给定一个完整的二叉树,任务是按照以下模式打印元素。让我们考虑树是:
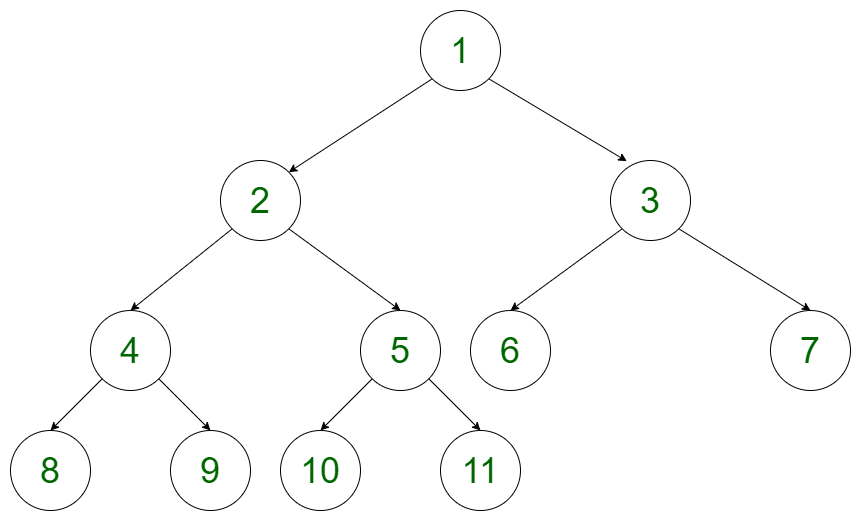
树的遍历方式如下:
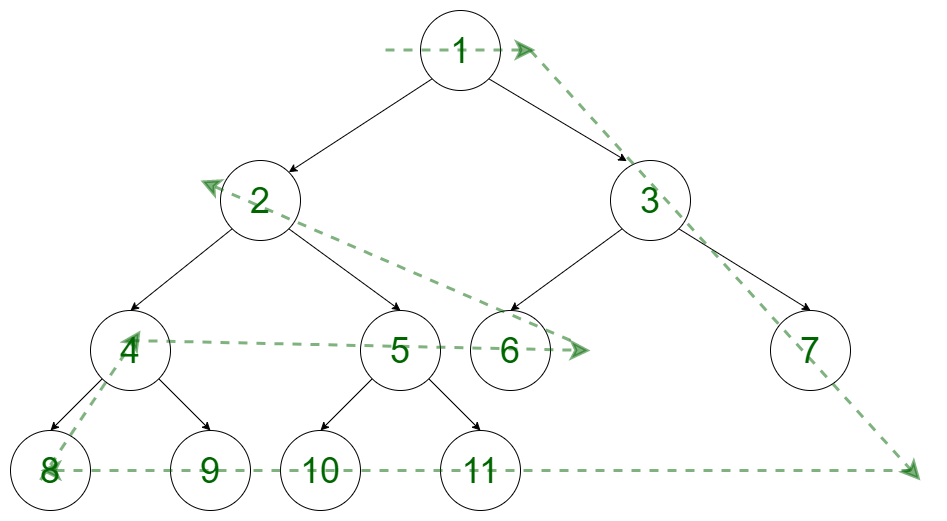
上述树的输出是:
1 3 7 11 10 9 8 4 5 6 2方法:想法是使用修改后的广度优先搜索函数将每一层的所有节点存储在一个向量数组中。与此同时,树需要遍历的最高级别也存储在一个变量中。在这个预计算任务之后,按照以下步骤来获得所需的答案:
- 创建矢量树[],其中树[I]将树的所有节点存储在I级。
- 取一个整数变量k ,它跟踪正在遍历的级别数,另一个整数变量path跟踪已完成的循环数。还创建了一个标志变量来跟踪树被遍历的方向。
- 现在,开始在每个级别打印最右边的节点,直到达到最大级别。
- 由于达到了最大水平,因此必须改变方向。在最后一层,从最右到左打印元素。并且maxLevel变量的值必须递减。
- 当树从下层遍历到上层时,最右边的元素被打印出来。由于在下一次迭代中, maxlevel值已更改,因此可以确保不会再次遍历最后一层中已经访问过的节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to print sideways
// traversal of complete binary tree
#include
using namespace std;
const int sz = 1e5;
int maxLevel = 0;
// Adjacency list representation
// of the tree
vector tree[sz + 1];
// Boolean array to mark all the
// vertices which are visited
bool vis[sz + 1];
// Integer array to store the level
// of each node
int level[sz + 1];
// Array of vector where ith index
// stores all the nodes at level i
vector nodes[sz + 1];
// Utility function to create an
// edge between two vertices
void addEdge(int a, int b)
{
// Add a to b's list
tree[a].push_back(b);
// Add b to a's list
tree[b].push_back(a);
}
// Modified Breadth-First Function
void bfs(int node)
{
// Create a queue of {child, parent}
queue > qu;
// Push root node in the front of
// the queue and mark as visited
qu.push({ node, 0 });
nodes[0].push_back(node);
vis[node] = true;
level[1] = 0;
while (!qu.empty()) {
pair p = qu.front();
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
qu.pop();
vis[p.first] = true;
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex s. If any adjacent has not
// been visited then enqueue it
for (int child : tree[p.first]) {
if (!vis[child]) {
qu.push({ child, p.first });
level[child] = level[p.first] + 1;
maxLevel = max(maxLevel, level[child]);
nodes[level[child]].push_back(child);
}
}
}
}
// Utility Function to display the pattern
void display()
{
// k represents the level no.
