在图中查找母顶点
什么是母顶点?
图 G = (V, E) 中的母顶点是一个顶点 v,使得 G 中的所有其他顶点都可以通过来自 v 的路径到达。
例子 :
Input : Below Graph
Output : 5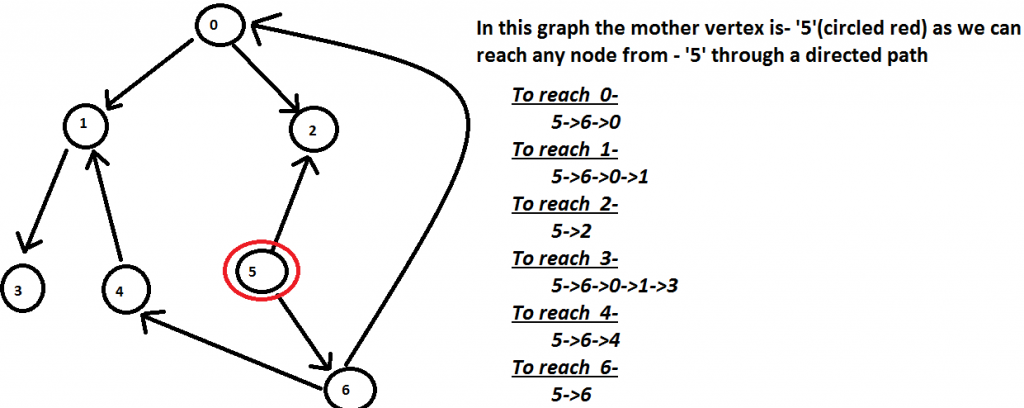
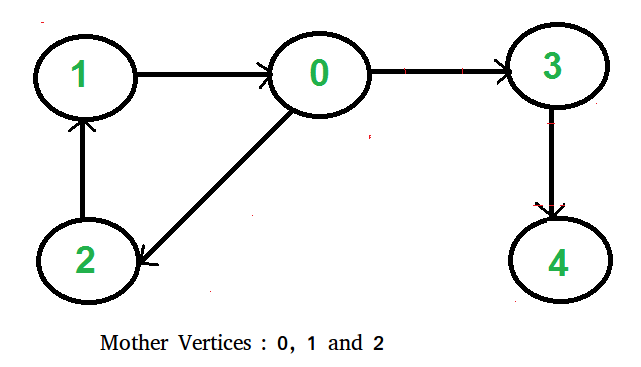
图中可以有多个母顶点。我们需要输出其中任何一个。例如,在下图中,顶点 0、1 和 2 是母顶点。
我们强烈建议您最小化您的浏览器并首先自己尝试。
如何找到母顶点?
- 案例 1:- 无向连通图:在这种情况下,所有顶点都是母顶点,因为我们可以到达图中的所有其他节点。
- 案例 2:- 无向/有向断开图:在这种情况下,没有母顶点,因为我们无法到达图中的所有其他节点。
- 案例3:-有向连通图:在这种情况下,我们必须在图中找到一个顶点-v,以便我们可以通过有向路径到达图中的所有其他节点。
一种天真的方法:
一种简单的方法是对所有顶点执行 DFS/BFS,并确定我们是否可以从该顶点到达所有顶点。这种方法需要 O(V(E+V)) 时间,对于大图来说效率非常低。
我们能做得更好吗?
我们可以在 O(V+E) 时间内找到一个母顶点。这个想法基于 Kosaraju 的强连通分量算法。在强连通分量图中,母顶点总是分量图中源分量的顶点。这个想法是基于以下事实。
如果存在母顶点(或多个顶点),则其中一个母顶点是 DFS 中最后完成的顶点。 (或者母顶点在 DFS 遍历中具有最长的完成时间)。
如果一个顶点的 DFS 递归调用结束,即该顶点的所有后代都已被访问,则称该顶点在 DFS 中已完成。
上述想法如何运作?
令最后完成的顶点为 v。基本上,我们需要证明如果 u 不是另一个母顶点,则不存在从另一个顶点 u 到 v 的边(或者不存在非母顶点 u 使得 u-→v是一条边)。可能有两种可能性。
- 在 v 之前为 u 进行递归 DFS 调用。如果存在边 u-→v,则 v 必须在 u 之前完成,因为 v 可以通过 u 到达,并且顶点在其所有后代之后完成。
- 在 u 之前对 v 进行递归 DFS 调用。同样在这种情况下,如果存在边 u-→v,则要么 v 必须在 u 之前完成(这与我们认为 v 在末尾完成的假设相矛盾)要么 u 应该可以从 v 到达(这意味着 u 是另一个母顶点) .
算法 :
- 对给定图进行 DFS 遍历。在进行遍历时,跟踪最后完成的顶点“v”。这一步需要 O(V+E) 时间。
- 如果存在母顶点(或顶点),则 v 必须是一个(或其中之一)。通过对 v 进行 DFS/BFS 来检查 v 是否是母顶点。这一步也需要 O(V+E) 时间。
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
// C++ program to find a mother vertex in O(V+E) time
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // adjacency lists
// A recursive function to print DFS starting from v
void DFSUtil(int v, vector &visited);
public:
Graph(int V);
void addEdge(int v, int w);
int findMother();
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
// A recursive function to print DFS starting from v
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, vector &visited)
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
// Returns a mother vertex if exists. Otherwise returns -1
int Graph::findMother()
{
// visited[] is used for DFS. Initially all are
// initialized as not visited
vector visited(V, false);
// To store last finished vertex (or mother vertex)
int v = 0;
// Do a DFS traversal and find the last finished
// vertex
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
DFSUtil(i, visited);
v = i;
}
}
// If there exist mother vertex (or vertices) in given
// graph, then v must be one (or one of them)
// Now check if v is actually a mother vertex (or graph
// has a mother vertex). We basically check if every vertex
// is reachable from v or not.
