黎曼和
定积分是微积分的重要组成部分。它们用于计算未定义公式的任意形状的面积、体积等。从分析上讲,它们只是在它们之上有限制的不定积分,但在图形上它们代表曲线下的面积。界限表示应该计算面积的边界。这些概念在电气工程、机器人技术等领域非常重要。为了定义积分,使用黎曼和,我们使用无限小的矩形计算任何曲线下的面积。让我们详细看看这种对定积分的解释。
黎曼近似
黎曼和是一种近似曲线下面积的方法。其背后的直觉是,如果我们将区域划分为非常小的矩形,我们可以计算每个矩形的面积,然后将它们相加得出整个区域的面积。这与定积分背后的直觉相同。因此,这些和也可用于近似和定义定积分。定积分只不过是带极限的积分,它们用于求任意曲线形状下的面积、体积等。考虑下图,目标是计算 x = a 和 x = b 之间的这条曲线与 x 轴之间的面积。
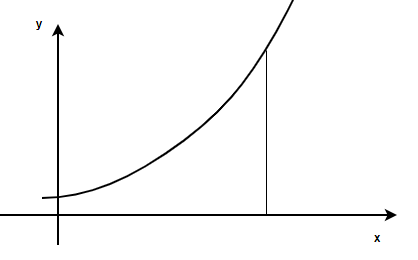
现在让我们从将给定区域划分为多个矩形开始,假设该区域被划分为“n”个等宽的矩形。请注意,这些矩形并未覆盖整个区域,因此它是该区域的近似值。但是随着矩形数量的增加,近似值越来越接近实际区域。
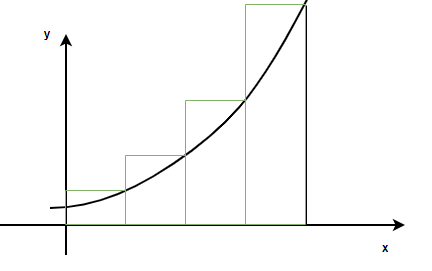
在定积分符号中,该区域将表示为,
![]()
该区域可以通过将曲线下的区域划分为 n 个大小相等的矩形来近似。因此,区间 [a, b] 被划分为由点定义的 n 个子区间。
a = x 0 < x 1 < x 2 < ...。 x n-2 < x n-1 < x n = b
那么,n个区间是,
[x 0 , x 1 ], [x 1 , x 2 ], ...。 [x n-1 , x n ]
因此,对于第 i个矩形,宽度将为 [x i-1 , x i ]。
第 i个矩形 A i = f(x i )(x i — x i-1 ) 的面积
所以总面积为![]()
这个和称为黎曼和。由于矩形的高度由区间的右极限决定,因此称为右黎曼和。下图显示了左黎曼和。
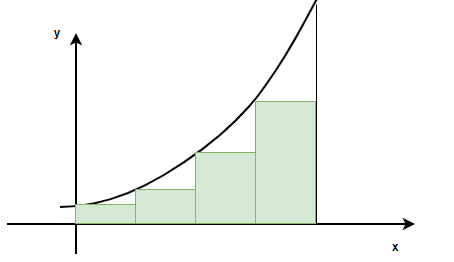
求和符号
The steps given below should be followed to find the summation notation of the riemann integral.
Step 1: Find out the width of each interval. Let’s denote the width of interval with ![]()
Step 2: Let xi denote the right-endpoint of the rectangle xi = a + ![]() .i
.i
Step 3: Define the area of each rectangle.
Step 4: Sum the areas
假设目标是计算函数f(x) = x 3的图形下的面积,面积将在 x = 0 到 x = 4 之间计算。
将区间分成四等份,区间为 [0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3] 和 [3, 4]。
那么,黎曼和可以写成:
A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) = ![]()
让我们计算正确的和 Riemann sum 。假设 x i表示第 i个矩形的右端点。
因此,x i = i 的公式。现在,函数在这些点的值变为,
f(x i ) = (i) 3
所以,A(i)=(高度)(宽度)
= (一) 3
黎曼和变为,
A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) = ![]()
⇒ A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) = ![]()
因此,这样几乎所有的黎曼和都可以用 sigma 表示法表示。
让我们解决这些概念的一些问题。
示例问题
问题一:选择如下图所示的黎曼积分类型。
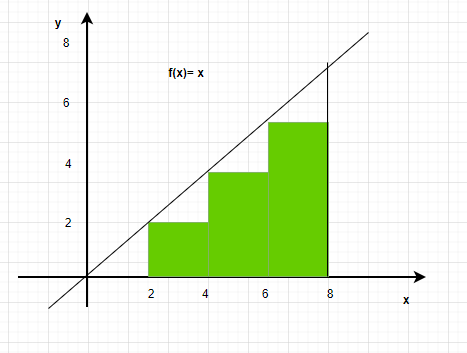
- 左黎曼和
- 右黎曼和
- 中点黎曼和
解决方案:
Since the values of the intervals are decided according to the left-end point of the interval. This is a left-Riemann Sum
Answer-(1).
问题2:计算上图中给出的函数的Left-Riemann Sum。
解决方案:
Dividing the interval into four equal parts that is n = 4. The width of each interval will be,
![]()
x0 = 0, x1 = 1, x2 = 2, x3 = 0 and x4 = 0
The value of the function in each interval will be the value of the function at the right-end of the interval.
![]()
⇒A = ![]()
⇒A =
⇒A = f(1)(2) + f(2)(2)+ f(3)(2) + f(4)(2)
⇒A = (f(1) + f(2) + f(3)+ f(4))(2)
⇒A = (1 + 2 + 3+ 4)(2)
⇒A = (10)(2)
⇒A = 20
问题3:考虑一个函数f(x) = 5 – 2x,它的面积是从x = 0到x = 4的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成4个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
回答:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 4 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 4,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 4
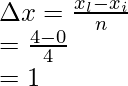
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]() i
i
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii):
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (5 – 2i)(1)
= 5 – 2i
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) + A(5)
= ![]()
问题 4:考虑一个函数f(x) = x 2 ,它的面积是从 x = 0 到 x = 3 的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成 3 个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
回答:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 3 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 3,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 3
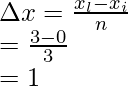
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]() i
i
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii)
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (i2)
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4) + A(5)
= ![]()
问题 5:考虑一个函数f(x) = √x,它的面积是由 x = 0 到 x = 4 的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成 4 个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
回答:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 4 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 4,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 4

Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]() i
i
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii)
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (√i)(1)
= √i
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4)
= ![]()
问题 6:考虑一个函数f(x) = x 2 ,它的面积是从 x = 0 到 x = 2 的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成 2 个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
回答:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 2 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 2,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 2
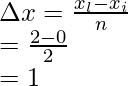
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]() i
i
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii):
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (i2)(1)
= i2
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4)
= ![]()
问题 7:考虑一个函数f(x) = 3(x + 3),它的面积是由 x = 0 到 x = 6 的黎曼和计算的,整个面积被分成 6 个矩形。用 sigma 符号求黎曼和
回答:
Step (i): Calculate the width
The whole length is divided into 4 equal parts,
xi = 0 and xl = 6,
Width of an interval is given by = ![]()
Where xi = initial point, and xl – last point and n= number of parts
n = 6
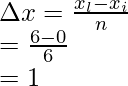
Step(ii):
a = 0,
xi = 0 + ![]() i
i
⇒ xi = i
Step (iii):
Ai = Height x Width
= f(xi) ![]()
= (3(i + 3))(1)
= 3(i + 3)
Total Area = A(1) + A(2) + A(3) + A(4)
= ![]()