// cycle represents how many
// cycles has been completed
int k = 0, path = 0;
int condn = (maxLevel) / 2 + 1;
bool flag = true;
// While there are nodes left to traverse
while (condn--) {
if (flag) {
// Traversing whole level from
// left to right
int j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
for (j = 0; j < nodes[k].size() - path; j++)
cout << nodes[k][j] << " ";
// Moving to new level
k++;
// Traversing rightmost unvisited
// element in path path as we
// move up to down
while (k < maxLevel) {
j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
cout << nodes[k][j - path] << " ";
k++;
}
j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
if (k > path)
for (j -= path; j >= 0; j--)
cout << nodes[k][j] << " ";
// Setting value of new maximum
// level upto which we have to traverse
// next time
maxLevel--;
// Updating from which level to
// start new path
k--;
path++;
flag = !flag;
}
else {
// Traversing each element of remaining
// last level from left to right
int j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
for (j = 0; j < nodes[k].size() - path; j++)
cout << nodes[k][j] << " ";
// Decrementing value of Max level
maxLevel--;
k--;
// Traversing rightmost unvisited
// element in path as we
// move down to up
while (k > path) {
int j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
cout << nodes[k][j - path] << " ";
k--;
}
j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
if (k == path)
for (j -= path; j >= 0; j--)
cout << nodes[k][j] << " ";
path++;
// Updating the level number from which
// a new cycle has to be started
k++;
flag = !flag;
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initialising the above mentioned
// complete binary tree
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// Adding edge to a binary tree
addEdge(i, 2 * i);
addEdge(i, 2 * i + 1);
}
// Calling modified bfs function
bfs(1);
display();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print sideways
// traversal of complete binary tree
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static int sz = (int) 1e5;
static int maxLevel = 0;
// Adjacency list representation
// of the tree
static Vector []tree = new Vector[sz + 1];
// Boolean array to mark all the
// vertices which are visited
static boolean []vis = new boolean[sz + 1];
// Integer array to store the level
// of each node
static int []level = new int[sz + 1];
// Array of vector where ith index
// stores all the nodes at level i
static Vector []nodes = new Vector[sz + 1];
// Utility function to create an
// edge between two vertices
static void addEdge(int a, int b)
{
// Add a to b's list
tree[a].add(b);
// Add b to a's list
tree[b].add(a);
}
// Modified Breadth-First Function
static void bfs(int node)
{
// Create a queue of {child, parent}
Queue qu = new LinkedList<>();
// Push root node in the front of
// the queue and mark as visited
qu.add(new pair( node, 0 ));
nodes[0].add(node);
vis[node] = true;
level[1] = 0;
while (!qu.isEmpty()) {
pair p = qu.peek();
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
qu.remove();
vis[p.first] = true;
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex s. If any adjacent has not
// been visited then enqueue it
for (int child : tree[p.first]) {
if (!vis[child]) {
qu.add(new pair( child, p.first ));
level[child] = level[p.first] + 1;
maxLevel = Math.max(maxLevel, level[child]);
nodes[level[child]].add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Utility Function to display the pattern
static void display()
{
// k represents the level no.
