计算与 X 之和为斐波那契数的节点
给定一棵树,所有节点的权重和一个整数X ,任务是计算所有节点i使得(weight[i] + X)是一个斐波那契数。
首先,很少有斐波那契数是:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 141, …
例子:
Input:
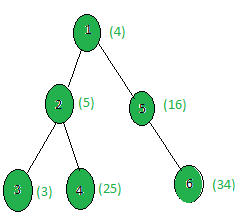
X = 5
Output: 2
Only the nodes 3 and 5 give a fibonacci number when 5 is added to them.
i.e. (3 + 5) = 8 and (16 + 5) = 21 are both Fibonacci numbers.
方法:在树上执行dfs,计算所有节点的权重与x为斐波那契数的总和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
int ans = 0, x;
vector graph[100];
vector weight(100);
// Function that returns true if
// x is a perfect square
bool isPerfectSquare(long double x)
{
// Find floating point value of
// square root of x
long double sr = sqrt(x);
// If square root is an integer
return ((sr - floor(sr)) == 0);
}
// Function that returns true
// if n is a fibonacci number
bool isFibonacci(int n)
{
return isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n + 4)
|| isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n - 4);
}
// Function to perform dfs
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If weight of the current node
// gives a fibonacci number
// when x is added to it
if (isFibonacci(weight[node] + x))
ans += 1;
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
x = 5;
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 4;
weight[2] = 5;
weight[3] = 3;
weight[4] = 25;
weight[5] = 16;
weight[6] = 34;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
graph[5].push_back(6);
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the
// above approach
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
class GFG{
static int ans = 0, x;
static ArrayList []graph = new ArrayList[100];
static ArrayList weight = new ArrayList();
// Function that returns true if
// x is a perfect square
static boolean isPerfectSquare(double x)
{
// Find floating point value of
// square root of x
double sr = Math.sqrt(x);
// If square root is an integer
return ((sr - Math.floor(sr)) == 0);
}
// Function that returns true
// if n is a fibonacci number
static boolean isFibonacci(int n)
{
return isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n + 4) ||
isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n - 4);
}
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If weight of the current node
// gives a fibonacci number
// when x is added to it
if (isFibonacci((int)weight.get(node) + x))
ans += 1;
for(int to : (ArrayList)graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
x = 5;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
weight.add(0);
graph[i] = new ArrayList();
}
// Weights of the node
weight.add(1, 4);
weight.add(2, 5);
weight.add(3, 3);
weight.add(4, 25);
weight.add(5, 16);
weight.add(6, 34);
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].add(2);
graph[2].add(3);
graph[2].add(4);
graph[1].add(5);
graph[5].add(6);
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76 Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import math
ans, x = 0, 0
graph = [[] for i in range(100)]
weight = [0]*(100)
# Function that returns true if
# x is a perfect square
def isPerfectSquare(x):
# Find floating point value of
# square root of x
sr = math.sqrt(x);
# If square root is an integer
return ((sr - math.floor(sr)) == 0)
# Function that returns true
# if n is a fibonacci number
def isFibonacci(n):
return isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n + 4) or isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n - 4)
# Function to perform dfs
def dfs(node, parent):
global ans
# If weight of the current node
# gives a fibonacci number
# when x is added to it
if (isFibonacci(weight[node] + x)):
ans += 1
for to in graph[node]:
if (to == parent):
continue
dfs(to, node)
x = 5
# Weights of the node
weight[1] = 4
weight[2] = 5
weight[3] = 3
weight[4] = 25
weight[5] = 16
weight[6] = 34
# Edges of the tree
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[2].append(4)
graph[1].append(5)
graph[5].append(6)
dfs(1, 1)
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by divyesh072019.C#
// C# implementation of the
// above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GFG{
static int ans = 0, x;
static ArrayList []graph = new ArrayList[100];
static ArrayList weight = new ArrayList();
// Function that returns true if
// x is a perfect square
static bool isPerfectSquare(double x)
{
// Find floating point value of
// square root of x
double sr = Math.Sqrt(x);
// If square root is an integer
return ((sr - Math.Floor(sr)) == 0);
}
// Function that returns true
// if n is a fibonacci number
static bool isFibonacci(int n)
{
return isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n + 4) ||
isPerfectSquare(5 * n * n - 4);
}
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If weight of the current node
// gives a fibonacci number
// when x is added to it
if (isFibonacci((int)weight[node] + x))
ans += 1;
foreach (int to in graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
x = 5;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
weight.Add(0);
graph[i] = new ArrayList();
}
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 4;
weight[2] = 5;
weight[3] = 3;
weight[4] = 25;
weight[5] = 16;
weight[6] = 34;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
graph[5].Add(6);
dfs(1, 1);
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56Javascript
输出:
2