给定一个数字N ,任务是找到整数N可以表示为斐波那契数的总和而不重复任何斐波那契数的方法数。
例子:
Input: N = 13
Output: 3
Explanation:
The possible ways to select N as 13 are: {13} {8, 5} {8, 3, 2}. Note that it is not possible to select {5 + 5 + 3} because 5 appears twice.
Input: N = 87
Output: 5
Explanation:
The possible ways to select N as 13 are: {55 + 21 + 8 + 3}, {55 + 21 + 8 + 2 + 1}, {55 + 21 + 5 + 3 + 2 + 1}, {55 + 13 + 8 + 5 + 3 + 2 + 1}, {34 + 21 + 13 + 8 + 5 + 3 + 2 + 1}.
天真的方法:天真的想法是写出加起来等于给定数字N 的所有可能组合。检查任何组合是否有重复的整数,然后不要增加计数器,否则每次将计数增加 1。最后返回计数。
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
Efficient Approach:思路是使用Dynamic Programming来优化上面的方法。以下是步骤:
- 让我们在斐波那契代码中表示一个数字。
Imagine Fibonacci coding by following way: the i-th bit of number corresponds to the i-th Fibonacci number.
For Example: 16 = 13 + 3 will be written as 100100.
- 为每个正数编写斐波那契代码,使得没有两个相邻位为1 。
- 对于所有数字都是如此,因为如果有两个相邻的位是 1 位,那么我们可以通过斐波那契数的属性将其转换为单个1 位。我们称这种表示为规范表示。
- 获取规范表示。生成几个斐波那契数(约90 ),然后尝试以降序减去所有这些数。
- 让我们将给定数字的规范表示的 1 位位置按递增顺序存储到数组 v 中,并将任何1 位分解为两个1 位,如下所示:
Starting canonical representation: 1000000001
After decomposing leftmost 1-bit into two smaller 1-bits: 0110000001
After decomposing 2’nd leftmost 1-bit into two smaller 1-bits: 0101100001
After decomposing 3’rd leftmost 1-bit into two smaller 1-bits: 0101011001
After decomposing 4’th leftmost 1-bit into two smaller 1-bits: 0101010111
- 经过多次这样的操作,我们将得到下一个1 位(或数字的结尾)。这个1位也可以分解,但只能移位一位。
- 初始化一个 dp 数组dp1[] , dp1[i]是表示一个数字的多种方法,该数字由数字的i最左边的1 位组成,用于所有剩余 1 位未分解的情况。此外,采用dp2[i] ,它标记了表示由数字的i 个最左边的1 位组成的数字的方式数,用于分解所有剩余1 位的情况。
For Example: N = 87
Canonical form of N = 101010100
Other 4 possible representations of N are 101010011, 101001111, 100111111, 011111111
下面是相同的插图:
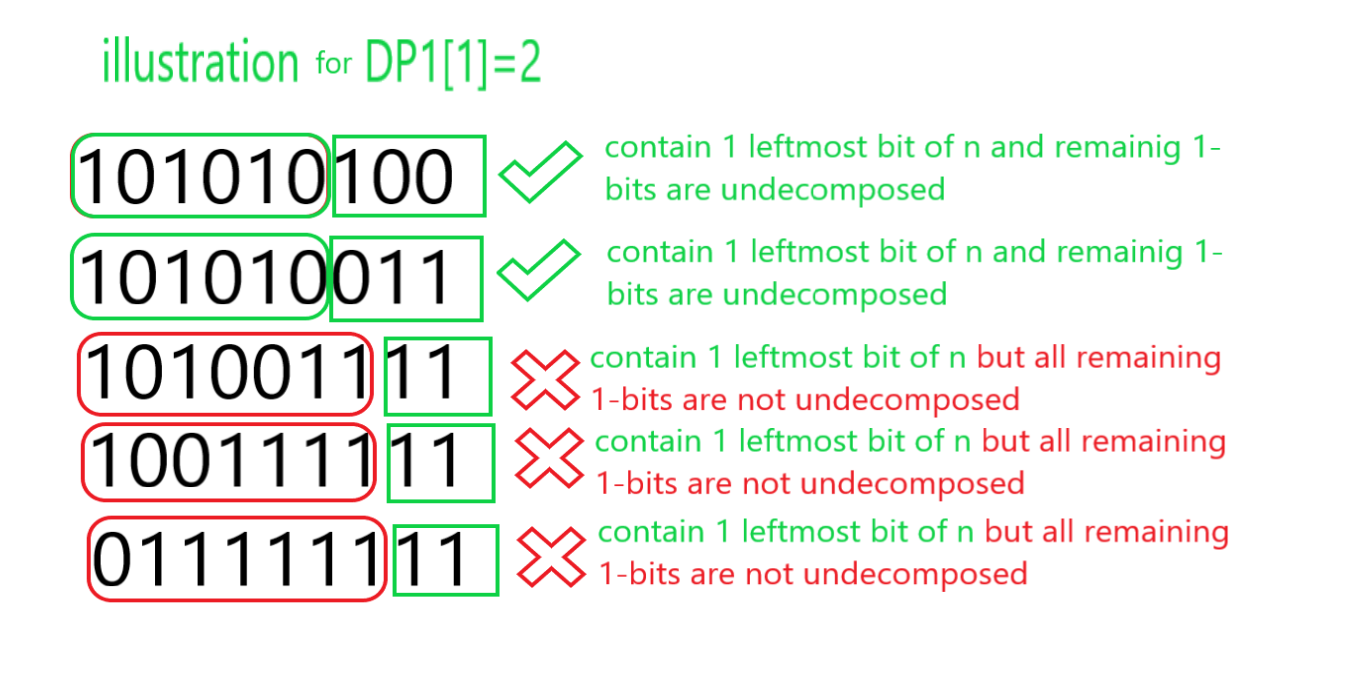

因此,答案是dp1[cnt] + dp2[cnt] ,其中cnt是规范表示中1 位的总数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
long long fib[101], dp1[101];
long long dp2[101], v[101];
// Function to generate the
// fibonacci number
void fibonacci()
{
// First two number of
// fibonacci sqequence
fib[1] = 1;
fib[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= 87; i++) {
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
}
}
// Function to find maximum ways to
// represent num as the sum of
// fibonacci number
int find(int num)
{
int cnt = 0;
// Generate the Canonical form
// of given number
