二叉树的所有边界节点之和
给定一棵二叉树,任务是打印树的所有边界节点的总和。
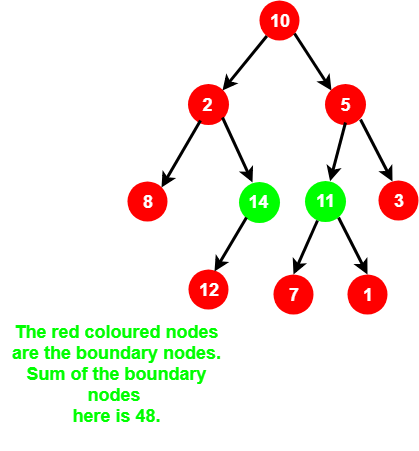
例子:
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
Output: 28
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
\ /
4 5
\
6
/ \
7 8
Output: 36方法:我们已经讨论过二叉树的边界遍历。在这里,我们将分四步求给定二叉树的边界节点之和:
- 将左边界的所有节点相加,
- 将左子树的所有叶子节点相加,
- 将右子树的所有叶子节点相加,
- 总结右边界的所有节点。
我们将不得不处理节点不会再次相加的一件事,即最左边的节点也是树的叶节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node has data,
// pointer to left child
// and a pointer to right child
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
// Utility function to create a node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to sum up all the left boundary nodes
// except the leaf nodes
void LeftBoundary(Node* root, int& sum_of_boundary_nodes)
{
if (root) {
if (root->left) {
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root->data;
LeftBoundary(root->left, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
}
else if (root->right) {
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root->data;
LeftBoundary(root->right, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
}
}
}
// Function to sum up all the right boundary nodes
// except the leaf nodes
void RightBoundary(Node* root, int& sum_of_boundary_nodes)
{
if (root) {
if (root->right) {
RightBoundary(root->right, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root->data;
}
else if (root->left) {
RightBoundary(root->left, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root->data;
}
}
}
// Function to sum up all the leaf nodes
// of a binary tree
void Leaves(Node* root, int& sum_of_boundary_nodes)
{
if (root) {
Leaves(root->left, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
// Sum it up if it is a leaf node
if (!(root->left) && !(root->right))
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root->data;
Leaves(root->right, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
}
}
// Function to return the sum of all the
// boundary nodes of the given binary tree
int sumOfBoundaryNodes(struct Node* root)
{
if (root) {
// Root node is also a boundary node
int sum_of_boundary_nodes = root->data;
// Sum up all the left nodes
// in TOP DOWN manner
LeftBoundary(root->left, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
// Sum up all the
// leaf nodes
Leaves(root->left, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
Leaves(root->right, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
// Sum up all the right nodes
// in BOTTOM UP manner
RightBoundary(root->right, sum_of_boundary_nodes);
// Return the sum of
// all the boundary nodes
return sum_of_boundary_nodes;
}
return 0;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(8);
root->left->right = newNode(14);
root->right->left = newNode(11);
root->right->right = newNode(3);
root->left->right->left = newNode(12);
root->right->left->right = newNode(1);
root->right->left->left = newNode(7);
cout << sumOfBoundaryNodes(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
static int sum_of_boundary_nodes=0;
// A binary tree node has data,
// pointer to left child
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
};
// Utility function to create a node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to sum up all the left boundary nodes
// except the leaf nodes
static void LeftBoundary(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
if (root.left != null)
{
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
LeftBoundary(root.left);
}
else if (root.right != null)
{
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
LeftBoundary(root.right);
}
}
}
// Function to sum up all the right boundary nodes
// except the leaf nodes
static void RightBoundary(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
if (root.right != null)
{
RightBoundary(root.right);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
}
else if (root.left != null)
{
RightBoundary(root.left);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
}
}
}
// Function to sum up all the leaf nodes
// of a binary tree
static void Leaves(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
Leaves(root.left);
// Sum it up if it is a leaf node
if ((root.left == null) && (root.right == null))
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
Leaves(root.right);
}
}
// Function to return the sum of all the
// boundary nodes of the given binary tree
static int sumOfBoundaryNodes( Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
// Root node is also a boundary node
sum_of_boundary_nodes = root.data;
// Sum up all the left nodes
// in TOP DOWN manner
LeftBoundary(root.left);
// Sum up all the
// leaf nodes
Leaves(root.left);
Leaves(root.right);
// Sum up all the right nodes
// in BOTTOM UP manner
RightBoundary(root.right);
// Return the sum of
// all the boundary nodes
return sum_of_boundary_nodes;
}
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = newNode(10);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.right = newNode(14);
