查找两个顶点之间的最大边不相交路径数
给定一个有向图和其中的两个顶点,源“s”和目标“t”,找出从 s 到 t 的边不相交路径的最大数量。如果两条路径不共享任何边,则称它们为边不相交。
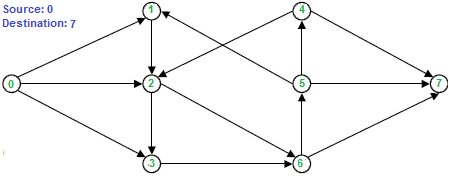
在上图中,从源 0 到目标 7 最多可以有两条边不相交的路径。下面以红色和蓝色突出显示的两条边缘不相交路径是 0-2-6-7 和 0-3-6-5-7。
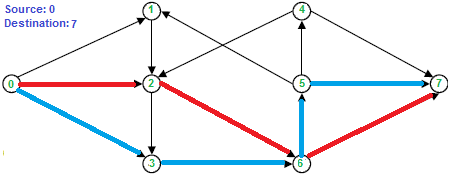
请注意,路径可能不同,但最大数量相同。例如,在上图中,另一组可能的路径分别是 0-1-2-6-7 和 0-3-6-5-7。
这个问题可以通过减少到最大流量问题来解决。以下是步骤。
1)将给定的源和目的地视为流网络中的源和汇。为每条边分配单位容量。
2)运行 Ford-Fulkerson 算法以找到从源到汇的最大流量。
3)最大流量等于边不相交路径的最大数量。
当我们运行 Ford-Fulkerson 时,我们将容量减少了一个单位。因此,边缘不能再次使用。所以最大流量等于边不相交路径的最大数量。
以下是上述算法的实现。大部分代码都取自这里。
C++
// C++ program to find maximum number of edge disjoint paths
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Number of vertices in given graph
#define V 8
/* Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink 't' in
residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path */
bool bfs(int rGraph[V][V], int s, int t, int parent[])
{
// Create a visited array and mark all vertices as not visited
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark source vertex
// as visited
queue q;
q.push(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int v=0; v 0)
{
q.push(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// If we reached sink in BFS starting from source, then return
// true, else false
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// Returns the maximum number of edge-disjoint paths from s to t.
// This function is copy of forFulkerson() discussed at http://goo.gl/wtQ4Ks
int findDisjointPaths(int graph[V][V], int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the residual graph with
// given capacities in the original graph as residual capacities
// in residual graph
int rGraph[V][V]; // Residual graph where rGraph[i][j] indicates
// residual capacity of edge from i to j (if there
// is an edge. If rGraph[i][j] is 0, then there is not)
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
int parent[V]; // This array is filled by BFS and to store path
int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
// Augment the flow while there is path from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
{
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along the
// path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the maximum flow
// through the path found.
int path_flow = INT_MAX;
for (v=t; v!=s; v=parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
path_flow = min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges
// along the path
for (v=t; v != s; v=parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
// Return the overall flow (max_flow is equal to maximum
// number of edge-disjoint paths)
return max_flow;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int graph[V][V] = { {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
int s = 0;
int t = 7;
cout << "There can be maximum " << findDisjointPaths(graph, s, t)
<< " edge-disjoint paths from " << s <<" to "<< t ;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find maximum number
// of edge disjoint paths
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Number of vertices in given graph
static int V = 8;
/* Returns true if there is a path from
source 's' to sink 't' in residual graph.
Also fills parent[] to store the path */
static boolean bfs(int rGraph[][], int s,
int t, int parent[])
{
// Create a visited array and
// mark all vertices as not visited
boolean []visited = new boolean[V];
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and
// mark source vertex as visited
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
int u = q.peek();
q.remove();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
if (visited[v] == false &&
rGraph[u][v] > 0)
{
q.add(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// If we reached sink in BFS
// starting from source, then
// return true, else false
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// Returns the maximum number of edge-disjoint
// paths from s to t. This function is copy of
// forFulkerson() discussed at http://goo.gl/wtQ4Ks
static int findDisjointPaths(int graph[][], int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the
// residual graph with given capacities
// in the original graph as residual capacities
// in residual graph
// Residual graph where rGraph[i][j] indicates
// residual capacity of edge from i to j (if there
// is an edge. If rGraph[i][j] is 0, then there is not)
int [][]rGraph = new int[V][V];
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
// This array is filled by BFS and to store path
int []parent = new int[V];
int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
// Augment the flow while there is path
// from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
{
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edges
// along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
// find the maximum flow through the path found.
