给定一个无向连通图和两个顶点A和B ,任务是找到顶点对{X, Y} 的数量,使得从X到Y 的任何路径都包含顶点A和B 。
笔记:
- { X, Y } 被视为等同于 { Y, X }。
- X != A, X != B, Y != A 和 Y != B。
例子:

For the above graph:
Input: A = 3, B = 5
Output:4
Explanation:
There are four pairs { X, Y } such that all the paths from the source X to the destination Y contain the vertices A, B. They are:
{1, 6}, {1, 7}, {2, 6} and {2, 7}.

For the above graph:
Input: A = 2, B = 1
Output: 1
Explanation:
There is only one pair { X, Y } such that all the paths from the source X to the destination Y contain the vertices A, B. That is:
{4, 3}.
方法:
- 对于给定的图,如果对于任何对{X, Y} ,如果除了给定的顶点A和B之外,它们之间存在其他路径,则这两个顶点不包括在最终答案中。那是因为我们需要对的数量,使得来自这些对的任何路径都包含顶点A和B 。
- 因此,我们对顶点对{ X, Y }感兴趣,这样删除顶点A (从B 开始)会断开从 X 到 Y 的连接,删除顶点B (从A 开始)会断开从 X 到的连接Y。
- 换句话说,如果 X 和 Y 在删除A和删除B时都属于图的不同组件,则对{X, Y}感兴趣。
因此,为了找到上述对,遵循以下步骤:
- 考虑一个随机有向连通图,其中一些互连的节点组连接到A并且一些互连的节点组连接到B 。 A和B之间可能有也可能没有节点。
- 如果我们同时删除A和B 会怎样?然后图形可以断开连接或保持连接。
- 如果图保持连通,则不存在顶点对,因为图中所有对{X, Y}都有其他路径,其中没有顶点A和B。
- 如果图形断开连接,则会出现两种情况:
- 在移除顶点 A 和 B 时,图被转换为两个不相连的组件。
- 在移除顶点 A 和 B 时,该图被转换为三个不相连的组件。
如果在移除顶点A和B 时,图被转换为两个不相连的组件,则出现三种情况:
- 当有一组互连的节点连接到顶点 A 时,一些独立的节点连接到 A 和 B,顶点 B 是图的叶节点:
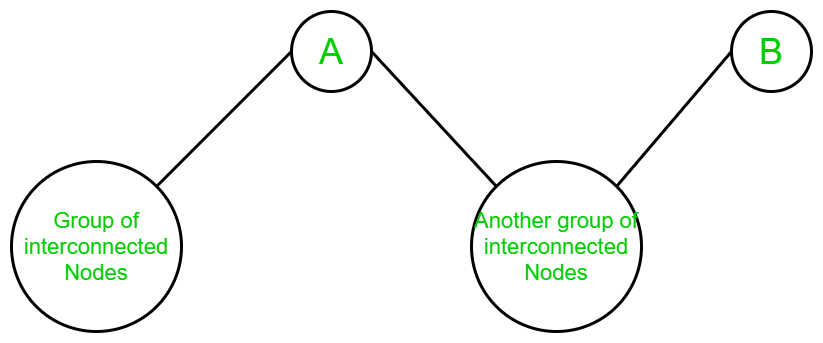
- 显然,在上图中,当顶点A和顶点B从中删除时,该图被转换为两个不同的组件。并且,任何组件都可以被丢弃,因为一个组件的顶点可能会到达任何其他组件的顶点而无需遍历顶点B 。所以不存在对。
- 当有一组互连的节点连接到顶点 B 时,一些独立的节点连接到 A 和 B,顶点 A 是图的叶节点:

- 显然,在上图中,当顶点A和顶点B从中删除时,该图被转换为两个不同的组件。并且,任何组件都可以被丢弃,因为一个组件的顶点可能会到达任何其他组件的顶点而无需遍历顶点A 。所以不存在对。
- 当顶点A和顶点B之间没有节点并且顶点A和B都不是图的叶节点时:

