给定一个有向图和一个节点X。任务是找到必须添加到图中的最小边数,以便可以从给定节点访问任何节点。
例子:
Input: X = 0
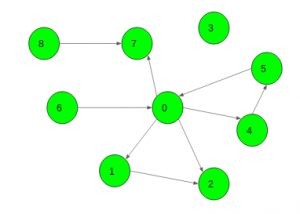
Output: 3
Input: X = 4
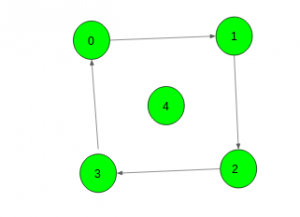
Output: 1
方法:首先,让我们使用简单的DFS将X可以到达的所有顶点标记为良好。然后,对于每个坏顶点(无法从X到达的顶点)v,计算从v可以到达的坏顶点的数量(也可以通过简单的DFS完成)。将此数字设为cnt v 。现在,以cnt v的非递增顺序遍历所有坏顶点。对于当前的不良顶点v,如果仍未将其标记为好,请从该顶点运行DFS,将所有可到达的顶点标记为好,然后将答案增加1(实际上,我们隐含地添加了边(s,v ))。可以证明,该解决方案给出了最佳答案。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 5010;
int n, x;
vector g[N];
// To check if the vertex has been
// visited or not
bool vis[N];
// To store if vertex is reachable
// from source or not
bool good[N];
int cnt;
void ADD_EDGE(int u, int v)
{
g[u].push_back(v);
}
// Function to find all good vertices
void dfs1(int v)
{
good[v] = true;
for (auto to : g[v])
if (!good[to])
dfs1(to);
}
// Function to find cnt of all unreachable vertices
void dfs2(int v)
{
vis[v] = true;
++cnt;
for (auto to : g[v])
if (!vis[to] && !good[to])
dfs2(to);
}
// Function to return the minimum edges required
int Minimum_Edges()
{
// Find all vertices reachable from the source
dfs1(x);
// To store all vertices with their cnt value
vector > val;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// If vertex is bad i.e. not reachable
if (!good[i]) {
cnt = 0;
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
// Find cnt of this vertex
dfs2(i);
val.push_back(make_pair(cnt, i));
}
}
// Sort all unreachable vertices in
// non-decreasing order of their cnt values
sort(val.begin(), val.end());
reverse(val.begin(), val.end());
// Find the minimum number of edges
// needed to be added
int ans = 0;
for (auto it : val) {
if (!good[it.second]) {
++ans;
dfs1(it.second);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of nodes and source node
n = 5, x = 4;
// Add edges to the graph
ADD_EDGE(0, 1);
ADD_EDGE(1, 2);
ADD_EDGE(2, 3);
ADD_EDGE(3, 0);
cout << Minimum_Edges();
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// pair
static class pair
{
int first,second;
pair(int a,int b)
{
first = a;
second = b;
}
}
static int N = 5010;
static int n, x;
static Vector> g = new Vector>();
// To check if the vertex has been
// visited or not
static boolean vis[] = new boolean[N];
// To store if vertex is reachable
// from source or not
static boolean good[] = new boolean[N];
static int cnt;
static void ADD_EDGE(int u, int v)
{
g.get(u).add(v);
}
// Function to find all good vertices
static void dfs1(int v)
{
good[v] = true;
for (int to = 0; to < g.get(v).size(); to++)
if (!good[g.get(v).get(to)])
dfs1(g.get(v).get(to));
}
// Function to find cnt of all unreachable vertices
static void dfs2(int v)
{
vis[v] = true;
++cnt;
for (int to = 0; to < g.get(v).size(); to++)
if (!vis[g.get(v).get(to)] && !good[g.get(v).get(to)])
dfs2(g.get(v).get(to));
}
// Function to return the minimum edges required
static int Minimum_Edges()
{
// Find all vertices reachable from the source
dfs1(x);
// To store all vertices with their cnt value
Vector val = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
// If vertex is bad i.e. not reachable
if (!good[i])
{
cnt = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < vis.length; j++)
vis[j] = false;
// Find cnt of this vertex
dfs2(i);
val.add(new pair(cnt, i));
}
}
// Sort all unreachable vertices in
// non-decreasing order of their cnt values
Collections.sort(val,new Comparator()
{
public int compare(pair p1, pair p2)
{
return p1.first - p2.first;
}
});
Collections.reverse(val);
// Find the minimum number of edges
// needed to be added
int ans = 0;
for (int it = 0; it < val.size(); it++)
{
if (!good[val.get(it).second])
{
++ans;
dfs1(val.get(it).second);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Number of nodes and source node
n = 5; x = 4;
for(int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++)
g.add(new Vector());
// Add edges to the graph
