无向图中的欧拉路径
给定一个无向图的邻接矩阵表示。查找图中是否有任何欧拉路径。如果没有路径打印“No Solution”。如果有任何路径打印路径。
例子:
Input : [[0, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
Output : 5 -> 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2
Input : [[0, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0]]
Output : "No Solution"这个问题的基本情况是,如果边数为奇数(即奇数度)的顶点数大于 2,则不存在欧拉路径。
如果它有解决方案并且所有节点都有偶数条边,那么我们可以从任何节点开始我们的路径。
如果它有解并且恰好两个顶点有奇数条边,那么我们必须从这两个顶点之一开始我们的路径。
不会有恰好一个顶点有奇数条边的情况,因为总共有偶数条边。
寻找路径的过程:
- 首先,取一个空栈和一个空路径。
- 如果所有顶点的边数都是偶数,则从其中任何一个开始。如果其中两个顶点的边数为奇数,则从其中一个开始。将变量 current 设置为此起始顶点。
- 如果当前顶点至少有一个相邻节点,则首先发现该节点,然后通过回溯发现当前节点。为此,将当前节点添加到堆栈中,删除当前节点和相邻节点之间的边,将当前节点设置为相邻节点。
- 如果当前节点没有任何邻居,则将其添加到路径并弹出堆栈将当前设置为弹出顶点。
- 重复过程 3 和 4,直到堆栈为空且当前节点没有任何邻居。
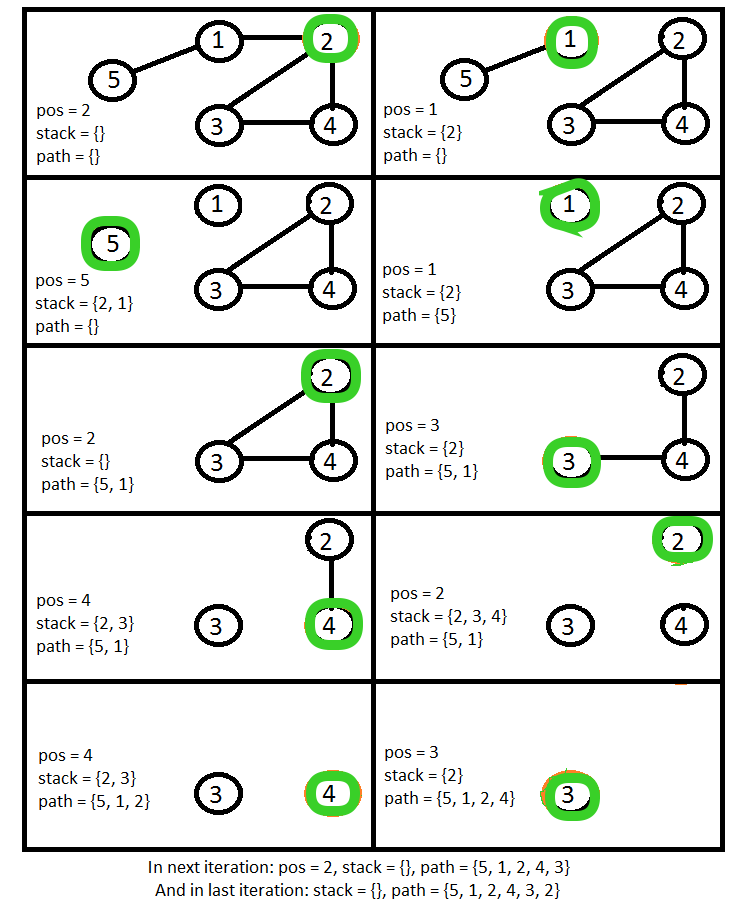
在过程路径变量保存欧拉路径之后。
C++
// Efficient C++ program to
// find out Eulerian path
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find out the path
// It takes the adjacency matrix
// representation of the graph as input
void findpath(int graph[][5], int n)
{
vector numofadj;
// Find out number of edges each vertex has
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
numofadj.push_back(accumulate(graph[i],
graph[i] + 5, 0));
// Find out how many vertex has odd number edges
int startpoint = 0, numofodd = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (numofadj[i] % 2 == 1)
{
numofodd++;
startpoint = i;
}
}
// If number of vertex with odd number of edges
// is greater than two return "No Solution".