- 显然,在上图中,当顶点A和顶点B从中删除时,该图被转换为两个不同的组件。在这里,一个组件的任何一个顶点都可以与另一个组件的任何顶点配对。因此,该图中的对数成为组件 1 和组件 2 中互连节点数的乘积。
如果在移除顶点 A 和 B 时,图被转换为三个不相连的组件,那么只会出现一种情况:
- 当有一组互连的节点连接到顶点 A、顶点 B 并且顶点 A 和顶点 B 之间还有另一组节点并且顶点 A 和 B 都不是叶子节点时:

- 在这种情况下,由于上述原因,可以丢弃顶点 A 和 B 之间的分量。并且,一旦丢弃,就直接是二元图中的情况 3。相同的概念适用于查找顶点数。
因此,上面的想法是通过以下步骤来实现的:
- 使用向量 STL 将图存储为邻接表。
- 运行 DFS,以便我们修复顶点B ,就像我们删除它一样。这可以使用 DFS函数的基本条件来完成,即在到达顶点B 时返回调用。
- 计算删除B后A无法到达的顶点。
- 重复上述两步,固定顶点 A 并计算去除顶点A后B无法到达的顶点数。
- 将两个计数存储在两个不同的变量中。这表示首先在删除B然后删除A 时设置的顶点数。
- 将两个计数相乘是必需的答案。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find the number
// of pairs such that the path between
// every pair contains two given vertices
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000001;
int c, n, m, a, b;
// Function to perform DFS on the given graph
// by fixing the a vertex
void dfs(int a, int b, vector v[], int vis[])
{
// To mark a particular vertex as visited
vis[a] = 1;
// Variable to store the count of the
// vertices which can be reached from a
c++;
// Performing the DFS by iterating over
// the visited array
for (auto i : v[a]) {
// If the vertex is not visited
// and removing the vertex b
if (!vis[i] && i != b)
dfs(i, b, v, vis);
}
}
// Function to return the number of pairs
// such that path between any two pairs
// consists the given two vertices A and B
void Calculate(vector v[])
{
// Initializing the visited array
// and assigning it with 0's
int vis[n + 1];
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
// Initially, the count of vertices is 0
c = 0;
// Performing DFS by removing the vertex B
dfs(a, b, v, vis);
// Count the vertices which cannot be
// reached after removing the vertex B
int ans1 = n - c - 1;
// Again reinitializing the visited array
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
// Setting the count of vertices to 0 to
// perform the DFS again
c = 0;
// Performing the DFS by removing the vertex A
dfs(b, a, v, vis);
// Count the vertices which cannot be
// reached after removing the vertex A
int ans2 = n - c - 1;
// Multiplying both the vertices set
cout << ans1 * ans2 << "\n";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
n = 7, m = 7, a = 3, b = 5;
int edges[][2] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 6 },
{ 6, 7 },
{ 7, 5 } };
vector v[n + 1];
// Loop to store the graph
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
v[edges[i][0]].push_back(edges[i][1]);
v[edges[i][1]].push_back(edges[i][0]);
}
Calculate(v);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find the number
// of pairs such that the path between
// every pair contains two given vertices
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int N = 1000001;
static int c, n, m, a, b;
// Function to perform DFS on the given graph
// by fixing the a vertex
static void dfs(int a, int b, Vector v[], int vis[])
{
// To mark a particular vertex as visited
vis[a] = 1;
// Variable to store the count of the
// vertices which can be reached from a
c++;
// Performing the DFS by iterating over
// the visited array
for (int i : v[a]) {
// If the vertex is not visited
// and removing the vertex b
if (vis[i] == 0 && i != b)
dfs(i, b, v, vis);
}
}
// Function to return the number of pairs
// such that path between any two pairs
// consists of the given two vertices A and B
static void Calculate(Vector v[])
{
// Initializing the visited array
// and assigning it with 0's
int []vis = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(vis, 0);
// Initially, the count of vertices is 0
c = 0;
// Performing DFS by removing the vertex B
dfs(a, b, v, vis);
// Count the vertices which cannot be
// reached after removing the vertex B
int ans1 = n - c - 1;
// Again reinitializing the visited array
Arrays.fill(vis, 0);
// Setting the count of vertices to 0 to
// perform the DFS again
c = 0;
// Performing the DFS by removing the vertex A
dfs(b, a, v, vis);
// Count the vertices which cannot be
// reached after removing the vertex A
int ans2 = n - c - 1;
// Multiplying both the vertices set
System.out.print(ans1 * ans2+ "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
n = 7;
m = 7;
a = 3;
b = 5;
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 6 },
{ 6, 7 },
{ 7, 5 } };
Vector []v = new Vector[n + 1];
