我们已经讨论了重叠子问题和最优子结构属性。
现在,让我们讨论最长递增子序列 (LIS) 问题作为可以使用动态规划解决的示例问题。
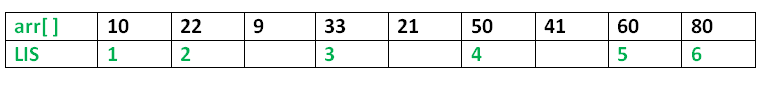
最长递增子序列 (LIS) 问题是找到给定序列的最长子序列的长度,使子序列的所有元素按递增顺序排序。例如,{10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60, 80}的LIS长度为6,LIS为{10, 22, 33, 50, 60, 80}。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {3, 10, 2, 1, 20}
Output: Length of LIS = 3
The longest increasing subsequence is 3, 10, 20
Input: arr[] = {3, 2}
Output: Length of LIS = 1
The longest increasing subsequences are {3} and {2}
Input: arr[] = {50, 3, 10, 7, 40, 80}
Output: Length of LIS = 4
The longest increasing subsequence is {3, 7, 40, 80}方法一:递归。
最优子结构:令 arr[0..n-1] 是输入数组,L(i) 是 LIS 的长度,以索引 i 结束,这样 arr[i] 是 LIS 的最后一个元素。
然后,L(i) 可以递归地写为:
L(i) = 1 + max( L(j) ) where 0 < j < i and arr[j] < arr[i]; or
L(i) = 1, if no such j exists.要找到给定数组的 LIS,我们需要返回 max(L(i)) 其中 0 < i < n。
形式上,以索引 i 结尾的最长递增子序列的长度将比以 i 之前的索引结尾的所有最长递增子序列的最大长度大 1,其中 arr[j] < arr[i] (j < i)。
因此,我们看到 LIS 问题满足最优子结构属性,因为主要问题可以使用子问题的解来解决。
下面给出的递归树将使方法更清晰:
Input : arr[] = {3, 10, 2, 11}
f(i): Denotes LIS of subarray ending at index 'i'
(LIS(1)=1)
f(4) {f(4) = 1 + max(f(1), f(2), f(3))}
/ | \
f(1) f(2) f(3) {f(3) = 1, f(2) and f(1) are > f(3)}
| | \
f(1) f(2) f(1) {f(2) = 1 + max(f(1)}
|
f(1) {f(1) = 1}下面是递归方法的实现:
C++
/* A Naive C/C++ recursive implementation
of LIS problem */
#include
#include
/* To make use of recursive calls, this
function must return two things:
1) Length of LIS ending with element arr[n-1].
We use max_ending_here for this purpose
2) Overall maximum as the LIS may end with
an element before arr[n-1] max_ref is
used this purpose.
The value of LIS of full array of size n
is stored in *max_ref which is our final result
*/
int _lis(int arr[], int n, int* max_ref)
{
/* Base case */
if (n == 1)
return 1;
// 'max_ending_here' is length of LIS
// ending with arr[n-1]
int res, max_ending_here = 1;
/* Recursively get all LIS ending with arr[0],
arr[1] ... arr[n-2]. If arr[i-1] is smaller
than arr[n-1], and max ending with arr[n-1]
needs to be updated, then update it */
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res = _lis(arr, i, max_ref);
if (arr[i - 1] < arr[n - 1]
&& res + 1 > max_ending_here)
max_ending_here = res + 1;
}
// Compare max_ending_here with the overall
// max. And update the overall max if needed
if (*max_ref < max_ending_here)
*max_ref = max_ending_here;
// Return length of LIS ending with arr[n-1]
return max_ending_here;
}
// The wrapper function for _lis()
int lis(int arr[], int n)
{
// The max variable holds the result
int max = 1;
// The function _lis() stores its result in max
_lis(arr, n, &max);
// returns max
return max;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Length of lis is %d", lis(arr, n));
return 0;
} Java
/* A Naive Java Program for LIS Implementation */
class LIS {
static int max_ref; // stores the LIS
/* To make use of recursive calls, this function must
return two things: 1) Length of LIS ending with element
arr[n-1]. We use max_ending_here for this purpose 2)
Overall maximum as the LIS may end with an element
before arr[n-1] max_ref is used this purpose.