// Reset all values in visited[] as false and do
// DFS beginning from v to check if all vertices are
// reachable from it or not.
fill(visited.begin(), visited.end(), false);
DFSUtil(v, visited);
for (int i=0; i Java
// Java program to find a mother
// vertex in O(V+E) time
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static void addEdge(int u, int v,
ArrayList> adj)
{
adj.get(u).add(v);
}
// A recursive function to print DFS starting from v
static void DFSUtil(ArrayList> g,
int v, boolean[] visited)
{
// Mark the current node as
// visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
for(int x : g.get(v))
{
if (!visited[x])
{
DFSUtil(g, x, visited);
}
}
}
// Returns a mother vertex if exists.
// Otherwise returns -1
static int motherVertex(ArrayList>g,
int V)
{
// visited[] is used for DFS. Initially
// all are initialized as not visited
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// To store last finished vertex
// (or mother vertex)
int v = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
DFSUtil(g, i, visited);
v = i;
}
}
// If there exist mother vertex (or vertices)
// in given graph, then v must be one
// (or one of them)
// Now check if v is actually a mother
// vertex (or graph has a mother vertex).
// We basically check if every vertex
// is reachable from v or not.
// Reset all values in visited[] as false
// and do DFS beginning from v to check
// if all vertices are reachable from
// it or not.
boolean[] check = new boolean[V];
DFSUtil(g, v, check);
for(boolean val : check)
{
if (!val)
{
return -1;
}
}
return v;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int V = 7;
int E = 8;
ArrayList<
ArrayList> adj = new ArrayList<
ArrayList>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj.add(new ArrayList());
}
addEdge(0, 1,adj);
addEdge(0, 2,adj);
addEdge(1, 3,adj);
addEdge(4, 1,adj);
addEdge(6, 4,adj);
addEdge(5, 6,adj);
addEdge(5, 2,adj);
addEdge(6, 0,adj);
System.out.println("The mother vertex is " +
motherVertex(adj, V));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Tanay Shah Python3
# program to find a mother vertex in O(V+E) time
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list
# representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self,vertices):
self.V = vertices #No. of vertices
self.graph = defaultdict(list) # default dictionary
# A recursive function to print DFS starting from v
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in self.graph[v]:
if visited[i] == False:
self.DFSUtil(i, visited)
# Add w to the list of v
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.graph[v].append(w)
# Returns a mother vertex if exists. Otherwise returns -1
def findMother(self):
# visited[] is used for DFS. Initially all are
# initialized as not visited
visited =[False]*(self.V)
# To store last finished vertex (or mother vertex)
v=0
# Do a DFS traversal and find the last finished
# vertex
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i]==False:
self.DFSUtil(i,visited)
v = i
# If there exist mother vertex (or vertices) in given
# graph, then v must be one (or one of them)
# Now check if v is actually a mother vertex (or graph
# has a mother vertex). We basically check if every vertex
# is reachable from v or not.
# Reset all values in visited[] as false and do
# DFS beginning from v to check if all vertices are
# reachable from it or not.
visited = [False]*(self.V)
self.DFSUtil(v, visited)
if any(i == False for i in visited):
return -1
else:
return v
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
g = Graph(7)
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 3)
g.addEdge(4, 1)
g.addEdge(6, 4)
g.addEdge(5, 6)
g.addEdge(5, 2)
g.addEdge(6, 0)
print ("A mother vertex is " + str(g.findMother()))
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program to find a mother
// vertex in O(V+E) time
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static void addEdge(int u, int v,
List> adj)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
}
// A recursive function to print DFS starting from v
static void DFSUtil(List> g,
int v, bool[] visited)
{
// Mark the current node as
// visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int x in g[v])
{
if (!visited[x])
{
DFSUtil(g, x, visited);
}
}
}
// Returns a mother vertex if exists.
// Otherwise returns -1
static int motherVertex(List>g,
int V)
{
// visited[] is used for DFS. Initially
// all are initialized as not visited
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
// To store last finished vertex
// (or mother vertex)
int v = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
DFSUtil(g, i, visited);
v = i;
}
}
// If there exist mother vertex (or vertices)
// in given graph, then v must be one
// (or one of them)
// Now check if v is actually a mother
// vertex (or graph has a mother vertex).
// We basically check if every vertex
// is reachable from v or not.
// Reset all values in visited[] as false
// and do DFS beginning from v to check
// if all vertices are reachable from
// it or not.
bool[] check = new bool[V];
DFSUtil(g, v, check);
foreach(bool val in check)
{
if (!val)
{
return -1;
}
}
return v;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int V = 7;
int E = 8;
List<
List> adj = new List>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj.Add(new List());
}
addEdge(0, 1,adj);
addEdge(0, 2,adj);
addEdge(1, 3,adj);
addEdge(4, 1,adj);
addEdge(6, 4,adj);
addEdge(5, 6,adj);
addEdge(5, 2,adj);
addEdge(6, 0,adj);
Console.WriteLine("The mother vertex is " +
motherVertex(adj, V));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
输出 :
A mother vertex is 5时间复杂度: O(V + E)