求和符号中的黎曼和
黎曼和允许我们计算任意函数的曲线下面积。这些公式帮助我们定义定积分。这些和背后的基本思想是将要计算的区域划分为小矩形并计算它们的面积之和。这些区域并不准确,但它们有助于了解实际区域。矩形的数量越多,我们就越接近实际区域。让我们看一下带有 sigma 符号的黎曼和。
黎曼和
定积分是微积分的重要组成部分。它们用于计算未定义公式的任意形状的面积、体积等。从分析上讲,它们只是在它们之上有限制的不定积分,但在图形上它们代表曲线下的面积。界限表示应该计算面积的边界。这些概念在电气工程、机器人等领域非常重要。为了定义积分,使用黎曼和,我们使用无限小的矩形计算任何曲线下的面积。让我们详细看看这种对定积分的解释。
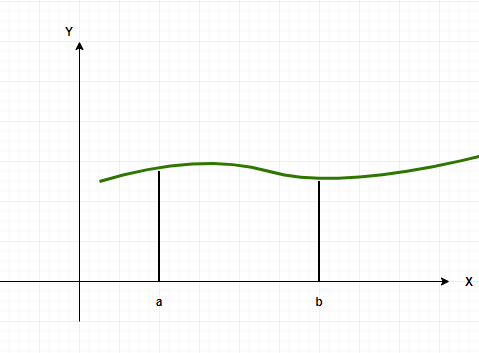
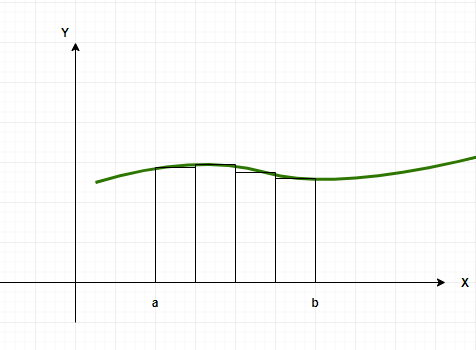
现在这个区域可以被划分为若干个矩形,假设这个区域被划分为“n”个等宽的矩形。其中一些矩形高于函数的实际值,一些低于函数的实际值,这意味着该区域在某些部分被高估和低估。这些矩形的高度由区间中间的函数值决定。
在定积分符号中,该区域将表示为,
![]()
该区域可以通过将曲线下的区域划分为 n 个大小相等的矩形来近似。因此,区间 [a, b] 被划分为由点定义的 n 个子区间。
a = x 0 < x 1 < x 2 < ...。 x n-2 < x n-1 < x n = b
那么,n个区间是,
[x 0 , x 1 ], [x 1 , x 2 ], ...。 [x n-1 , x n ]
因此,对于第 i个矩形,宽度将为 [x i-1 , x i ]。
第 i个矩形 A i = f( ![]() )(x i - x i-1 )
)(x i - x i-1 )
所以总面积为![]()
这个和称为黎曼和。
西格玛符号中的黎曼和
假设目标是计算函数f(x) = x 2的图形下的面积,则面积将在 x = 0.5 到 x = 4.5 的范围内计算。
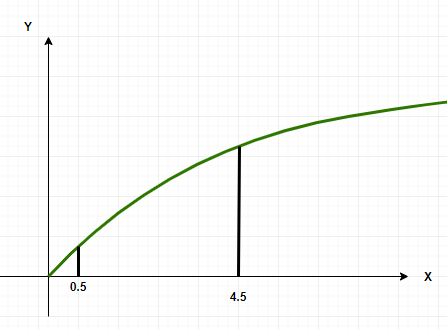
将区间分成四等份,区间为 [0.5, 1.5]、[1.5, 2.5]、[2.5, 3.5] 和 [3.5, 4.5]。
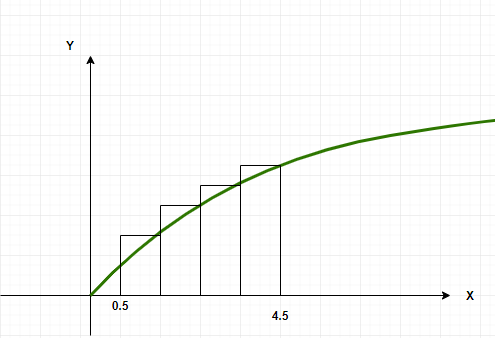
那么,黎曼和可以写成:
A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) = ![]()
设区间的高度为矩形末端的函数值。这称为右和黎曼和。令 x i表示第 i个矩形的右端点。
因此,x i = 0.5 + i 的公式。现在,函数在这些点的值变为,
f(x i ) = (0.5 + i) 2
所以,A(i)=(高度)(宽度)
= (0.5 + i) 2
黎曼和变为,
A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) = ![]()
⇒ A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) = ![]()
因此,通过这种方式,几乎所有的黎曼和都可以用 sigma 表示法表示。
总结一下整个过程,
Step 1: Find out the width of each interval. Let’s denote the width of interval with ![]()
Step 2: Let xi denote the right-endpoint of the rectangle xi = a + ![]() x.i
x.i
Step 3: Define the area of each rectangle.
Step 4: Sum the areas
示例问题
问题1:考虑一个函数f(x),它的面积是从x = 4到x = 10的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成5个矩形。求区间宽度。
解决方案:
The whole length is divided into 5 equal parts,
xi = 4 and xl = 10,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi – initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 5
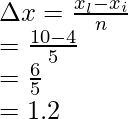
问题2:考虑一个函数f(x) = x,它的面积是从x = 0到x = 5的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成5个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
解决方案:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 5 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 5,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 5
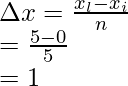
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]()
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii)
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (i)
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) + A(5)
= ![]()
问题 3:考虑一个函数f(x) = 5 – x,它的面积是由 x = 0 到 x = 5 的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成 5 个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
解决方案:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 5 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 5,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 5
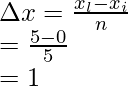
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]()
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii)
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (5 – i)(1)
= 5 – i
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) + A(5)
= ![]()
问题 4:考虑一个函数f(x) = √x,它的面积是由 x = 0 到 x = 4 的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成 4 个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
解决方案:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 4 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 4,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 4
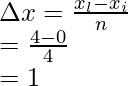
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]()
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii)
Ai = Height × Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (√i)(1)
= √i
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4)
= ![]()
问题5:考虑一个函数f(x) = e x + 1,它的面积是从x = 0到x = 4的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成4个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
解决方案:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 4 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 4,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 4
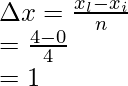
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]()
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii)
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (ei + 1)(1)
= ei + 1
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4)
= ![]()
问题6:考虑一个函数f(x) = x 2 + x,它的面积是从x = 0到x = 6的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成3个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
解决方案:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 4 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 6,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 3
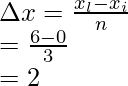
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]()
⇒ xi = 2i
Step (iii)
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (i2 + i)(2)
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) + A(5) + A(6)
= ![]()