The value of LIS of full array of size n is stored in
*max_ref which is our final result */
static int _lis(int arr[], int n)
{
// base case
if (n == 1)
return 1;
// 'max_ending_here' is length of LIS ending with
// arr[n-1]
int res, max_ending_here = 1;
/* Recursively get all LIS ending with arr[0],
arr[1] ... arr[n-2]. If arr[i-1] is smaller
than arr[n-1], and max ending with arr[n-1] needs
to be updated, then update it */
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res = _lis(arr, i);
if (arr[i - 1] < arr[n - 1]
&& res + 1 > max_ending_here)
max_ending_here = res + 1;
}
// Compare max_ending_here with the overall max. And
// update the overall max if needed
if (max_ref < max_ending_here)
max_ref = max_ending_here;
// Return length of LIS ending with arr[n-1]
return max_ending_here;
}
// The wrapper function for _lis()
static int lis(int arr[], int n)
{
// The max variable holds the result
max_ref = 1;
// The function _lis() stores its result in max
_lis(arr, n);
// returns max
return max_ref;
}
// driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n)
+ "\n");
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra*/Python
# A naive Python implementation of LIS problem
""" To make use of recursive calls, this function must return
two things:
1) Length of LIS ending with element arr[n-1]. We use
max_ending_here for this purpose
2) Overall maximum as the LIS may end with an element
before arr[n-1] max_ref is used this purpose.
The value of LIS of full array of size n is stored in
*max_ref which is our final result """
# global variable to store the maximum
global maximum
def _lis(arr, n):
# to allow the access of global variable
global maximum
# Base Case
if n == 1:
return 1
# maxEndingHere is the length of LIS ending with arr[n-1]
maxEndingHere = 1
"""Recursively get all LIS ending with arr[0], arr[1]..arr[n-2]
IF arr[n-1] is maller than arr[n-1], and max ending with
arr[n-1] needs to be updated, then update it"""
for i in xrange(1, n):
res = _lis(arr, i)
if arr[i-1] < arr[n-1] and res+1 > maxEndingHere:
maxEndingHere = res + 1
# Compare maxEndingHere with overall maximum. And
# update the overall maximum if needed
maximum = max(maximum, maxEndingHere)
return maxEndingHere
def lis(arr):
# to allow the access of global variable
global maximum
# lenght of arr
n = len(arr)
# maximum variable holds the result
maximum = 1
# The function _lis() stores its result in maximum
_lis(arr, n)
return maximum
# Driver program to test the above function
arr = [10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60]
n = len(arr)
print "Length of lis is ", lis(arr)
# This code is contributed by NIKHIL KUMAR SINGHC#
using System;
/* A Naive C# Program for LIS Implementation */
class LIS {
static int max_ref; // stores the LIS
/* To make use of recursive calls, this function must
return two things: 1) Length of LIS ending with element
arr[n-1]. We use max_ending_here for this purpose 2)
Overall maximum as the LIS may end with an element
before arr[n-1] max_ref is used this purpose.
The value of LIS of full array of size n is stored in
*max_ref which is our final result */
static int _lis(int[] arr, int n)
{
// base case
if (n == 1)
return 1;
// 'max_ending_here' is length of LIS ending with
// arr[n-1]
int res, max_ending_here = 1;
/* Recursively get all LIS ending with arr[0],
arr[1] ... arr[n-2]. If arr[i-1] is smaller
than arr[n-1], and max ending with arr[n-1] needs
to be updated, then update it */
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res = _lis(arr, i);
if (arr[i - 1] < arr[n - 1]
&& res + 1 > max_ending_here)
max_ending_here = res + 1;
}
// Compare max_ending_here with the overall max. And
// update the overall max if needed
if (max_ref < max_ending_here)
max_ref = max_ending_here;
// Return length of LIS ending with arr[n-1]
return max_ending_here;
}
// The wrapper function for _lis()
static int lis(int[] arr, int n)
{
// The max variable holds the result
max_ref = 1;
// The function _lis() stores its result in max
_lis(arr, n);
// returns max
return max_ref;
}
// driver program to test above functions
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n)
+ "\n");
}
}Javascript
C++
/* Dynamic Programming C++ implementation
of LIS problem */
#include
using namespace std;
/* lis() returns the length of the longest
increasing subsequence in arr[] of size n */