ADD_EDGE(0, 1);
ADD_EDGE(1, 2);
ADD_EDGE(2, 3);
ADD_EDGE(3, 0);
System.out.println( Minimum_Edges());
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
N = 5010
g = [[] for i in range(N)]
# To check if the vertex
# has been visited or not
vis = [False for i in range(N)]
# To store if vertex is reachable
# from source or not
good = [False for i in range(N)]
def ADD_EDGE(u, v):
g[u].append(v)
# Function to find all good vertices
def dfs1(v):
good[v] = True
for to in g[v]:
if not good[to]:
dfs1(to)
# Function to find cnt of
# all unreachable vertices
def dfs2(v):
global cnt
vis[v] = True
cnt += 1
for to in g[v]:
if not vis[to] and not good[to]:
dfs2(to)
# Function to return
# the minimum edges required
def Minimum_Edges():
global vis, cnt
# Find all vertices reachable
# from the source
dfs1(x)
# To store all vertices
# with their cnt value
val = []
for i in range(0, n):
# If vertex is bad i.e. not reachable
if not good[i]:
cnt = 0
vis = [False for i in range(N)]
# Find cnt of this vertex
dfs2(i)
val.append((cnt, i))
# Sort all unreachable vertices
# in non-decreasing order of
# their cnt values
val.sort(reverse = True)
# Find the minimum number of edges
# needed to be added
ans = 0
for it in val:
if not good[it[1]]:
ans += 1
dfs1(it[1])
return ans
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of nodes and source node
n, x = 5, 4
# Add edges to the graph
ADD_EDGE(0, 1)
ADD_EDGE(1, 2)
ADD_EDGE(2, 3)
ADD_EDGE(3, 0)
print(Minimum_Edges())
# This code is contributed by Rituraj JainC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// pair
class pair
{
public int first,second;
public pair(int a,int b)
{
first = a;
second = b;
}
}
static int N = 5010;
static int n, x;
static ArrayList g = new ArrayList();
// To check if the vertex has been
// visited or not
static bool []vis = new bool[N];
// To store if vertex is reachable
// from source or not
static bool []good = new bool[N];
static int cnt;
static void Add_EDGE(int u, int v)
{
((ArrayList)g[u]).Add(v);
}
// Function to find all good vertices
static void dfs1(int v)
{
good[v] = true;
for (int to = 0; to < ((ArrayList)g[v]).Count; to++)
if (!good[(int)((ArrayList)g[v])[to]])
dfs1((int)((ArrayList)g[v])[to]);
}
// Function to find cnt of all unreachable vertices
static void dfs2(int v)
{
vis[v] = true;
++cnt;
for (int to = 0; to < ((ArrayList)g[v]).Count; to++)
if (!vis[(int)((ArrayList)g[v])[to]] && !good[(int)((ArrayList)g[v])[to]])
dfs2((int)((ArrayList)g[v])[to]);
}
class sortHelper : IComparer
{
int IComparer.Compare(object a, object b)
{
pair first = (pair)a;
pair second = (pair)b;
return first.first - second.first;
}
}
// Function to return the minimum edges required
static int Minimum_Edges()
{
// Find all vertices reachable from the source
dfs1(x);
// To store all vertices with their cnt value
ArrayList val = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
// If vertex is bad i.e. not reachable
if (!good[i])
{
cnt = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < vis.Length; j++)
vis[j] = false;
// Find cnt of this vertex
dfs2(i);
val.Add(new pair(cnt, i));
}
}
// Sort all unreachable vertices in
// non-decreasing order of their cnt values
val.Sort(new sortHelper());
// Find the minimum number of edges
// needed to be Added
int ans = 0;
for (int it = 0; it < val.Count; it++)
{
if (!good[((pair)val[it]).second])
{
++ans;
dfs1(((pair)val[it]).second);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string []args)
{
// Number of nodes and source node
n = 5; x = 4;
for(int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++)
g.Add(new ArrayList());
// Add edges to the graph
Add_EDGE(0, 1);
Add_EDGE(1, 2);
Add_EDGE(2, 3);
Add_EDGE(3, 0);
Console.WriteLine(Minimum_Edges());
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56输出:
1如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。