for(int i= 0; i <= n; i++) {
v[i] = new Vector();
}
// Loop to store the graph
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
v[edges[i][0]].add(edges[i][1]);
v[edges[i][1]].add(edges[i][0]);
}
Calculate(v);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Python3
# Python 3 program to find the number
# of pairs such that the path between
# every pair contains two given vertices
N = 1000001
c = 0
n = 0
m = 0
a = 0
b = 0
# Function to perform DFS on the given graph
# by fixing the a vertex
def dfs(a,b,v,vis):
global c
# To mark a particular vertex as visited
vis[a] = 1
# Variable to store the count of the
# vertices which can be reached from a
c += 1
# Performing the DFS by iterating over
# the visited array
for i in v[a]:
# If the vertex is not visited
# and removing the vertex b
if (vis[i]==0 and i != b):
dfs(i, b, v, vis)
# Function to return the number of pairs
# such that path between any two pairs
# consists of the given two vertices A and B
def Calculate(v):
global c
# Initializing the visited array
# and assigning it with 0's
vis = [0 for i in range(n + 1)]
# Initially, the count of vertices is 0
c = 0
# Performing DFS by removing the vertex B
dfs(a, b, v, vis)
# Count the vertices which cannot be
# reached after removing the vertex B
ans1 = n - c - 1
# Again reinitializing the visited array
vis = [0 for i in range(len(vis))]
# Setting the count of vertices to 0 to
# perform the DFS again
c = 0
# Performing the DFS by removing the vertex A
dfs(b, a, v, vis)
# Count the vertices which cannot be
# reached after removing the vertex A
ans2 = n - c - 1
# Multiplying both the vertices set
print(ans1 * ans2)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 7
m = 7
a = 3
b = 5
edges = [[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4], [4, 5], [5, 6], [6, 7], [7, 5]]
v = [[] for i in range(n + 1)]
# Loop to store the graph
for i in range(m):
v[edges[i][0]].append(edges[i][1])
v[edges[i][1]].append(edges[i][0])
Calculate(v)
# This code is contributed by Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# program to find the number
// of pairs such that the path between
// every pair contains two given vertices
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int N = 1000001;
static int c, n, m, a, b;
// Function to perform DFS on the given graph
// by fixing the a vertex
static void dfs(int a, int b, List []v, int []vis)
{
// To mark a particular vertex as visited
vis[a] = 1;
// Variable to store the count of the
// vertices which can be reached from a
c++;
// Performing the DFS by iterating over
// the visited array
foreach (int i in v[a]) {
// If the vertex is not visited
// and removing the vertex b
if (vis[i] == 0 && i != b)
dfs(i, b, v, vis);
}
}
// Function to return the number of pairs
// such that path between any two pairs
// consists of the given two vertices A and B
static void Calculate(List []v)
{
// Initializing the visited array
// and assigning it with 0's
int []vis = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
vis[i] = 0;
// Initially, the count of vertices is 0
c = 0;
// Performing DFS by removing the vertex B
dfs(a, b, v, vis);
// Count the vertices which cannot be
// reached after removing the vertex B
int ans1 = n - c - 1;
// Again reinitializing the visited array
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
vis[i] = 0;
// Setting the count of vertices to 0 to
// perform the DFS again
c = 0;
// Performing the DFS by removing the vertex A
dfs(b, a, v, vis);
// Count the vertices which cannot be
// reached after removing the vertex A
int ans2 = n - c - 1;
// Multiplying both the vertices set
Console.Write(ans1 * ans2+ "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
n = 7;
m = 7;
a = 3;
b = 5;
int [,]edges = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 5, 6 },
{ 6, 7 },
{ 7, 5 } };
List []v = new List[n + 1];
for(int i= 0; i <= n; i++) {
v[i] = new List();
}
// Loop to store the graph
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
v[edges[i,0]].Add(edges[i,1]);
v[edges[i,1]].Add(edges[i,0]);
}
Calculate(v);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh 输出:
4时间复杂度分析:
- 这里,DFS 执行了两次。因此,整体时间复杂度为O(V + E) 。
辅助空间:O(V + E)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。