int path_flow = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
path_flow = Math.min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and
// reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
// Return the overall flow (max_flow is equal to
// maximum number of edge-disjoint paths)
return max_flow;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int graph[][] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
int s = 0;
int t = 7;
System.out.println("There can be maximum " +
findDisjointPaths(graph, s, t) +
" edge-disjoint paths from " +
s + " to "+ t);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 Python
# Python program to find maximum number of edge disjoint paths
# Complexity : (E*(V^3))
# Total augmenting path = VE
# and BFS with adj matrix takes :V^2 times
from collections import defaultdict
#This class represents a directed graph using
# adjacency matrix representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self,graph):
self.graph = graph # residual graph
self. ROW = len(graph)
'''Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink 't' in
residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path '''
def BFS(self,s, t, parent):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited =[False]*(self.ROW)
# Create a queue for BFS
queue=[]
# Mark the source node as visited and enqueue it
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
# Standard BFS Loop
while queue:
#Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
u = queue.pop(0)
# Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex u
# If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark it
# visited and enqueue it
for ind, val in enumerate(self.graph[u]):
if visited[ind] == False and val > 0 :
queue.append(ind)
visited[ind] = True
parent[ind] = u
# If we reached sink in BFS starting from source, then return
# true, else false
return True if visited[t] else False
# Returns the maximum number of edge-disjoint paths from
#s to t in the given graph
def findDisjointPaths(self, source, sink):
# This array is filled by BFS and to store path
parent = [-1]*(self.ROW)
max_flow = 0 # There is no flow initially
# Augment the flow while there is path from source to sink
while self.BFS(source, sink, parent) :
# Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along the
# path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the maximum flow
# through the path found.
path_flow = float("Inf")
s = sink
while(s != source):
path_flow = min (path_flow, self.graph[parent[s]][s])
s = parent[s]
# Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow
# update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges
# along the path
v = sink
while(v != source):
u = parent[v]
self.graph[u][v] -= path_flow
self.graph[v][u] += path_flow
v = parent[v]
return max_flow
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
graph = [[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
g = Graph(graph)
source = 0; sink = 7
print ("There can be maximum %d edge-disjoint paths from %d to %d" %
(g.findDisjointPaths(source, sink), source, sink))
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program to find maximum number
// of edge disjoint paths
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Number of vertices in given graph
static int V = 8;
/* Returns true if there is a path from
source 's' to sink 't' in residual graph.
Also fills parent[] to store the path */
static bool bfs(int [,]rGraph, int s,
int t, int []parent)
{
// Create a visited array and
// mark all vertices as not visited
bool []visited = new bool[V];
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex
// and mark source vertex as visited
Queue q = new Queue ();
q.Enqueue(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (q.Count != 0)
{
int u = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
if (visited[v] == false &&
rGraph[u, v] > 0)
{
q.Enqueue(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// If we reached sink in BFS
// starting from source, then
// return true, else false
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// Returns the maximum number of edge-disjoint
// paths from s to t. This function is copy of
// forFulkerson() discussed at http://goo.gl/wtQ4Ks
static int findDisjointPaths(int [,]graph,
int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the
// residual graph with given capacities
// in the original graph as residual capacities
// in residual graph
// Residual graph where rGraph[i,j] indicates
// residual capacity of edge from i to j (if there
// is an edge. If rGraph[i,j] is 0, then there is not)
int [,]rGraph = new int[V, V];
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u, v] = graph[u, v];
// This array is filled by BFS and
// to store path
int []parent = new int[V];
int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
// Augment the flow while there is path
// from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
{
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edges
// along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
// find the maximum flow through the path found.
int path_flow = int.MaxValue;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
path_flow = Math.Min(path_flow,
rGraph[u, v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges
// and reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u, v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v, u] += path_flow;
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
// Return the overall flow (max_flow is equal to
// maximum number of edge-disjoint paths)
return max_flow;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create a graph shown
// in the above example
int [,]graph = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
int s = 0;
int t = 7;
Console.WriteLine("There can be maximum " +
findDisjointPaths(graph, s, t) +
" edge-disjoint paths from " +
s + " to "+ t);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
输出:
There can be maximum 2 edge-disjoint paths from 0 to 7 时间复杂度:与 Ford-Fulkerson 的 Edmonds-Karp 实现的时间复杂度相同(参见此处讨论的时间复杂度)