给定N 个节点和M个顶点的无向图。您还将获得K 个边作为selected[] 。通过在给定选定边的任意两个顶点之间添加单个边来最大化节点1到节点N之间的最短路径长度的任务。
注意:您可以在任何两个选定的顶点之间添加一条边,这些顶点之间已经有一条边。
Input: N = 5, M = 4, K = 2, selected[] = {2, 4}
Below is the given graph:
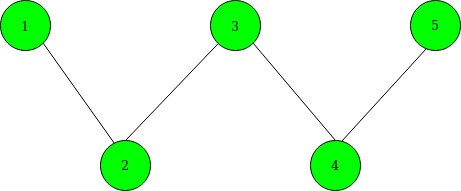
Output: 3
Explanation:
Before adding an edge between 2 and 4, the Shortest Path becomes: 1–>2–>3–>4–>5.
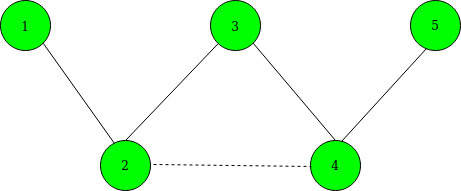
After adding an edge between 2 and 4, the Shortest Path becomes 1–>2–>4–>5. Below is the graph after adding edges. denoted by the dashed line.
Input: N = 5 M = 5 K = 3 selected[] = {1, 3, 5}
Below is the given graph:
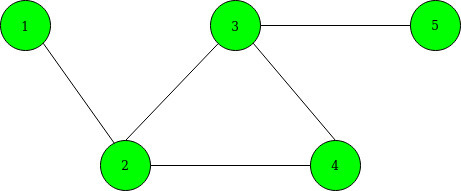
Output: 3
Explanation:
We can add an edge between 3 and 5 as they have already an edge between them. so, the shortest path becomes 1–>2–>3–>5. Below is the graph after adding edges. denoted by the dashed line.

方法:想法是使用广度优先搜索来查找从顶点1和N到每个选定顶点的距离。对于选定的顶点 i,让x i表示到节点 1 的距离, y i表示到节点N的距离。以下是步骤:
- 维护一个具有2行和N列的二维矩阵(比如dist[2][] )。
- 在第一行中,使用 BFS Traversal 保持节点1和图中其他顶点之间的最短距离。
- 在第二行中,使用 BFS Traversal 保持节点N与图的其他顶点之间的最短距离。
- 现在,从selected[] 中选择两个选定的顶点a和b ,以最小化 min(xa + yb, ya + xb) 的值。为此,请执行以下操作:
- 创建一个对向量并将 (x i – y i ) 的值与它们各自选定的节点一起存储。
- 对上述成对向量进行排序。
- 将best初始化为 0 ,将max初始化为 -INF 。
- 现在遍历上述对向量,并为每个选定的节点(例如 a)更新(best, max + dist[1][a])的best到最大值,并将 max 更新到(max, dist[0])的最大值[一种])。
- 在上述操作之后, (dist[0][N-1] 和 best + 1)的最大值给出了最小的最短路径。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int INF = 1e9 + 7;
int N, M;
// To store graph as adjacency list
vector edges[200005];
// To store the shortest path
int dist[2][200000];
// Function that performs BFS Traversal
void bfs(int* dist, int s)
{
int q[200000];
// Fill initially each distance as INF
fill(dist, dist + N, INF);
int qh = 0, qt = 0;
q[qh++] = s;
dist[s] = 0;
// Perform BFS
while (qt < qh) {
int x = q[qt++];
// Traverse the current edges
for (int y : edges[x]) {
if (dist[y] == INF) {
// Update the distance
dist[y] = dist[x] + 1;
// Insert in queue
q[qh++] = y;
}
}
}
}
// Function that maximizes the shortest
// path between source and destination
// vertex by adding a single edge between
// given selected nodes
void shortestPathCost(int selected[], int K)
{
vector > data;
// To update the shortest distance
// between node 1 to other vertices
bfs(dist[0], 0);
// To update the shortest distance
// between node N to other vertices
bfs(dist[1], N - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
// Store the values x[i] - y[i]
data.emplace_back(dist[0][selected[i]]
- dist[1][selected[i]],
selected[i]);
}
// Sort all the vectors of pairs
sort(data.begin(), data.end());
int best = 0;
int MAX = -INF;
// Traverse data[]
for (auto it : data) {
int a = it.second;
best = max(best,
MAX + dist[1][a]);
// Maximize x[a] - y[b]
MAX= max(MAX, dist[0][a]);
}
// Print minimum cost
printf("%d\n", min(dist[0][N - 1], best + 1));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given nodes and edges
N = 5, M = 4;
int K = 2;
int selected[] = { 1, 3 };
// Sort the selected nodes
sort(selected, selected + K);
// Given edges
edges[0].push_back(1);
edges[1].push_back(0);
edges[1].push_back(2);
edges[2].push_back(1);
edges[2].push_back(3);
edges[3].push_back(2);
edges[3].push_back(4);
edges[4].push_back(3);
// Function Call
shortestPathCost(selected, K);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
static int INF = (int)1e9 + 7;
static int N, M;
// To store graph as adjacency list
static ArrayList> edges;
// To store the shortest path
static int[][] dist = new int[2][200000];
// Function that performs BFS Traversal
static void bfs(int[] dist, int s)
{
int[] q = new int[200000];
// Fill initially each distance as INF