for (int i = 87; i > 0; i--) {
if (num >= fib[i]) {
v[cnt++] = i;
num -= fib[i];
}
}
// Reverse the number
reverse(v, v + cnt);
// Base condition of dp1 and dp2
dp1[0] = 1;
dp2[0] = (v[0] - 1) / 2;
// Iterate from 1 to cnt
for (int i = 1; i < cnt; i++) {
// Calculate dp1[]
dp1[i] = dp1[i - 1] + dp2[i - 1];
// Calculate dp2[]
dp2[i] = ((v[i] - v[i - 1]) / 2)
* dp2[i - 1]
+ ((v[i] - v[i - 1] - 1) / 2)
* dp1[i - 1];
}
// Return final ans
return (dp1[cnt - 1] + dp2[cnt - 1]);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Function call to generate the
// fibonacci numbers
fibonacci();
// Given Number
int num = 13;
// Function Call
cout << find(num);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static long[] fib = new long[101];
static long[] dp1 = new long[101];
static long[] dp2 = new long[101];
static long[] v = new long[101];
// Function to generate the
// fibonacci number
static void fibonacci()
{
// First two number of
// fibonacci sqequence
fib[1] = 1;
fib[2] = 2;
for(int i = 3; i <= 87; i++)
{
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
}
}
// Function to find maximum ways to
// represent num as the sum of
// fibonacci number
static long find(int num)
{
int cnt = 0;
// Generate the Canonical form
// of given number
for(int i = 87; i > 0; i--)
{
if (num >= fib[i])
{
v[cnt++] = i;
num -= fib[i];
}
}
// Reverse the number
for(int i = 0; i < cnt / 2; i++)
{
long t = v[i];
v[i] = v[cnt - i - 1];
v[cnt - i - 1] = t;
}
// Base condition of dp1 and dp2
dp1[0] = 1;
dp2[0] = (v[0] - 1) / 2;
// Iterate from 1 to cnt
for(int i = 1; i < cnt; i++)
{
// Calculate dp1[]
dp1[i] = dp1[i - 1] + dp2[i - 1];
// Calculate dp2[]
dp2[i] = ((v[i] - v[i - 1]) / 2) *
dp2[i - 1] +
((v[i] - v[i - 1] - 1) / 2) *
dp1[i - 1];
}
// Return final ans
return (dp1[cnt - 1] + dp2[cnt - 1]);
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Function call to generate the
// fibonacci numbers
fibonacci();
// Given number
int num = 13;
// Function call
System.out.print(find(num));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeatPython3
# Python3 program for the above approach
fib = [0] * 101
dp1 = [0] * 101
dp2 = [0] * 101
v = [0] * 101
# Function to generate the
# fibonacci number
def fibonacci():
# First two number of
# fibonacci sqequence
fib[1] = 1
fib[2] = 2