if (numofodd > 2)
{
cout << "No Solution" << endl;
return;
}
// If there is a path find the path
// Initialize empty stack and path
// take the starting current as discussed
stack stack;
vector path;
int cur = startpoint;
// Loop will run until there is element in the stack
// or current edge has some neighbour.
while (!stack.empty() or
accumulate(graph[cur],
graph[cur] + 5, 0) != 0)
{
// If current node has not any neighbour
// add it to path and pop stack
// set new current to the popped element
if (accumulate(graph[cur],
graph[cur] + 5, 0) == 0)
{
path.push_back(cur);
cur = stack.top();
stack.pop();
}
// If the current vertex has at least one
// neighbour add the current vertex to stack,
// remove the edge between them and set the
// current to its neighbour.
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (graph[cur][i] == 1)
{
stack.push(cur);
graph[cur][i] = 0;
graph[i][cur] = 0;
cur = i;
break;
}
}
}
}
// print the path
for (auto ele : path) cout << ele << " -> ";
cout << cur << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Test case 1
int graph1[][5] = {{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
int n = sizeof(graph1) / sizeof(graph1[0]);
findpath(graph1, n);
// Test case 2
int graph2[][5] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0}};
n = sizeof(graph1) / sizeof(graph1[0]);
findpath(graph2, n);
// Test case 3
int graph3[][5] = {{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 0, 1, 0}};
n = sizeof(graph1) / sizeof(graph1[0]);
findpath(graph3, n);
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Java
// Efficient Java program to
// find out Eulerian path
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to find out the path
// It takes the adjacency matrix
// representation of the graph as input
static void findpath(int[][] graph, int n)
{
Vector numofadj = new Vector<>();
// Find out number of edges each vertex has
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
numofadj.add(accumulate(graph[i], 0));
// Find out how many vertex has odd number edges
int startPoint = 0, numofodd = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (numofadj.elementAt(i) % 2 == 1)
{
numofodd++;
startPoint = i;
}
}
// If number of vertex with odd number of edges
// is greater than two return "No Solution".
if (numofodd > 2)
{
System.out.println("No Solution");
return;
}
// If there is a path find the path
// Initialize empty stack and path
// take the starting current as discussed
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
Vector path = new Vector<>();
int cur = startPoint;
// Loop will run until there is element in the stack
// or current edge has some neighbour.
while (!stack.isEmpty() || accumulate(graph[cur], 0) != 0)
{
// If current node has not any neighbour
// add it to path and pop stack
// set new current to the popped element
if (accumulate(graph[cur], 0) == 0)
{
path.add(cur);
cur = stack.pop();
// If the current vertex has at least one
// neighbour add the current vertex to stack,
// remove the edge between them and set the
// current to its neighbour.
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (graph[cur][i] == 1)
{
stack.add(cur);
graph[cur][i] = 0;
graph[i][cur] = 0;
cur = i;
break;
}
}
}
}
// print the path
for (int ele : path)
System.out.print(ele + " -> ");
System.out.println(cur);
}
static int accumulate(int[] arr, int sum)
{
for (int i : arr)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Test case 1
int[][] graph1 = { { 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
int n = graph1.length;
findpath(graph1, n);
// Test case 2
int[][] graph2 = { { 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 } };
n = graph2.length;
findpath(graph2, n);
// Test case 3
int[][] graph3 = { { 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
n = graph3.length;
findpath(graph3, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Efficient Python3 program to
# find out Eulerian path
# Function to find out the path
# It takes the adjacency matrix
# representation of the graph as input
def findpath(graph, n):
numofadj = []
# Find out number of edges each
# vertex has
for i in range(n):
numofadj.append(sum(graph[i]))
# Find out how many vertex has
# odd number edges
startpoint, numofodd = 0, 0
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
if (numofadj[i] % 2 == 1):
