+4.0i) std::complex mycomplex (3.0, 4.0); // prints the absolute value of the complex number cout << "The absolute value of " << mycomplex << " is: "; cout << abs(mycomplex) << endl; // prints the argument of the complex number cout << "The argument of " << mycomplex << " is: "; cout << arg(mycomplex) << endl; return 0; } 输出:
The absolute value of (3,4) is: 5 The argument of (3,4) is: 0.927295 - polar() –它从幅度和相位角度构造一个复数。
实=幅度*余弦(相角)
虚数=大小*正弦(相角)// Program illustrating the use of polar() #include// std::complex, std::polar #include using namespace std; // driver function int main () { cout << "The complex whose magnitude is " << 2.0; cout << " and phase angle is " << 0.5; // use of polar() cout << " is " << polar (2.0, 0.5) << endl; return 0; } 输出:
The complex whose magnitude is 2 and phase angle is 0.5 is (1.75517,0.958851) - norm() –用于查找复数的范数(绝对值)。如果z = x + iy是具有实部x和虚部y的复数,则z的复共轭定义为z’(z bar)= x – iy,并且z的绝对值(也称为范数)定义为:
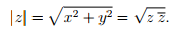
// example to illustrate the use of norm() #include// for std::complex, std::norm #include using namespace std; // driver function int main () { // initializing the complex: (3.0+4.0i) std::complex mycomplex (3.0, 4.0); // use of norm() cout << "The norm of " << mycomplex << " is " << norm(mycomplex) < 输出:
The norm of (3,4) is 25. - conj() –返回复数x的共轭。复数(real,imag)的共轭是(real,-imag)。
// Illustrating the use of conj() #includeusing namespace std; // std::complex, std::conj #include // driver program int main () { std::complex mycomplex (10.0,2.0); cout << "The conjugate of " << mycomplex << " is: "; // use of conj() cout << conj(mycomplex) << endl; return 0; } 输出:
The conjugate of (10,2) is (10,-2) - proj() –返回z(复数)在黎曼球面上的投影。 z的投影为z,除复数无穷外,根据z虚数分量的符号,复数无限性映射到具有INFINITY的实数分量和虚数分量为0.0或-0.0(在支持的情况下)的复数值。
// Illustrating the use of proj() #includeusing namespace std; // For std::complex, std::proj #include // driver program int main() { std::complex c1(1, 2); cout << "proj" << c1 << " = " << proj(c1) << endl; std::complex c2(INFINITY, -1); cout << "proj" << c2 << " = " << proj(c2) << endl; std::complex c3(0, -INFINITY); cout << "proj" << c3 << " = " << proj(c3) << endl; } 输出:
proj(1,2) = (1,2) proj(inf,-1) = (inf,-0) proj(0,-inf) = (inf,-0) - sqrt() –使用主体分支返回x的平方根,该主体的切割沿负实轴。
// Illustrating the use of sqrt() #includeusing namespace std; // For std::ccomplex, stdc::sqrt #include // driver program int main() { // use of sqrt() cout << "Square root of -4 is " << sqrt(std::complex (-4, 0)) << endl << "Square root of (-4,-0), the other side of the cut, is " << sqrt(std::complex (-4, -0.0)) << endl; } 输出:
Square root of -4 is (0,2) Square root of (-4,-0), the other side of the cut, is (0,-2)
下一篇文章:C++中的复数套装2
要从最佳影片策划和实践问题去学习,检查了C++基础课程为基础,以先进的C++和C++ STL课程基础加上STL。要完成从学习语言到DS Algo等的更多准备工作,请参阅“完整面试准备课程” 。