给定一棵树,其中每个顶点V都有一个值A [V]存储在其中。任务是找到使树的所有顶点中存储的值等于零所需的最少操作数。
每个操作包括以下两个步骤:
- 选择一个子树,使该子树包含顶点1。
- 将子树的所有顶点的值增加/减少1。
考虑以下树:
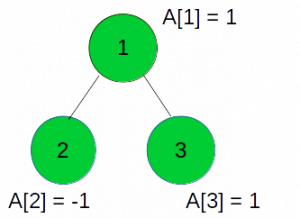
注意:顶点中的数字表示顶点数,A [V]表示顶点的值,如上所述。
对于以下树,我们执行以下3个操作以使值成为所有顶点
等于零: 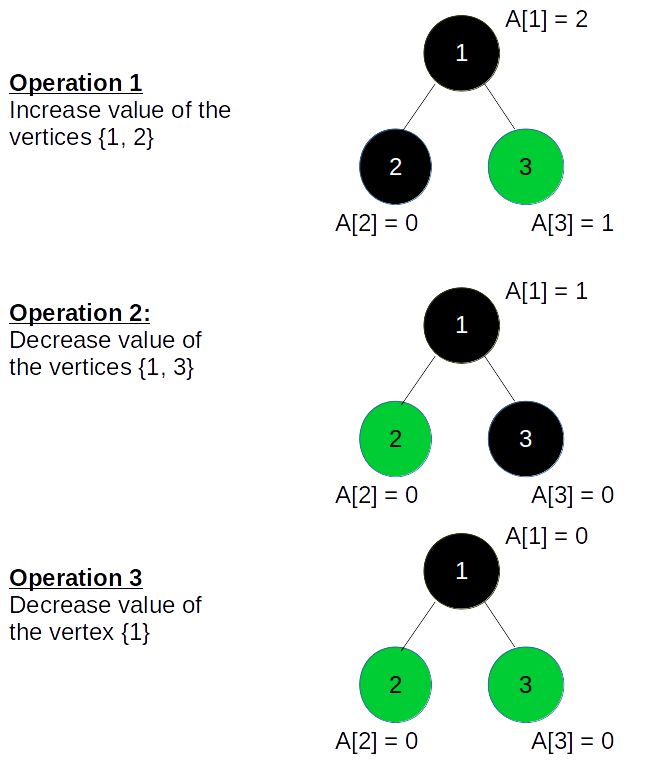
注意:黑色的顶点表示所选的子树。
我们可以使用动态编程解决此问题。
令dp [i] [0]表示选择以i为根的任何子树并且所有顶点的值增加1的操作数。
类似地,dp [i] [1]表示选择以i为根的任何子树并且所有顶点的值都减少1的操作数。
对于所有叶子,如果说叶子节点V使得某个叶子节点U的A [V] = 0,即dp [i] [ 1] = A [V]和dp [i] [0] = 0
现在,如果我们在某个非叶节点中说v,我们看一下它的所有子节点,如果说对V的一个子节点i进行X i次加法运算,那么我们需要对节点的所有子节点i应用max(X i v),增加对任何以v为根的子树的操作。类似地,我们对减少节点V的操作进行相同的操作。
答案是节点1的增加和减少操作的总和,因为这些操作仅应用于具有节点1的子树。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// CPP program to find the Minimum Operations
// to modify values of all tree vertices to zero
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function to add an edge in an
// undirected graph
void addEdge(vector adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
// A utility function to print the adjacency list
// representation of graph
void printGraph(vector adj[], int V)
{
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
cout << "\n Adjacency list of vertex "
<< v << "\n head ";
for (auto x : adj[v])
cout << "-> " << x;
printf("\n");
}
}
// Utility Function for findMinOperation()
void findMinOperationUtil(int dp[][2], vector adj[],
int A[], int src, int parent)
{
// Base Case for current node
dp[src][0] = dp[src][1] = 0;
// iterate over the adjacency list for src
for (auto V : adj[src]) {
if (V == parent)
continue;
// calculate DP table for each child V
findMinOperationUtil(dp, adj, A, V, src);
// Number of Increase Type operations for node src
// is equal to maximum of number of increase operations
// required by each of its child
dp[src][0] = max(dp[src][0], dp[V][0]);
// Number of Decrease Type operations for node src
// is equal to maximum of number of decrease operations
// required by each of its child
dp[src][1] = max(dp[src][1], dp[V][1]);
}
// After performing operations for subtree rooted at src
// A[src] changes by the net difference of increase and
// decrease type operations
A[src - 1] += dp[src][0] - dp[src][1];
// for negative value of node src
if (A[src - 1] > 0) {
dp[src][1] += A[src - 1];
}
else {
dp[src][0] += abs(A[src - 1]);
}
}
// Returns the minimum operations required to make
// value of all vertices equal to zero, uses
// findMinOperationUtil()
int findMinOperation(vector adj[], int A[], int V)
{
// Initialise DP table
int dp[V + 1][2];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
// find dp[1][0] and dp[1][1]
findMinOperationUtil(dp, adj, A, 1, 0);
int minOperations = dp[1][0] + dp[1][1];
return minOperations;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int V = 5;
// Build the Graph/Tree
vector adj[V + 1];
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
int A[] = { 1, -1, 1 };
int minOperations = findMinOperation(adj, A, V);
cout << minOperations;
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to find the Minimum Operations
# to modify values of all tree vertices to zero
# A utility function to add an
# edge in an undirected graph
def addEdge(adj, u, v):
adj[u].append(v)
adj[v].append(u)
# A utility function to print the adjacency
# list representation of graph
def printGraph(adj, V):
for v in range(0, V):
print("Adjacency list of vertex", v)
print("head", end = " ")
for x in adj[v]:
print("->", x, end = "")
print()
# Utility Function for findMinOperation()
def findMinOperationUtil(dp, adj, A, src, parent):
# Base Case for current node
dp[src][0] = dp[src][1] = 0
# Iterate over the adjacency list for src
for V in adj[src]:
if V == parent:
continue
# calculate DP table for each child V
findMinOperationUtil(dp, adj, A, V, src)
# Number of Increase Type operations for node src
# is equal to maximum of number of increase operations
# required by each of its child
dp[src][0] = max(dp[src][0], dp[V][0])
# Number of Decrease Type operations for node
# src is equal to maximum of number of decrease
# operations required by each of its child
dp[src][1] = max(dp[src][1], dp[V][1])
# After performing operations for subtree rooted
# at src A[src] changes by the net difference of
# increase and decrease type operations
A[src - 1] += dp[src][0] - dp[src][1]
# for negative value of node src
if A[src - 1] > 0:
dp[src][1] += A[src - 1]
else:
dp[src][0] += abs(A[src - 1])
# Returns the minimum operations required to
# make value of all vertices equal to zero,
# uses findMinOperationUtil()
def findMinOperation(adj, A, V):
# Initialise DP table
dp = [[0, 0] for i in range(V + 1)]
# find dp[1][0] and dp[1][1]
findMinOperationUtil(dp, adj, A, 1, 0)
minOperations = dp[1][0] + dp[1][1]
return minOperations
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
V = 5
# Build the Graph/Tree
adj = [[] for i in range(V + 1)]
addEdge(adj, 1, 2)
addEdge(adj, 1, 3)
A = [1, -1, 1]
minOperations = findMinOperation(adj, A, V)
print(minOperations)
# This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain输出:
3
时间复杂度:O(V),其中V是树中的节点数。
辅助空间:O(V),其中V是树中的节点数。
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。