给定一个大小为N的 2D 阵列Plates[][] ,每行代表N 个矩形板的长度和宽度,任务是找到可以相互放置的最大板数。
注意:只有当一个盘子的长度和宽度严格小于那个盘子时,它才能放在另一个盘子上。
例子:
Input: Plates[][] = [ [3, 5], [6, 7], [7, 2], [2, 3] ]
Output: 3
Explanation: Plates can be arranged in this manner [ 6, 7 ] => [ 3, 5 ] => [ 2, 3 ].
Input: Plates[][] = [ [6, 4], [ 5, 7 ], [1, 2], [ 3, 3 ], [ 7, 9 ] ]
Output: 4
Explanation: Plates can be arranged in this manner [ 7, 9 ] => [ 5, 7 ] => [ 3, 3 ] => [ 1, 2 ].
方法:该问题是最长递增子序列问题的变体。唯一的区别是在 LIS 中,如果i < j ,则第i个元素将始终位于第j个元素之前。但在这里,板块的选择并不取决于指数。因此,要获得此指标限制,需要按面积降序对所有板块进行排序。
If (i < j) and area of ith plate is also greater than jth plate, then ith plate will always come before(down) the jth plate.
递归方法:
每个板有两种可能的选择,即要么将其包含在序列中,要么将其丢弃。只有当其长度和宽度小于先前包含的板时,才能包含该板。
数组plates[][] = [ [6, 7], [3, 5], [7, 2] ]的递归树如下:
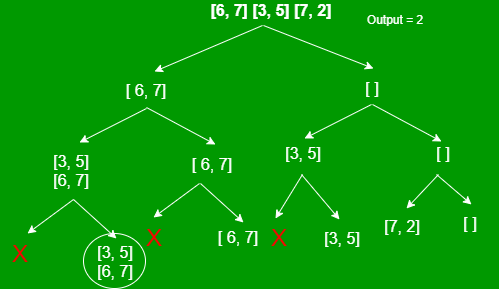
下面是递归方法的实现:
C++
// C++ Program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Comparator function to sort plates
// in decreasing order of area
bool comp(vector v1,
vector v2)
{
return v1[0] * v1[1] > v2[0] * v2[1];
}
// Recursive function to count and return
// the max number of plates that can be placed
int countPlates(vector >& plates,
int lastLength, int lastWidth,
int i, int n)
{
// If no plate remains
if (i == n)
return 0;
int taken = 0, notTaken = 0;
// If length and width of previous plate
// exceeds that of the current plate
if (lastLength > plates[i][0]
&& lastWidth > plates[i][1]) {
// Calculate including the plate
taken = 1 + countPlates(plates, plates[i][0],
plates[i][1], i + 1, n);
// Calculate excluding the plate
notTaken = countPlates(plates, lastLength,
lastWidth, i + 1, n);
}
// Otherwise
else
// Calculate only excluding the plate
notTaken = countPlates(plates, lastLength,
lastWidth, i + 1, n);
return max(taken, notTaken);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector > plates = { { 6, 4 }, { 5, 7 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 3, 3 }, { 7, 9 } };
int n = plates.size();
// Sorting plates in decreasing order of area
sort(plates.begin(), plates.end(), comp);
// Assuming first plate to be of maximum size
int lastLength = INT_MAX;
int lastWidth = INT_MAX;
cout << countPlates(plates, lastLength,
lastWidth, 0, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Recursive function to count and return
// the max number of plates that can be placed
static int countPlates(int[][] plates,
int lastLength,
int lastWidth,
int i, int n)
{
// If no plate remains
if (i == n)
return 0;
int taken = 0, notTaken = 0;
// If length and width of previous plate
// exceeds that of the current plate
if (lastLength > plates[i][0] &&
lastWidth > plates[i][1])
{
// Calculate including the plate
taken = 1 + countPlates(plates, plates[i][0],
plates[i][1], i + 1, n);
// Calculate excluding the plate
notTaken = countPlates(plates, lastLength,
lastWidth, i + 1, n);
}
// Otherwise
else
// Calculate only excluding the plate
notTaken = countPlates(plates, lastLength,
lastWidth, i + 1, n);
return Math.max(taken, notTaken);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] plates = { { 6, 4 }, { 5, 7 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 3, 3 }, { 7, 9 } };
int n = plates.length;
// Sorting plates in decreasing order of area
Arrays.sort(plates, (v1, v2)-> (v2[0] * v2[1]) -
(v1[0] * v1[1]));
// Assuming first plate to be of maximum size
int lastLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int lastWidth = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(countPlates(plates, lastLength,
lastWidth, 0, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeatJavascript
C++
// C++ Program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Comparator function to sort plates
// in decreasing order of area
bool comp(vector v1, vector v2)
{
return v1[0] * v1[1] > v2[0] * v2[1];
}
// Function to count and return the max
// number of plates that can be placed
int countPlates(vector >& plates, int n)
{
// Stores the maximum
// number of plates
int maximum_plates = 1;
vector dp(n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int cur = dp[i];
// For each i-th plate, traverse
// all the previous plates
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// If i-th plate is smaller than j-th plate
if (plates[i][0] < plates[j][0]
&& plates[i][1] < plates[j][1]) {
// Include the j-th plate only if current
// count exceeds the previously stored count
if (cur + dp[j] > dp[i]) {
dp[i] = cur + dp[j];
// Update the maximum count
maximum_plates = max(maximum_plates, dp[i]);
}
}
}
}
return maximum_plates;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector > plates = { { 6, 4 }, { 5, 7 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 3, 3 }, { 7, 9 } };
int n = plates.size();
// Sorting plates in decreasing order of area
sort(plates.begin(), plates.end(), comp);
cout << countPlates(plates, n);
return 0;
} Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(2 N )
辅助空间:O(N)
动态规划方法:上述方法可以使用动态规划进行优化,如下图所示。

下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ Program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Comparator function to sort plates
// in decreasing order of area
bool comp(vector v1, vector v2)
{
return v1[0] * v1[1] > v2[0] * v2[1];
}
// Function to count and return the max
// number of plates that can be placed
int countPlates(vector >& plates, int n)
{
// Stores the maximum
// number of plates
int maximum_plates = 1;
vector dp(n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int cur = dp[i];
// For each i-th plate, traverse
// all the previous plates
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// If i-th plate is smaller than j-th plate
if (plates[i][0] < plates[j][0]
&& plates[i][1] < plates[j][1]) {
// Include the j-th plate only if current
// count exceeds the previously stored count
if (cur + dp[j] > dp[i]) {
dp[i] = cur + dp[j];
// Update the maximum count
maximum_plates = max(maximum_plates, dp[i]);
}
}
}
}
return maximum_plates;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector > plates = { { 6, 4 }, { 5, 7 },
{ 1, 2 }, { 3, 3 }, { 7, 9 } };
int n = plates.size();
// Sorting plates in decreasing order of area
sort(plates.begin(), plates.end(), comp);
cout << countPlates(plates, n);
return 0;
}
Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。