编写一个程序,检查给定的链表是否包含循环,如果存在循环,则返回循环中的节点数。例如,在下面的链表中存在一个循环,并且循环的长度为 4。如果不存在循环,则该函数应返回 0。
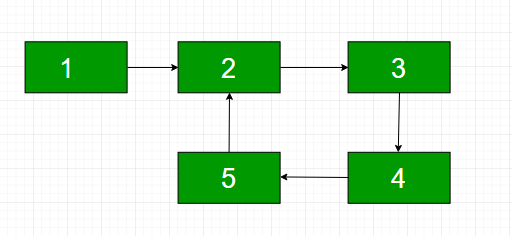
方法:在这篇文章中,我们将使用Map的概念来存储链表中存在的节点的地址作为键,并将它们的位置作为值存储。
以下是分步方法:
- 遍历链表的每一个节点,并保持从一开始的位置。在每个节点之后增加位置。
- 检查该节点是否存在于 Map 中。
- 如果地图不包含该节点的地址,请将其连同其位置一起插入到地图中。
- 如果地图已经包含该节点的地址,则返回它们位置之间的差异。
- 如果没有找到这样的节点,则返回 0。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find length of loop
// in a linked list using Map
#include
using namespace std;
// Linked List node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
Node(int num)
{
data = num;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Function detects and counts loop
// nodes in the list. If loop is not there,
// then returns 0
int countNodesinLoop(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* p = head;
int pos = 0;
// Maintain a map to store addresses
// of node and their position
unordered_map m;
// Traverse through the linked list
while (p != NULL) {
// If the node is not present in the map
if (m.find(p) == m.end()) {
m[p] = pos;
pos++;
}
// if the node is present
else {
// Return difference between
// position of the present node and
// position where that node occured before
return (pos - m[p]);
}
p = p->next;
}
// Return 0 to indicate
// there is no loop
return 0;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Create nodes of the linked list
struct Node* head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
head->next->next = new Node(3);
head->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5);
// Create a loop for testing the function
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next;
// Call the function for the above linked list
cout << countNodesinLoop(head) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find length of loop
// in a linked list using Map
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int num)
{
data = num;
next = null;
}
}
// Function detects and counts loop
// nodes in the list. If loop is not there,
// then returns 0
public static int countNodesinLoop(Node head)
{
Node p = head;
int pos = 0;
// Maintain a map to store addresses
// of node and their position
HashMap m = new HashMap();
// Traverse through the linked list
while (p != null)
{
// If the node is not present in the map
if (!m.containsKey(p))
{
m.put(p, pos);
pos++;
}
// If the node is present
else
{
// Return difference between
// position of the present
// node and position where
// that node occured before
return (pos - m.get(p));
}
p = p.next;
}
// Return 0 to indicate
// there is no loop
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Create nodes of the linked list
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
// Create a loop for testing the function
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next;
// Call the function for the above linked list
System.out.println(countNodesinLoop(head));
}
}
// This code is contributed by adityapande88 Python3
# Python3 program to find length of loop
# in a linked list using Map
# Linked List node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Function detects and counts loop
# nodes in the list. If loop is not there,
# then returns 0
def countNodesinLoop(head):
p = head;
pos = 0;
# Maintain a map to store addresses
# of node and their position
m = dict()
# Traverse through the linked list
while (p != None):
# If the node is not present in the map
if (p not in m):
m[p] = pos;
pos += 1
# if the node is present
else:
# Return difference between
# position of the present node and
# position where that node occured before
return (pos - m[p]);
p = p.next;
# Return 0 to indicate
# there is no loop
return 0;
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Create nodes of the linked list
head = Node(1);
head.next = Node(2);
head.next.next = Node(3);
head.next.next.next = Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = Node(5);
# Create a loop for testing the function
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next;
# Call the function for the above linked list
print(countNodesinLoop(head))
# This code is contributed by Pratham76C#
// C# program to find length of loop
// in a linked list using Map
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
// Constructor
public Node(int num)
{
data = num;
next = null;
}
}
// Function detects and counts loop
// nodes in the list. If loop is not there,
// then returns 0
public static int countNodesinLoop(Node head)
{
Node p = head;
int pos = 0;
// Maintain a map to store addresses
// of node and their position
Dictionary m = new Dictionary();
// Traverse through the linked list
while (p != null)
{
// If the node is not present in the map
if (!m.ContainsKey(p))
{
m[p] = pos;
pos++;
}
// If the node is present
else
{
// Return difference between
// position of the present
// node and position where
// that node occured before
return (pos - m[p]);
}
p = p.next;
}
// Return 0 to indicate
// there is no loop
return 0;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create nodes of the linked list
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
// Create a loop for testing the function
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next;
// Call the function for the above linked list
Console.Write(countNodesinLoop(head));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56 输出
4类似文章:使用 Floyd 循环检测算法在链表中查找循环的长度
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live