用于在链表中查找循环长度的Python程序
编写一个函数detectAndCountLoop()检查给定的链表是否包含循环,如果存在循环,则返回循环中的节点数。例如,循环存在于下面的链接列表中,循环的长度为 4。如果循环不存在,则函数应返回 0。
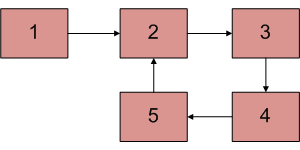
方法:
众所周知,弗洛伊德的循环检测算法在快速和慢速指针在一个公共点相遇时终止。也知道这个公共点是循环节点之一。将此公共点的地址存储在指针变量say (ptr) 中。然后用 1 初始化一个计数器,从公共点开始,继续访问下一个节点并增加计数器,直到再次到达公共指针。
此时,计数器的值将等于循环的长度。
算法:
- 使用 Floyd 循环检测算法找到循环中的公共点
- 将指针存储在临时变量中并保持计数 = 0
- 遍历链表,直到再次到达同一个节点,并在移动到下一个节点时增加计数。
- 将计数打印为循环长度
Python3
# Python program to detect a loop and
# find the length of the loop
# Node defining class
class Node:
# Function to make a node
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.next = None
# Linked List defining and loop
# length finding class
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize the
# head of the linked list
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new
# node at the end
def AddNode(self, val):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(val)
else:
curr = self.head
while(curr.next):
curr = curr.next
curr.next = Node(val)
# Function to create a loop in the
# Linked List. This function creates
# a loop by connecting the last node
# to n^th node of the linked list,
# (counting first node as 1)
def CreateLoop(self, n):
# LoopNode is the connecting node to
# the last node of linked list
LoopNode = self.head
for _ in range(1, n):
LoopNode = LoopNode.next
# end is the last node of the
# Linked List
end = self.head
while(end.next):
end = end.next
# Creating the loop
end.next = LoopNode
# Function to detect the loop and return
# the length of the loop if the returned
# value is zero, which means that either
# the linked list is empty or the linked
# list doesn't have any loop
def detectLoop(self):
# If linked list is empty then there
# is no loop, so return 0
if self.head is None:
return 0
# Using Floyd’s Cycle-Finding
# Algorithm/ Slow-Fast Pointer Method
slow = self.head
fast = self.head
# To show that both slow and fast
# are at start of the Linked List
flag = 0
while(slow and slow.next and fast and
fast.next and fast.next.next):
if slow == fast and flag != 0:
# Means loop is confirmed in the
# Linked List. Now slow and fast
# are both at the same node which
# is part of the loop
count = 1
slow = slow.next
while(slow != fast):
slow = slow.next
count += 1
return count
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
flag = 1
return 0 # No loop
# Setting up the code
# Making a Linked List and
# adding the nodes
myLL = LinkedList()
myLL.AddNode(1)
myLL.AddNode(2)
myLL.AddNode(3)
myLL.AddNode(4)
myLL.AddNode(5)
# Creating a loop in the linked List
# Loop is created by connecting the
# last node of linked list to n^th node
# 1<= n <= len(LinkedList)
myLL.CreateLoop(2)
# Checking for Loop in the Linked List
# and printing the length of the loop
loopLength = myLL.detectLoop()
if myLL.head is None:
print("Linked list is empty")
else:
print(str(loopLength))
# This code is contributed by _Ashutosh输出:
4复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历一次链表。 - 辅助空间: O(1)。
因为不需要额外的空间。
请参阅完整文章在链表中查找循环长度以获取更多详细信息!