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
int qh = 0, qt = 0;
q[qh++] = s;
dist[s] = 0;
// Perform BFS
while (qt < qh)
{
int x = q[qt++];
// Traverse the current edges
for(Integer y : edges.get(x))
{
if (dist[y] == INF)
{
// Update the distance
dist[y] = dist[x] + 1;
// Insert in queue
q[qh++] = y;
}
}
}
}
// Function that maximizes the shortest
// path between source and destination
// vertex by adding a single edge between
// given selected nodes
static void shortestPathCost(int selected[], int K)
{
ArrayList data = new ArrayList<>();
// To update the shortest distance
// between node 1 to other vertices
bfs(dist[0], 0);
// To update the shortest distance
// between node N to other vertices
bfs(dist[1], N - 1);
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
{
// Store the values x[i] - y[i]
data.add(new int[]{dist[0][selected[i]] -
dist[1][selected[i]],
selected[i]});
}
// Sort all the vectors of pairs
Collections.sort(data, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int best = 0;
int MAX = -INF;
// Traverse data[]
for(int[] it : data)
{
int a = it[1];
best = Math.max(best,
MAX + dist[1][a]);
// Maximize x[a] - y[b]
MAX = Math.max(MAX, dist[0][a]);
}
// Print minimum cost
System.out.println(Math.min(dist[0][N - 1],
best + 1));
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Given nodes and edges
N = 5; M = 4;
int K = 2;
int selected[] = { 1, 3 };
// Sort the selected nodes
Arrays.sort(selected);
edges = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 200005; i++)
edges.add(new ArrayList());
// Given edges
edges.get(0).add(1);
edges.get(1).add(0);
edges.get(1).add(2);
edges.get(2).add(1);
edges.get(2).add(3);
edges.get(3).add(2);
edges.get(3).add(4);
edges.get(4).add(3);
// Function Call
shortestPathCost(selected, K);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function that performs BFS Traversal
def bfs(x, s):
global edges, dist
q = [0 for i in range(200000)]
# Fill initially each distance as INF
# fill(dist, dist + N, INF)
qh, qt = 0, 0
q[qh] = s
qh += 1
dist[x][s] = 0
# Perform BFS
while (qt < qh):
xx = q[qt]
qt += 1
# Traverse the current edges
for y in edges[xx]:
if (dist[x][y] == 10**18):
# Update the distance
dist[x][y] = dist[x][xx] + 1
# Insert in queue
q[qh] = y
qh += 1
# Function that maximizes the shortest
# path between source and destination
# vertex by adding a single edge between
# given selected nodes
def shortestPathCost(selected, K):
global dist, edges
data = []
# To update the shortest distance
# between node 1 to other vertices
bfs(0, 0)
# To update the shortest distance
# between node N to other vertices
bfs(1, N - 1)
for i in range(K):
# Store the values x[i] - y[i]
data.append([dist[0][selected[i]]- dist[1][selected[i]], selected[i]])
# Sort all the vectors of pairs
data = sorted(data)
best = 0
MAX = -10**18
# Traverse data[]
for it in data:
a = it[1]
best = max(best,MAX + dist[1][a])
# Maximize x[a] - y[b]
MAX= max(MAX, dist[0][a])
# Prminimum cost
print(min(dist[0][N - 1], best + 1))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given nodes and edges
edges = [[] for i in range(5)]
dist = [[10**18 for i in range(1000005)] for i in range(2)]
N,M = 5, 4
K = 2
selected = [1, 3]
# Sort the selected nodes
selected = sorted(selected)
# Given edges
edges[0].append(1)
edges[1].append(0)
edges[1].append(2)
edges[2].append(1)
edges[2].append(3)
edges[3].append(2)
edges[3].append(4)
edges[4].append(3)
# Function Call
shortestPathCost(selected, K)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 293时间复杂度: O(N*log N + M)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live