给定一个具有N个顶点和M 个边的无向图,每个顶点都与一个成本相关联,并且给定了一个源顶点S。任务是从源顶点S找到最大成本路径,使得没有边被连续访问 2 次或更多次。
例子:
Input: N = 5, M = 5, source = 1, cost[] = {2, 2, 8, 6, 9}, Below is the given graph:
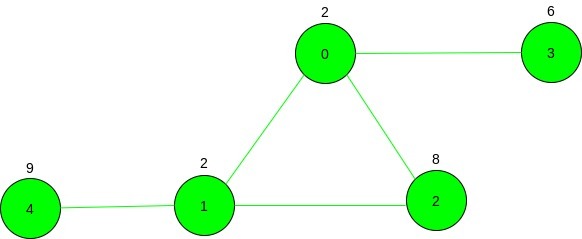
Output: 21
Explanation:
The maximum cost path matrix is given as:
1 -> 2 -> 0 -> 1 -> 4
Cost = 2 + 8 + 2 + 2 + 9 = 21
Input: N = 8, M = 8, source = 3, cost[] = {10, 11, 4, 12, 3, 4, 7, 9}

Output: 46
Explanation:
The maximum cost path matrix is given as:
3 -> 0 -> 2 -> 1 -> 7
方法:思路是检查图中是否存在循环,然后遍历循环的所有顶点,然后向代价最大的叶子节点遍历图。如果循环不存在,则问题陈述将转换为在任何有向图中查找最大成本路径。
以下是程序中使用的声明:
- dp[i]:存储遍历节点“i”及其所有子节点的总成本。
- vis[i]:标记已经访问过的节点。
- canTake:存储最大成本路径的所有节点的结果总和,不包括叶顶点及其子节点(如果存在)。
- best:存储最大成本叶节点及其子节点(如果存在)的成本。
- check:布尔变量,用作标志在图中查找循环,当找到循环时,其值变为0。
以下是步骤:
- 执行 DFS 遍历,标志变量检查设置为“1”,最初表示未找到循环。
- 同时为每个节点构建dp[]并更新最大成本,直到遍历该节点。
- 如果发现相邻节点已被访问并且它不是父节点,则找到循环并将检查值设置为0 。
- 将循环所有节点的成本添加到canTake 。
- 遍历遍历节点的相邻节点后,没有找到循环,则表示从循环到叶顶点的路径的成本,如果dp[i]大于best ,则将best更新为dp[i] 。
- 遍历图形后,打印canTake和best的总和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 100000;
// To store the resulting
// sum of the cost
int canTake;
// To store largest
// cost leaf vertex
int best;
int dp[N];
bool vis[N];
// DFS Traversal to find the update
// the maximum cost of from any
// node to leaf
int dfs(vector >& g,
int* cost, int u, int pre)
{
// Mark vertex as visited
vis[u] = true;
// Store vertex initial cost
dp[u] = cost[u];
// Initially assuming edge
// not to be traversed
bool check = 1;
int cur = cost[u];
for (auto& x : g[u]) {
// Back edge found so,
// edge can be part of
// traversal
if (vis[x] && x != pre) {
check = 0;
}
// New vertex is found
else if (!vis[x]) {
// Bitwise AND the current
// check with the returned
// check by the previous
// DFS Call
check &= dfs(g, cost, x, u);
// Adds parent and its
// children cost
cur = max(cur,
cost[u] + dp[x]);
}
}
// Updates total cost of parent
// including child nodes
dp[u] = cur;
// Edge is part of the cycle
if (!check) {
// Add cost of vertex
// to the answer
canTake += cost[u];
}
else {
// Updates the largest
// cost leaf vertex
best = max(best, dp[u]);
}
return check;
}
// Function to find the maximum cost
// from source vertex such that no
// two edges is traversed twice
int FindMaxCost(vector >& g,
int* cost, int source)
{
// DFS Call
dfs(g, cost, source, -1);
// Print the maximum cost
cout << canTake + best;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 5, m = 5;
// Cost Array
int cost[] = { 2, 2, 8, 6, 9 };
vector > g(n);
// Given Graph
g[0].push_back(1);
g[1].push_back(0);
g[0].push_back(2);
g[2].push_back(0);
g[0].push_back(3);
g[3].push_back(0);
g[1].push_back(2);
g[2].push_back(1);
g[1].push_back(4);
g[4].push_back(1);
// Given Source Node
int source = 1;
// Function Call
FindMaxCost(g, cost, source);
return 0;
}Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int N = 100000;
// To store the resulting
// sum of the cost
static int canTake;
// To store largest
// cost leaf vertex
static int best;
static int []dp = new int[N];
static boolean []vis = new boolean[N];
// DFS Traversal to find the update
// the maximum cost of from any
// node to leaf
static boolean dfs(Vector []g,
int []cost, int u, int pre)
{
// Mark vertex as visited
vis[u] = true;
// Store vertex initial cost
dp[u] = cost[u];
// Initially assuming edge
// not to be traversed
boolean check = true;
int cur = cost[u];
for(int x : g[u])
{
// Back edge found so,
// edge can be part of
// traversal
if (vis[x] && x != pre)
{
check = false;
}
// New vertex is found
else if (!vis[x])
{
// Bitwise AND the current
// check with the returned
// check by the previous
// DFS Call
check = dfs(g, cost, x, u) ?