int lis(int arr[], int n)
{
int lis[n];
lis[0] = 1;
/* Compute optimized LIS values in
bottom up manner */
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
lis[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[i] < lis[j] + 1)
lis[i] = lis[j] + 1;
}
// Return maximum value in lis[]
return *max_element(lis, lis + n);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Length of lis is %d\n", lis(arr, n));
return 0;
} Java
/* Dynamic Programming Java implementation
of LIS problem */
class LIS {
/* lis() returns the length of the longest
increasing subsequence in arr[] of size n */
static int lis(int arr[], int n)
{
int lis[] = new int[n];
int i, j, max = 0;
/* Initialize LIS values for all indexes */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
lis[i] = 1;
/* Compute optimized LIS values in
bottom up manner */
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[i] < lis[j] + 1)
lis[i] = lis[j] + 1;
/* Pick maximum of all LIS values */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (max < lis[i])
max = lis[i];
return max;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n)
+ "\n");
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra*/Python
# Dynamic programming Python implementation
# of LIS problem
# lis returns length of the longest
# increasing subsequence in arr of size n
def lis(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Declare the list (array) for LIS and
# initialize LIS values for all indexes
lis = [1]*n
# Compute optimized LIS values in bottom up manner
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(0, i):
if arr[i] > arr[j] and lis[i] < lis[j] + 1:
lis[i] = lis[j]+1
# Initialize maximum to 0 to get
# the maximum of all LIS
maximum = 0
# Pick maximum of all LIS values
for i in range(n):
maximum = max(maximum, lis[i])
return maximum
# end of lis function
# Driver program to test above function
arr = [10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60]
print "Length of lis is", lis(arr)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar SinghC#
/* Dynamic Programming C# implementation of LIS problem */
using System;
class LIS {
/* lis() returns the length of the longest increasing
subsequence in arr[] of size n */
static int lis(int[] arr, int n)
{
int[] lis = new int[n];
int i, j, max = 0;
/* Initialize LIS values for all indexes */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
lis[i] = 1;
/* Compute optimized LIS values in bottom up manner
*/
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[i] < lis[j] + 1)
lis[i] = lis[j] + 1;
/* Pick maximum of all LIS values */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (max < lis[i])
max = lis[i];
return max;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n)
+ "\n");
}
// This code is contributed by Ryuga
}Javascript
Python3
# Dynamic Programming Approach of Finding LIS by reducing the problem to longest common Subsequence
def lis(a):
n=len(a)
# Creating the sorted list
b=sorted(list(set(a)))
m=len(b)
# Creating dp table for storing the answers of sub problems
dp=[[-1 for i in range(m+1)] for j in range(n+1)]
# Finding Longest common Subsequence of the two arrays
for i in range(n+1):
for j in range(m+1):
if i==0 or j==0:
dp[i][j]=0
elif a[i-1]==b[j-1]:
dp[i][j]=1+dp[i-1][j-1]
else:
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])
return dp[-1][-1]
# Driver program to test above function
arr = [10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60]
print("Length of lis is ", lis(arr))
# This code is Contributed by Dheeraj Khatri输出:
Length of lis is 5复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:这种递归方法的时间复杂度是指数级的,因为存在重叠子问题的情况,如上面的递归树图所示。
- 辅助空间: O(1)。除了内部堆栈空间外,没有用于存储值的外部空间。
方法二:动态规划。
我们可以看到,在上述递归解决方案中,有很多子问题被一次又一次地解决了。所以这个问题具有重叠子结构的性质,并且可以通过使用 Memoization 或 Tabulation 来避免相同子问题的重新计算。
方法的模拟将使事情变得清楚:
Input : arr[] = {3, 10, 2, 11}
LIS[] = {1, 1, 1, 1} (initially)迭代模拟:
- arr[2] > arr[1] {LIS[2] = max(LIS [2], LIS[1]+1)=2}
- arr[3] < arr[1] {无变化}
- arr[3] < arr[2] {无变化}
- arr[4] > arr[1] {LIS[4] = max(LIS [4], LIS[1]+1)=2}
- arr[4] > arr[2] {LIS[4] = max(LIS [4], LIS[2]+1)=3}
- arr[4] > arr[3] {LIS[4] = max(LIS [4], LIS[3]+1)=3}
我们可以通过使用制表来避免重新计算子问题,如下面的代码所示:
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
/* Dynamic Programming C++ implementation
of LIS problem */
#include
using namespace std;
/* lis() returns the length of the longest