numofodd += 1
startpoint = i
# If number of vertex with odd number of edges
# is greater than two return "No Solution".
if (numofodd > 2):
print("No Solution")
return
# If there is a path find the path
# Initialize empty stack and path
# take the starting current as discussed
stack = []
path = []
cur = startpoint
# Loop will run until there is element in the
# stack or current edge has some neighbour.
while (len(stack) > 0 or sum(graph[cur])!= 0):
# If current node has not any neighbour
# add it to path and pop stack set new
# current to the popped element
if (sum(graph[cur]) == 0):
path.append(cur)
cur = stack[-1]
del stack[-1]
# If the current vertex has at least one
# neighbour add the current vertex to stack,
# remove the edge between them and set the
# current to its neighbour.
else:
for i in range(n):
if (graph[cur][i] == 1):
stack.append(cur)
graph[cur][i] = 0
graph[i][cur] = 0
cur = i
break
# Print the path
for ele in path:
print(ele, end = " -> ")
print(cur)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Test case 1
graph1 = [ [ 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 ] ]
n = len(graph1)
findpath(graph1, n)
# Test case 2
graph2 = [ [ 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 ] ]
n = len(graph2)
findpath(graph2, n)
# Test case 3
graph3 = [ [ 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 1, 0 ] ]
n = len(graph3)
findpath(graph3, n)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// Efficient C# program to
// find out Eulerian path
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to find out the path
// It takes the adjacency matrix
// representation of the graph
// as input
static void findpath(int[,] graph,
int n)
{
List numofadj =
new List();
// Find out number of edges
// each vertex has
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
numofadj.Add(accumulate(graph,
i, 0));
// Find out how many vertex has
// odd number edges
int startPoint = 0, numofodd = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (numofadj[i] % 2 == 1)
{
numofodd++;
startPoint = i;
}
}
// If number of vertex with odd
// number of edges is greater than
// two return "No Solution".
if (numofodd > 2)
{
Console.WriteLine("No Solution");
return;
}
// If there is a path find the path
// Initialize empty stack and path
// take the starting current as
// discussed
Stack stack = new Stack();
List path = new List();
int cur = startPoint;
// Loop will run until there is element
// in the stack or current edge has some
// neighbour.
while (stack.Count != 0 ||
accumulate(graph, cur, 0) != 0)
{
// If current node has not any
// neighbour add it to path and
// pop stack set new current to
// the popped element
if (accumulate(graph,cur, 0) == 0)
{
path.Add(cur);
cur = stack.Pop();
// If the current vertex has at
// least one neighbour add the
// current vertex to stack, remove
// the edge between them and set the
// current to its neighbour.
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (graph[cur, i] == 1)
{
stack.Push(cur);
graph[cur, i] = 0;
graph[i, cur] = 0;
cur = i;
break;
}
}
}
}
// print the path
foreach (int ele in path)
Console.Write(ele + " -> ");
Console.WriteLine(cur);
}
static int accumulate(int[,] matrix,
int row, int sum)
{
int []arr = GetRow(matrix,
row);
foreach (int i in arr)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
public static int[] GetRow(int[,] matrix,
int row)
{
var rowLength = matrix.GetLength(1);
var rowVector = new int[rowLength];
for (var i = 0; i < rowLength; i++)
rowVector[i] = matrix[row, i];
return rowVector;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Test case 1
int[,] graph1 = {{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
int n = graph1.GetLength(0);
findpath(graph1, n);
// Test case 2
int[,] graph2 = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0}};
n = graph2.GetLength(0);
findpath(graph2, n);
// Test case 3
int[,] graph3 = {{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 0, 1, 0}};
n = graph3.GetLength(0);
findpath(graph3, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji 输出:
4 -> 0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
No Solution
4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 4 -> 0 -> 1 -> 3时间复杂度:
该算法的运行时间复杂度为 O(E)。该算法也可用于查找欧拉回路。如果路径的第一个和最后一个顶点相同,那么它将是一个欧拉回路。