false : true;
// Adds parent and its
// children cost
cur = Math.max(cur, cost[u] +
dp[x]);
}
}
// Updates total cost of parent
// including child nodes
dp[u] = cur;
// Edge is part of the cycle
if (!check)
{
// Add cost of vertex
// to the answer
canTake += cost[u];
}
else
{
// Updates the largest
// cost leaf vertex
best = Math.max(best, dp[u]);
}
return check;
}
// Function to find the maximum cost
// from source vertex such that no
// two edges is traversed twice
static void FindMaxCost(Vector [] g,
int []cost, int source)
{
// DFS call
dfs(g, cost, source, -1);
// Print the maximum cost
System.out.print(canTake + best);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5, m = 5;
// Cost Array
int cost[] = { 2, 2, 8, 6, 9 };
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector []g = new Vector[n];
for(int i = 0; i < g.length; i++)
g[i] = new Vector();
// Given Graph
g[0].add(1);
g[1].add(0);
g[0].add(2);
g[2].add(0);
g[0].add(3);
g[3].add(0);
g[1].add(2);
g[2].add(1);
g[1].add(4);
g[4].add(1);
// Given Source Node
int source = 1;
// Function call
FindMaxCost(g, cost, source);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarPython3
# Python3 program for the above approach
N = 100000
# To store the resulting
# sum of the cost
canTake = 0
# To store largest
# cost leaf vertex
best = 0
dp = [0 for i in range(N)]
vis = [0 for i in range(N)]
# DFS Traversal to find the update
# the maximum cost of from any
# node to leaf
def dfs(g, cost, u, pre):
global canTake, best
# Mark vertex as visited
vis[u] = True
# Store vertex initial cost
dp[u] = cost[u]
# Initially assuming edge
# not to be traversed
check = 1
cur = cost[u]
for x in g[u]:
# Back edge found so,
# edge can be part of
# traversal
if (vis[x] and x != pre):
check = 0
# New vertex is found
elif (not vis[x]):
# Bitwise AND the current
# check with the returned
# check by the previous
# DFS Call
check &= dfs(g, cost, x, u)
# Adds parent and its
# children cost
cur = max(cur, cost[u] + dp[x])
# Updates total cost of parent
# including child nodes
dp[u] = cur
# Edge is part of the cycle
if (not check):
# Add cost of vertex
# to the answer
canTake += cost[u]
else:
# Updates the largest
# cost leaf vertex
best = max(best, dp[u])
return check
# Function to find the maximum cost
# from source vertex such that no
# two edges is traversed twice
def FindMaxCost(g, cost, source):
# DFS Call
dfs(g, cost, source, -1)
# Print the maximum cost
print(canTake + best)
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
n = 5
m = 5
# Cost Array
cost = [ 2, 2, 8, 6, 9 ]
g = [[] for i in range(n)]
# Given Graph
g[0].append(1)
g[1].append(0)
g[0].append(2)
g[2].append(0)
g[0].append(3)
g[3].append(0)
g[1].append(2)
g[2].append(1)
g[1].append(4)
g[4].append(1)
# Given Source Node
source = 1
# Function Call
FindMaxCost(g, cost, source)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program for
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int N = 100000;
// To store the resulting
// sum of the cost
static int canTake;
// To store largest
// cost leaf vertex
static int best;
static int []dp = new int[N];
static bool []vis = new bool[N];
// DFS Traversal to find the update
// the maximum cost of from any
// node to leaf
static bool dfs(List []g,
int []cost,
int u, int pre)
{
// Mark vertex as visited
vis[u] = true;
// Store vertex initial cost
dp[u] = cost[u];
// Initially assuming edge
// not to be traversed
bool check = true;
int cur = cost[u];
foreach(int x in g[u])
{
// Back edge found so,
// edge can be part of
// traversal
if (vis[x] && x != pre)
{
check = false;
}
// New vertex is found
else if (!vis[x])
{
// Bitwise AND the current
// check with the returned
// check by the previous
// DFS Call
check = dfs(g, cost, x, u) ?
false : true;
// Adds parent and its
// children cost
cur = Math.Max(cur, cost[u] + dp[x]);
}
}
// Updates total cost of parent
// including child nodes
dp[u] = cur;
// Edge is part of the cycle
if (!check)
{
// Add cost of vertex
// to the answer
canTake += cost[u];
}
else
{
// Updates the largest
// cost leaf vertex
best = Math.Max(best, dp[u]);
}
return check;
}
// Function to find the maximum cost
// from source vertex such that no
// two edges is traversed twice
static void FindMaxCost(List [] g,
int []cost, int source)
{
// DFS call
dfs(g, cost, source, -1);
// Print the maximum cost
Console.Write(canTake + best);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5, m = 5;
// Cost Array
int []cost = {2, 2, 8, 6, 9};
List []g = new List[n];
for(int i = 0; i < g.Length; i++)
g[i] = new List();
// Given Graph
g[0].Add(1);
g[1].Add(0);
g[0].Add(2);
g[2].Add(0);
g[0].Add(3);
g[3].Add(0);
g[1].Add(2);
g[2].Add(1);
g[1].Add(4);
g[4].Add(1);
// Given Source Node
int source = 1;
// Function call
FindMaxCost(g, cost, source);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh输出:
21时间复杂度: O(N + M) ,其中 N 是顶点数,M 是边数。
辅助空间: O(N + M) ,其中 N 是顶点数,M 是边数。
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live