给定一组点,任务是找到给定点的凸包。凸包是包含所有点的最小凸多边形。
请先检查这篇文章:凸包|设置1(贾维斯算法或包装) 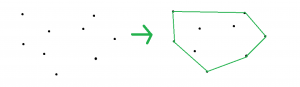
例子:
Input: Points[] = {{0, 3}, {2, 2}, {1, 1}, {2, 1}, {3, 0}, {0, 0}, {3, 3}}
Output:
(0, 0)
(3, 0)
(3, 3)
(0, 3)
方法:单调链算法在O(n * log(n))时间内构造凸包。我们必须先对这些点进行排序,然后以O(n)的时间计算上下船体。这些点将相对于x坐标进行排序(如果x坐标为平局,则相对于y坐标),然后我们将找到最左边的点,然后尝试沿顺时针方向旋转并找到下一个点然后重复该步骤,直到到达最右边,然后再次沿顺时针方向旋转,找到下部船体。
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
#define llu long long int
using namespace std;
struct Point {
llu x, y;
bool operator<(Point p)
{
return x < p.x || (x == p.x && y < p.y);
}
};
// Cross product of two vectors OA and OB
// returns positive for counter clockwise
// turn and negative for clockwise turn
llu cross_product(Point O, Point A, Point B)
{
return (A.x - O.x) * (B.y - O.y)
- (A.y - O.y) * (B.x - O.x);
}
// Returns a list of points on the convex hull
// in counter-clockwise order
vector convex_hull(vector A)
{
int n = A.size(), k = 0;
if (n <= 3)
return A;
vector ans(2 * n);
// Sort points lexicographically
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
// Build lower hull
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// If the point at K-1 position is not a part
// of hull as vector from ans[k-2] to ans[k-1]
// and ans[k-2] to A[i] has a clockwise turn
while (k >= 2 && cross_product(ans[k - 2],
ans[k - 1], A[i]) <= 0)
k--;
ans[k++] = A[i];
}
// Build upper hull
for (size_t i = n - 1, t = k + 1; i > 0; --i) {
// If the point at K-1 position is not a part
// of hull as vector from ans[k-2] to ans[k-1]
// and ans[k-2] to A[i] has a clockwise turn
while (k >= t && cross_product(ans[k - 2],
ans[k - 1], A[i - 1]) <= 0)
k--;
ans[k++] = A[i - 1];
}
// Resize the array to desired size
ans.resize(k - 1);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector points;
// Add points
points.push_back({ 0, 3 });
points.push_back({ 2, 2 });
points.push_back({ 1, 1 });
points.push_back({ 2, 1 });
points.push_back({ 3, 0 });
points.push_back({ 0, 0 });
points.push_back({ 3, 3 });
// Find the convex hull
vector ans = convex_hull(points);
// Print the convex hull
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
cout << "(" << ans[i].x << ", "
<< ans[i].y << ")" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
(0, 0)
(3, 0)
(3, 3)
(0, 3)
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。