// cycle represents how many
// cycles has been completed
int k = 0, path = 0;
int condn = (maxLevel) / 2 + 1;
boolean flag = true;
// While there are nodes left to traverse
while (condn-- > 0) {
if (flag) {
// Traversing whole level from
// left to right
int j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
for (j = 0; j < nodes[k].size() - path; j++)
System.out.print(nodes[k].get(j)+ " ");
// Moving to new level
k++;
// Traversing rightmost unvisited
// element in path path as we
// move up to down
while (k < maxLevel) {
j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
System.out.print(nodes[k].get(j - path)+ " ");
k++;
}
j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
if (k > path)
for (j -= path; j >= 0; j--)
System.out.print(nodes[k].get(j)+ " ");
// Setting value of new maximum
// level upto which we have to traverse
// next time
maxLevel--;
// Updating from which level to
// start new path
k--;
path++;
flag = !flag;
}
else {
// Traversing each element of remaining
// last level from left to right
int j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
for (j = 0; j < nodes[k].size() - path; j++)
System.out.print(nodes[k].get(j)+ " ");
// Decrementing value of Max level
maxLevel--;
k--;
// Traversing rightmost unvisited
// element in path as we
// move down to up
while (k > path) {
int c = nodes[k].size() - 1;
System.out.print(nodes[k].get(c - path)+ " ");
k--;
}
j = nodes[k].size() - 1;
if (k == path)
for (j -= path; j >= 0; j--)
System.out.print(nodes[k].get(j)+ " ");
path++;
// Updating the level number from which
// a new cycle has to be started
k++;
flag = !flag;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < tree.length; i++) {
tree[i] = new Vector<>();
nodes[i] = new Vector<>();
}
// Initialising the above mentioned
// complete binary tree
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// Adding edge to a binary tree
addEdge(i, 2 * i);
addEdge(i, 2 * i + 1);
}
// Calling modified bfs function
bfs(1);
display();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 program to prsideways
# traversal of complete binary tree
from collections import deque
sz = 10**5
maxLevel = 0
# Adjacency list representation
# of the tree
tree = [[] for i in range(sz + 1)]
# Boolean array to mark all the
# vertices which are visited
vis = [False]*(sz + 1)
# Integer array to store the level
# of each node
level = [0]*(sz + 1)
# Array of vector where ith index
# stores all the nodes at level i
nodes = [[] for i in range(sz + 1)]
# Utility function to create an
# edge between two vertices
def addEdge(a, b):
# Add a to b's list
tree[a].append(b)
# Add b to a's list
tree[b].append(a)
# Modified Breadth-First Function
def bfs(node):
global maxLevel
# Create a queue of {child, parent}
qu = deque()
# Push root node in the front of
# the queue and mark as visited
qu.append([node, 0])
nodes[0].append(node)
vis[node] = True
level[1] = 0
while (len(qu) > 0):
p = qu.popleft()
# Dequeue a vertex from queue
vis[p[0]] = True
# Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
# vertex s. If any adjacent has not
# been visited then enqueue it
for child in tree[p[0]]:
if (vis[child] == False):
qu.append([child, p[0]])
level[child] = level[p[0]] + 1
maxLevel = max(maxLevel, level[child])
nodes[level[child]].append(child)
# Utility Function to display the pattern
def display():
