给定一组点,凸包是包含所有给定点的最小凸多边形。
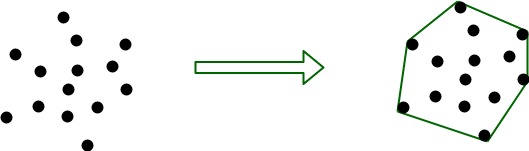
输入是由 x 和 y 坐标指定的点数组。输出是这组点的凸包,按 x 坐标的升序排列。
例子 :
Input : points[] = {{0, 3}, {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {4, 4},
{0, 0}, {1, 2}, {3, 1}, {3, 3}};
Output : The points in convex hull are:
(0, 0) (0, 3) (3, 1) (4, 4)
Input : points[] = {{0, 3}, {1, 1}
Output : Not Possible
There must be at least three points to form a hull.
Input : points[] = {(0, 0), (0, 4), (-4, 0), (5, 0),
(0, -6), (1, 0)};
Output : (-4, 0), (5, 0), (0, -6), (0, 4)
我们已经讨论了以下凸包问题的算法。
凸包 |设置 1(Jarvis 的算法或包装)
凸包 |第 2 组(格雷厄姆扫描)
QuickHull 算法是一种类似于 QuickSort 的分而治之的算法。让 a[0…n-1] 是点的输入数组。以下是寻找这些点的凸包的步骤。
- 找到具有最小 x 坐标的点,例如 min_x,类似地,找到具有最大 x 坐标的点 max_x。
- 做一条连接这两个点的线,比如L 。这条线将整个集合分为两部分。一个接一个地取下这两个部分并继续进行。
- 对于零件,找到距线 L 最大距离的点 P。P 与点 min_x、max_x 形成一个三角形。很明显,位于这个三角形内的点永远不可能是凸包的一部分。
- 上述步骤将问题分成两个子问题(递归解决)。现在连接点 P 和 min_x 的线以及连接点 P 和 max_x 的线是新线,位于三角形外的点是点集。重复点号。 3 直到这条线没有一点剩下。将此点的端点添加到凸包。
下面是上述想法的 C++ 实现。该实现使用 set 来存储点,以便可以按排序顺序打印点。一个点被表示为一对。
// C++ program to implement Quick Hull algorithm
// to find convex hull.
#include
using namespace std;
// iPair is integer pairs
#define iPair pair
// Stores the result (points of convex hull)
set hull;
// Returns the side of point p with respect to line
// joining points p1 and p2.
int findSide(iPair p1, iPair p2, iPair p)
{
int val = (p.second - p1.second) * (p2.first - p1.first) -
(p2.second - p1.second) * (p.first - p1.first);
if (val > 0)
return 1;
if (val < 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
// returns a value proportional to the distance
// between the point p and the line joining the
// points p1 and p2
int lineDist(iPair p1, iPair p2, iPair p)
{
return abs ((p.second - p1.second) * (p2.first - p1.first) -
(p2.second - p1.second) * (p.first - p1.first));
}
// End points of line L are p1 and p2. side can have value
// 1 or -1 specifying each of the parts made by the line L
void quickHull(iPair a[], int n, iPair p1, iPair p2, int side)
{
int ind = -1;
int max_dist = 0;
// finding the point with maximum distance
// from L and also on the specified side of L.
for (int i=0; i max_dist)
{
ind = i;
max_dist = temp;
}
}
// If no point is found, add the end points
// of L to the convex hull.
if (ind == -1)
{
hull.insert(p1);
hull.insert(p2);
return;
}
// Recur for the two parts divided by a[ind]
quickHull(a, n, a[ind], p1, -findSide(a[ind], p1, p2));
quickHull(a, n, a[ind], p2, -findSide(a[ind], p2, p1));
}
void printHull(iPair a[], int n)
{
// a[i].second -> y-coordinate of the ith point
if (n < 3)
{
cout << "Convex hull not possible\n";
return;
}
// Finding the point with minimum and
// maximum x-coordinate
int min_x = 0, max_x = 0;
for (int i=1; i a[max_x].first)
max_x = i;
}
// Recursively find convex hull points on
// one side of line joining a[min_x] and
// a[max_x]
quickHull(a, n, a[min_x], a[max_x], 1);
// Recursively find convex hull points on
// other side of line joining a[min_x] and
// a[max_x]
quickHull(a, n, a[min_x], a[max_x], -1);
cout << "The points in Convex Hull are:\n";
while (!hull.empty())
{
cout << "(" <<( *hull.begin()).first << ", "
<< (*hull.begin()).second << ") ";
hull.erase(hull.begin());
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
iPair a[] = {{0, 3}, {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {4, 4},
{0, 0}, {1, 2}, {3, 1}, {3, 3}};
int n = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]);
printHull(a, n);
return 0;
}
输入 :
The points in Convex Hull are:
(0, 0) (0, 3) (3, 1) (4, 4)
时间复杂度:分析类似于快速排序。平均而言,我们得到的时间复杂度为 O(n Log n),但在最坏的情况下,它可以变成 O(n 2 )
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。