给定一棵包含所有节点权重的树,任务是计算权重为斐波纳契数的节点数。
例子:
Input: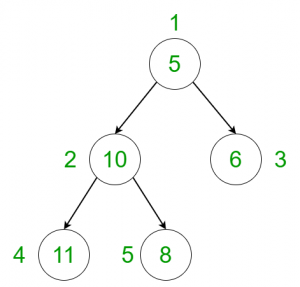
Output: 2
Explanation:
Nodes having weights 5 and 8 are fibonacci nodes.
Input: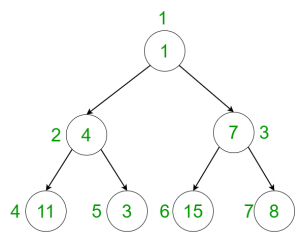
Output: 3
Explanation:
Nodes having weights 1, 3 and 8 are fibonacci nodes.
方法:想法是在树上执行dfs,并为每个节点检查权重是否为斐波那契数。
- 使用动态编程生成包含所有斐波那契数的哈希。
- 使用深度优先搜索遍历,遍历树的每个节点,并通过检查该元素是否存在于预先计算的哈希中来检查该节点是否为斐波那契数。
- 最后,打印斐波那契节点的总数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to count the number of nodes
// in the tree whose weight is a
// Fibonacci number
#include
using namespace std;
const int sz = 1e5;
int ans = 0;
vector graph[100];
vector weight(100);
// To store all fibonacci numbers
set fib;
// Function to generate fibonacci numbers using
// Dynamic Programming and create hash table
// to check Fibonacci numbers
void fibonacci()
{
// Inserting the first two Fibonacci numbers
// in the hash
int prev = 0, curr = 1, len = 2;
fib.insert(prev);
fib.insert(curr);
// Computing the Fibonacci numbers until
// the maximum number and storing them
// in the hash
while (len <= sz) {
int temp = curr + prev;
fib.insert(temp);
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
len++;
}
}
// Function to perform dfs
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// Check if the weight of the node
// is a Fibonacci number or not
if (fib.find(weight[node]) != fib.end())
ans += 1;
// Performing DFS to iterate the
// remaining nodes
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
// Generate fibonacci numbers
fibonacci();
// Call the dfs function to
// traverse through the tree
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to count the number of nodes
// in the tree whose weight is a
// Fibonacci number
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int sz = (int) 1e5;
static int ans = 0;
static Vector []graph = new Vector[100];
static int []weight = new int[100];
// To store all fibonacci numbers
static HashSet fib = new HashSet();
// Function to generate fibonacci numbers using
// Dynamic Programming and create hash table
// to check Fibonacci numbers
static void fibonacci()
{
// Inserting the first two Fibonacci numbers
// in the hash
int prev = 0, curr = 1, len = 2;
fib.add(prev);
fib.add(curr);
// Computing the Fibonacci numbers until
// the maximum number and storing them
// in the hash
while (len <= sz) {
int temp = curr + prev;
fib.add(temp);
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
len++;
}
}
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// Check if the weight of the node
// is a Fibonacci number or not
if (fib.contains(weight[node]))
ans += 1;
// Performing DFS to iterate the
// remaining nodes
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
graph[i] = new Vector();
}
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].add(2);
graph[2].add(3);
graph[2].add(4);
graph[1].add(5);
// Generate fibonacci numbers
fibonacci();
// Call the dfs function to
// traverse through the tree
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.print(ans +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Python3
# Python 3 program to count the number of nodes
# in the tree whose weight is a
# Fibonacci number
sz = 1e5
ans = 0
graph = [[] for i in range(100)]
weight = [0 for i in range(100)]
# To store all fibonacci numbers
fib = set()
# Function to generate fibonacci numbers using
# Dynamic Programming and create hash table
# to check Fibonacci numbers
def fibonacci():
# Inserting the first two Fibonacci numbers
# in the hash
prev = 0
curr = 1
len1 = 2
fib.add(prev)
fib.add(curr)
# Computing the Fibonacci numbers until
# the maximum number and storing them
# in the hash
while (len1 <= sz):
temp = curr + prev
fib.add(temp)
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
len1 += 1
# Function to perform dfs
def dfs(node, parent):
global ans
# Check if the weight of the node
# is a Fibonacci number or not
if (weight[node] in fib):
ans += 1
# Performing DFS to iterate the
# remaining nodes
for to in graph[node]:
if (to == parent):
continue
dfs(to, node)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5
weight[2] = 10
weight[3] = 11
weight[4] = 8
weight[5] = 6
# Edges of the tree
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[2].append(4)
graph[1].append(5)
# Generate fibonacci numbers
fibonacci()
# Call the dfs function to
# traverse through the tree
dfs(1, 1)
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# program to count the number of nodes
// in the tree whose weight is a
// Fibonacci number
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
static int sz = (int) 1e5;
static int ans = 0;
static List []graph = new List[100];
static int []weight = new int[100];
// To store all fibonacci numbers
static HashSet fib = new HashSet();
// Function to generate fibonacci numbers using
// Dynamic Programming and create hash table
// to check Fibonacci numbers
static void fibonacci()
{
// Inserting the first two Fibonacci numbers
// in the hash
int prev = 0, curr = 1, len = 2;
fib.Add(prev);
fib.Add(curr);
// Computing the Fibonacci numbers until
// the maximum number and storing them
// in the hash
while (len <= sz) {
int temp = curr + prev;
fib.Add(temp);
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
len++;
}
}
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// Check if the weight of the node
// is a Fibonacci number or not
if (fib.Contains(weight[node]))
ans += 1;
// Performing DFS to iterate the
// remaining nodes
foreach (int to in graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
graph[i] = new List();
}
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
// Generate fibonacci numbers
fibonacci();
// Call the dfs function to
// traverse through the tree
dfs(1, 1);
Console.Write(ans +"\n");
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji 输出:
2
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(N)。
在dfs中,树的每个节点都处理一次,因此,如果树中总共有N个节点,则由于dfs而导致的复杂度为O(N)。同样,为了处理每个节点,使用了fibonacci()函数,该函数的复杂度也为O(N),但由于此函数仅执行一次,因此不会影响整体时间复杂度。因此,时间复杂度为O(N)。 - 辅助空间: O(N)。
斐波那契散列集使用了额外的空间,因此空间复杂度为O(N)。