increasing subsequence in arr[] of size n */
int lis(int arr[], int n)
{
int lis[n];
lis[0] = 1;
/* Compute optimized LIS values in
bottom up manner */
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
lis[i] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[i] < lis[j] + 1)
lis[i] = lis[j] + 1;
}
// Return maximum value in lis[]
return *max_element(lis, lis + n);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Length of lis is %d\n", lis(arr, n));
return 0;
}
Java
/* Dynamic Programming Java implementation
of LIS problem */
class LIS {
/* lis() returns the length of the longest
increasing subsequence in arr[] of size n */
static int lis(int arr[], int n)
{
int lis[] = new int[n];
int i, j, max = 0;
/* Initialize LIS values for all indexes */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
lis[i] = 1;
/* Compute optimized LIS values in
bottom up manner */
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[i] < lis[j] + 1)
lis[i] = lis[j] + 1;
/* Pick maximum of all LIS values */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (max < lis[i])
max = lis[i];
return max;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n)
+ "\n");
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra*/
Python
# Dynamic programming Python implementation
# of LIS problem
# lis returns length of the longest
# increasing subsequence in arr of size n
def lis(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Declare the list (array) for LIS and
# initialize LIS values for all indexes
lis = [1]*n
# Compute optimized LIS values in bottom up manner
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(0, i):
if arr[i] > arr[j] and lis[i] < lis[j] + 1:
lis[i] = lis[j]+1
# Initialize maximum to 0 to get
# the maximum of all LIS
maximum = 0
# Pick maximum of all LIS values
for i in range(n):
maximum = max(maximum, lis[i])
return maximum
# end of lis function
# Driver program to test above function
arr = [10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60]
print "Length of lis is", lis(arr)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh
C#
/* Dynamic Programming C# implementation of LIS problem */
using System;
class LIS {
/* lis() returns the length of the longest increasing
subsequence in arr[] of size n */
static int lis(int[] arr, int n)
{
int[] lis = new int[n];
int i, j, max = 0;
/* Initialize LIS values for all indexes */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
lis[i] = 1;
/* Compute optimized LIS values in bottom up manner
*/
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && lis[i] < lis[j] + 1)
lis[i] = lis[j] + 1;
/* Pick maximum of all LIS values */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (max < lis[i])
max = lis[i];
return max;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Length of lis is " + lis(arr, n)
+ "\n");
}
// This code is contributed by Ryuga
}
Javascript
Length of lis is 5复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n 2 )。
由于使用了嵌套循环。 - 辅助空间: O(n)。
使用任何数组在每个索引处存储 LIS 值。
注意:上述动态规划 (DP) 解决方案的时间复杂度为 O(n^2),而 LIS 问题有一个 O(N log N) 解决方案。我们没有在这里讨论 O(N log N) 解决方案,因为这篇文章的目的是用一个简单的例子来解释动态规划。请参阅下面的帖子以了解 O(N log N) 解决方案。
最长递增子序列大小 (N log N)
方法 3:动态规划
如果我们仔细观察这个问题,那么我们可以将这个问题转化为最长公共子序列问题。首先,我们将创建另一个原始数组的唯一元素数组并对其进行排序。现在,我们数组的最长递增子序列必须作为排序数组中的一个子序列出现。这就是为什么我们的问题现在简化为找到两个数组之间的公共子序列。
Eg. arr =[50,3,10,7,40,80]
// Sorted array
arr1 = [3,7,10,40,50,80]
// LIS is longest common subsequence between the two arrays
ans = 4
The longest increasing subsequence is {3, 7, 40, 80}
蟒蛇3
# Dynamic Programming Approach of Finding LIS by reducing the problem to longest common Subsequence
def lis(a):
n=len(a)
# Creating the sorted list
b=sorted(list(set(a)))
m=len(b)
# Creating dp table for storing the answers of sub problems
dp=[[-1 for i in range(m+1)] for j in range(n+1)]
# Finding Longest common Subsequence of the two arrays
for i in range(n+1):
for j in range(m+1):
if i==0 or j==0:
dp[i][j]=0
elif a[i-1]==b[j-1]:
dp[i][j]=1+dp[i-1][j-1]
else:
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])
return dp[-1][-1]
# Driver program to test above function
arr = [10, 22, 9, 33, 21, 50, 41, 60]
print("Length of lis is ", lis(arr))
# This code is Contributed by Dheeraj Khatri
Length of lis is 5复杂度分析:O(n*n)
由于使用了嵌套循环
空间复杂度:O(n*n)
因为矩阵用于存储值。
- 打印数组的 LIS
- 基于 LIS 的最新文章!
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。