root.right.left = newNode(11);
root.right.right = newNode(3);
root.left.right.left = newNode(12);
root.right.left.right = newNode(1);
root.right.left.left = newNode(7);
System.out.println(sumOfBoundaryNodes(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by andrew1234Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# A binary tree node has data,
# pointer to left child
# and a pointer to right child
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.left = None
self.right = None
sum_of_boundary_nodes = 0
# Utility function to create a node
def newNode(data):
temp = Node()
temp.data = data;
return temp;
# Function to sum up all the
# left boundary nodes except
# the leaf nodes
def LeftBoundary(root):
global sum_of_boundary_nodes
if (root != None):
if (root.left != None):
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
LeftBoundary(root.left);
elif (root.right != None):
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
LeftBoundary(root.right);
# Function to sum up all the right
# boundary nodes except the leaf nodes
def RightBoundary(root):
global sum_of_boundary_nodes
if (root != None):
if (root.right != None):
RightBoundary(root.right);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
elif (root.left != None):
RightBoundary(root.left);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
# Function to sum up all the leaf nodes
# of a binary tree
def Leaves(root):
global sum_of_boundary_nodes
if (root != None):
Leaves(root.left);
# Sum it up if it is a leaf node
if ((root.left == None) and
(root.right == None)):
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
Leaves(root.right);
# Function to return the sum of all the
# boundary nodes of the given binary tree
def sumOfBoundaryNodes(root):
global sum_of_boundary_nodes
if (root != None):
# Root node is also a boundary node
sum_of_boundary_nodes = root.data;
# Sum up all the left nodes
# in TOP DOWN manner
LeftBoundary(root.left);
# Sum up all the
# leaf nodes
Leaves(root.left);
Leaves(root.right);
# Sum up all the right nodes
# in BOTTOM UP manner
RightBoundary(root.right);
# Return the sum of
# all the boundary nodes
return sum_of_boundary_nodes;
return 0;
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
root = newNode(10);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.right = newNode(14);
root.right.left = newNode(11);
root.right.right = newNode(3);
root.left.right.left = newNode(12);
root.right.left.right = newNode(1);
root.right.left.left = newNode(7);
print(sumOfBoundaryNodes(root));
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int sum_of_boundary_nodes = 0;
// A binary tree node has data,
// pointer to left child
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
};
// Utility function to create a node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
temp.data = data;
return temp;
}
// Function to sum up all the left boundary
// nodes except the leaf nodes
static void LeftBoundary(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
if (root.left != null)
{
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
LeftBoundary(root.left);
}
else if (root.right != null)
{
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
LeftBoundary(root.right);
}
}
}
// Function to sum up all the right boundary
// nodes except the leaf nodes
static void RightBoundary(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
if (root.right != null)
{
RightBoundary(root.right);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
}
else if (root.left != null)
{
RightBoundary(root.left);
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
}
}
}
// Function to sum up all the leaf nodes
// of a binary tree
static void Leaves(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
Leaves(root.left);
// Sum it up if it is a leaf node
if ((root.left == null) &&
(root.right == null))
sum_of_boundary_nodes += root.data;
Leaves(root.right);
}
}
// Function to return the sum of all the
// boundary nodes of the given binary tree
static int sumOfBoundaryNodes(Node root)
{
if (root != null)
{
// Root node is also a boundary node
sum_of_boundary_nodes = root.data;
// Sum up all the left nodes
// in TOP DOWN manner
LeftBoundary(root.left);
// Sum up all the
// leaf nodes
Leaves(root.left);
Leaves(root.right);
// Sum up all the right nodes
// in BOTTOM UP manner
RightBoundary(root.right);
// Return the sum of
// all the boundary nodes
return sum_of_boundary_nodes;
}
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = newNode(10);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.right = newNode(14);
root.right.left = newNode(11);
root.right.right = newNode(3);
root.left.right.left = newNode(12);
root.right.left.right = newNode(1);
root.right.left.left = newNode(7);
Console.WriteLine(sumOfBoundaryNodes(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghJavascript
输出:
48时间复杂度: O(N),其中 N 是二叉树中的节点数。