给定具有N个顶点和M个边的无向非加权图。任务是找到两个不相交的良好顶点集。如果对于图中的每个边缘UV,至少一个端点属于X(即U或V或U和V都属于X),则将X称为“好”。
如果无法进行此类设置,则打印-1。
例子:
Input :
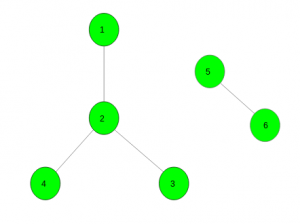
Output : {1 3 4 5} ,{2 6}
One disjoint good set contains vertices {1, 3, 4, 5} and other contains {2, 6}.
Input :

Output : -1
方法:
观察结果之一是,没有U和V在同一集合中的边缘UV。两个好的集合形成了图的二等分,因此该图必须是二等分的。而且,两党也是足够的。在此处阅读有关分区的信息。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find two disjoint
// good sets of vertices in a given graph
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 100005
// For the graph
vector gr[N], dis[2];
bool vis[N];
int colour[N];
bool bip;
// Function to add edge
void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].push_back(y);
gr[y].push_back(x);
}
// Bipartie function
void dfs(int x, int col)
{
vis[x] = true;
colour[x] = col;
// Check for child vertices
for (auto i : gr[x]) {
// If it is not visited
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i, col ^ 1);
// If it is already visited
else if (colour[i] == col)
bip = false;
}
}
// Function to find two disjoint
// good sets of vertices in a given graph
void goodsets(int n)
{
// Initially assume that graph is bipartie
bip = true;
// For every unvisited vertex call dfs
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i, 0);
// If graph is not bipartie
if (!bip)
cout << -1;
else {
// Differentiate two sets
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dis[colour[i]].push_back(i);
// Print vertices belongs to both sets
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dis[i].size(); j++)
cout << dis[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 6, m = 4;
// Add edges
Add_edge(1, 2);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(2, 4);
Add_edge(5, 6);
// Function call
goodsets(n);
} Java
// Java program to find two disjoint
// good sets of vertices in a given graph
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int N = 100005;
// For the graph
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] gr = new Vector[N],
dis = new Vector[2];
static
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
dis[i] = new Vector<>();
}
static boolean[] vis = new boolean[N];
static int[] color = new int[N];
static boolean bip;
// Function to add edge
static void add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].add(y);
gr[y].add(x);
}
// Bipartie function
static void dfs(int x, int col)
{
vis[x] = true;
color[x] = col;
// Check for child vertices
for (int i : gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i, col ^ 1);
// If it is already visited
else if (color[i] == col)
bip = false;
}
}
// Function to find two disjoint
// good sets of vertices in a given graph
static void goodsets(int n)
{
// Initially assume that graph is bipartie
bip = true;
// For every unvisited vertex call dfs
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i, 0);
// If graph is not bipartie
if (!bip)
System.out.println(-1);
else
{
// Differentiate two sets
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dis[color[i]].add(i);
// Print vertices belongs to both sets
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dis[i].size(); j++)
System.out.print(dis[i].elementAt(j) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 6, m = 4;
// Add edges
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(2, 3);
add_edge(2, 4);
add_edge(5, 6);
// Function call
goodsets(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python 3
# Python 3 program to find two disjoint
# good sets of vertices in a given graph
N = 100005
# For the graph
gr = [[] for i in range(N)]
dis = [[] for i in range(2)]
vis = [False for i in range(N)]
colour = [0 for i in range(N)]
bip = 0
# Function to add edge
def Add_edge(x, y):
gr[x].append(y)
gr[y].append(x)
# Bipartie function
def dfs(x, col):
vis[x] = True
colour[x] = col
# Check for child vertices
for i in gr[x]:
# If it is not visited
if (vis[i] == False):
dfs(i, col ^ 1)
# If it is already visited
elif (colour[i] == col):
bip = False
# Function to find two disjoint
# good sets of vertices in a given graph
def goodsets(n):
# Initially assume that
# graph is bipartie
bip = True
# For every unvisited vertex call dfs
for i in range(1, n + 1, 1):
if (vis[i] == False):
dfs(i, 0)
# If graph is not bipartie
if (bip == 0):
print(-1)
else:
# Differentiate two sets
for i in range(1, n + 1, 1):
dis[colour[i]].append(i)
# Print vertices belongs to both sets
for i in range(2):
for j in range(len(dis[i])):
print(dis[i][j], end = " ")
print('\n', end = "")
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 6
m = 4
# Add edges
Add_edge(1, 2)
Add_edge(2, 3)
Add_edge(2, 4)
Add_edge(5, 6)
# Function call
goodsets(n)
# This code is contributed
# by Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# program to find two
// disjoint good sets of
// vertices in a given graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int N = 100005;
// For the graph
static List[] gr =
new List[N],
dis = new List[2];
static bool[] vis = new bool[N];
static int[] color = new int[N];
static bool bip;
// Function to add edge
static void add_edge(int x,
int y)
{
gr[x].Add(y);
gr[y].Add(x);
}
// Bipartie function
static void dfs(int x,
int col)
{
vis[x] = true;
color[x] = col;
// Check for child vertices
foreach (int i in gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i, col ^ 1);
// If it is already visited
else if (color[i] == col)
bip = false;
}
}
// Function to find two disjoint
// good sets of vertices in a
// given graph
static void goodsets(int n)
{
// Initially assume that
// graph is bipartie
bip = true;
// For every unvisited
// vertex call dfs
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i, 0);
// If graph is not bipartie
if (!bip)
Console.WriteLine(-1);
else
{
// Differentiate two sets
for (int i = 1;
i <= n; i++)
dis[color[i]].Add(i);
// Print vertices belongs
// to both sets
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0;
j < dis[i].Count; j++)
Console.Write(dis[i][j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 6, m = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
gr[i] = new List();
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
dis[i] = new List();
// Add edges
add_edge(1, 2);
add_edge(2, 3);
add_edge(2, 4);
add_edge(5, 6);
// Function call
goodsets(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput 输出:
1 3 4 5
2 6
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。