for i in range(3, 87 + 1):
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2]
# Function to find maximum ways to
# represent num as the sum of
# fibonacci number
def find(num):
cnt = 0
# Generate the Canonical form
# of given number
for i in range(87, 0, -1):
if(num >= fib[i]):
v[cnt] = i
cnt += 1
num -= fib[i]
# Reverse the number
v[::-1]
# Base condition of dp1 and dp2
dp1[0] = 1
dp2[0] = (v[0] - 1) // 2
# Iterate from 1 to cnt
for i in range(1, cnt):
# Calculate dp1[]
dp1[i] = dp1[i - 1] + dp2[i - 1]
# Calculate dp2[]
dp2[i] = (((v[i] - v[i - 1]) // 2) *
dp2[i - 1] +
((v[i] - v[i - 1] - 1) // 2) *
dp1[i - 1])
# Return final ans
return dp1[cnt - 1] + dp2[cnt - 1]
# Driver Code
# Function call to generate the
# fibonacci numbers
fibonacci()
# Given number
num = 13
# Function call
print(find(num))
# This code is contributed by Shivam SinghC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
static long[] fib = new long[101];
static long[] dp1 = new long[101];
static long[] dp2 = new long[101];
static long[] v = new long[101];
// Function to generate the
// fibonacci number
static void fibonacci()
{
// First two number of
// fibonacci sqequence
fib[1] = 1;
fib[2] = 2;
for(int i = 3; i <= 87; i++)
{
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
}
}
// Function to find maximum ways to
// represent num as the sum of
// fibonacci number
static long find(long num)
{
int cnt = 0;
// Generate the Canonical form
// of given number
for(int i = 87; i > 0; i--)
{
if (num >= fib[i])
{
v[cnt++] = i;
num -= fib[i];
}
}
// Reverse the number
for(int i = 0; i < cnt / 2; i++)
{
long t = v[i];
v[i] = v[cnt - i - 1];
v[cnt - i - 1] = t;
}
// Base condition of dp1 and dp2
dp1[0] = 1;
dp2[0] = (v[0] - 1) / 2;
// Iterate from 1 to cnt
for(int i = 1; i < cnt; i++)
{
// Calculate dp1[]
dp1[i] = dp1[i - 1] + dp2[i - 1];
// Calculate dp2[]
dp2[i] = ((v[i] - v[i - 1]) / 2) *
dp2[i - 1] +
((v[i] - v[i - 1] - 1) / 2) *
dp1[i - 1];
}
// Return final ans
return (dp1[cnt - 1] + dp2[cnt - 1]);
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// Function call to generate the
// fibonacci numbers
fibonacci();
// Given number
int num = 13;
// Function call
Console.Write(find(num));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07Javascript
3时间复杂度: O(log N)
辅助空间: O(log N)