global maxLevel
# k represents the level no.
# cycle represents how many
# cycles has been completed
k = 0
path = 0
condn = (maxLevel) // 2 + 1
flag = True
# While there are nodes left to traverse
while (condn):
if (flag):
# Traversing whole level from
# left to right
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1
for j in range(len(nodes[k])- path):
print(nodes[k][j],end=" ")
# Moving to new level
k += 1
# Traversing rightmost unvisited
# element in path path as we
# move up to down
while (k < maxLevel):
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1
print(nodes[k][j - path], end=" ")
k += 1
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1
if (k > path):
while j >= 0:
j -= path
print(nodes[k][j], end=" ")
j -= 1
# Setting value of new maximum
# level upto which we have to traverse
# next time
maxLevel -= 1
# Updating from which level to
# start new path
k -= 1
path += 1
flag = not flag
else:
# Traversing each element of remaining
# last level from left to right
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1
for j in range(len(nodes[k]) - path):
print(nodes[k][j], end=" ")
# Decrementing value of Max level
maxLevel -= 1
k -= 1
# Traversing rightmost unvisited
# element in path as we
# move down to up
while (k > path):
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1
print(nodes[k][j - path], end=" ")
k -= 1
j = len(nodes[k]) - 1
if (k == path):
while j >= 0:
j -= path
print(nodes[k][j],end=" ")
j -= 1
path += 1
# Updating the level number from which
# a new cycle has to be started
k += 1
flag = not flag
condn -= 1
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Initialising the above mentioned
# complete binary tree
for i in range(1,6):
# Adding edge to a binary tree
addEdge(i, 2 * i)
addEdge(i, 2 * i + 1)
# Calling modified bfs function
bfs(1)
display()
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program to print sideways
// traversal of complete binary tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static int sz = (int) 1e5;
static int maxLevel = 0;
// Adjacency list representation
// of the tree
static List []tree = new List[sz + 1];
// Boolean array to mark all the
// vertices which are visited
static bool []vis = new bool[sz + 1];
// int array to store the level
// of each node
static int []level = new int[sz + 1];
// Array of vector where ith index
// stores all the nodes at level i
static List []nodes = new List[sz + 1];
// Utility function to create an
// edge between two vertices
static void addEdge(int a, int b)
{
// Add a to b's list
tree[a].Add(b);
// Add b to a's list
tree[b].Add(a);
}
// Modified Breadth-First Function
static void bfs(int node)
{
// Create a queue of {child, parent}
Queue qu = new Queue();
// Push root node in the front of
// the queue and mark as visited
qu.Enqueue(new pair( node, 0 ));
nodes[0].Add(node);
vis[node] = true;
level[1] = 0;
while (qu.Count != 0) {
pair p = qu.Peek();
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
qu.Dequeue();
vis[p.first] = true;
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex s. If any adjacent has not
// been visited then enqueue it
foreach (int child in tree[p.first]) {
if (!vis[child]) {
qu.Enqueue(new pair( child, p.first ));
level[child] = level[p.first] + 1;
maxLevel = Math.Max(maxLevel, level[child]);
nodes[level[child]].Add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Utility Function to display the pattern
static void display()
{
// k represents the level no.
// cycle represents how many
// cycles has been completed
int k = 0, path = 0;
int condn = (maxLevel) / 2 + 1;
bool flag = true;
// While there are nodes left to traverse
while (condn-- > 0) {
if (flag) {
// Traversing whole level from
// left to right
int j = nodes[k].Count - 1;
for (j = 0; j < nodes[k].Count - path; j++)
Console.Write(nodes[k][j]+ " ");
// Moving to new level
k++;
// Traversing rightmost unvisited
// element in path path as we
// move up to down
while (k < maxLevel) {
j = nodes[k].Count - 1;
Console.Write(nodes[k][j - path]+ " ");
k++;
}
j = nodes[k].Count - 1;
if (k > path)
for (j -= path; j >= 0; j--)
Console.Write(nodes[k][j]+ " ");
// Setting value of new maximum
// level upto which we have to traverse
// next time
maxLevel--;
// Updating from which level to
// start new path
k--;
path++;
flag = !flag;
}
else {
// Traversing each element of remaining
// last level from left to right
int j = nodes[k].Count - 1;
for (j = 0; j < nodes[k].Count - path; j++)
Console.Write(nodes[k][j]+ " ");
// Decrementing value of Max level
maxLevel--;
k--;
// Traversing rightmost unvisited
// element in path as we
// move down to up
while (k > path) {
int c = nodes[k].Count - 1;
Console.Write(nodes[k]+ " ");
k--;
}
j = nodes[k].Count - 1;
if (k == path)
for (j -= path; j >= 0; j--)
Console.Write(nodes[k][j]+ " ");
path++;
// Updating the level number from which
// a new cycle has to be started
k++;
flag = !flag;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < tree.Length; i++) {
tree[i] = new List();
nodes[i] = new List();
}
// Initialising the above mentioned
// complete binary tree
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// Adding edge to a binary tree
addEdge(i, 2 * i);
addEdge(i, 2 * i + 1);
}
// Calling modified bfs function
bfs(1);
display();
}
}
// This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
1 3 7 11 10 9 8 4 5 6 2如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live