1. 超平面:
从几何上讲,超平面是一个几何实体,其维度比其周围空间的维度小 1。
这是什么意思?
意思如下。例如,如果您采用 3D 空间,则超平面是一个 1 维的几何实体。所以它将是二维的,而 3D 空间中的二维实体将是一个平面。现在,如果您采用 2 个维度,那么 1 个无维度将是一维几何实体,即一条线等等。
- 超平面通常由一个方程描述如下
X T n + b =0
-
如果我们将其扩展为 n 个变量,我们将得到这样的结果
X 1 n 1 + X 2 n 2 + X 3 n 3 + ……….. + X n n n + b = 0
-
在二维空间中,我们会得到类似这样的东西,它只不过是一条直线的方程。
X 1 n 1 + X 2 n 2 + b = 0
例子:
让我们考虑一个 2D 几何体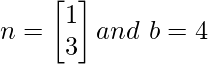 虽然它是一个 2D 几何体,但 X 的值将是
虽然它是一个 2D 几何体,但 X 的值将是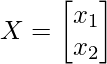 所以根据超平面方程可以解为
所以根据超平面方程可以解为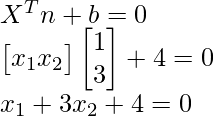 所以正如你从解中看到的,超平面是一条直线的方程。
所以正如你从解中看到的,超平面是一条直线的方程。
2. 子空间:
超平面通常不是子空间。然而,如果我们有形式的超平面,
X T n =0
也就是说,如果平面通过原点,那么超平面也成为子空间。
3.半空间:
考虑下面给出的这个二维图片。

所以,这里我们在 X 1和 X 2 中有一个二维空间,正如我们之前讨论过的,二维方程将是一条线,它是一个超平面。所以,这条线的方程写为
X T n + b =0
所以,对于这两个维度,我们可以像之前讨论的那样写这一行
X 1 n 1 + X 2 n 2 + b = 0
从上图中可以看出,整个二维空间被分成了两个空间;一个在这条线的这一侧(+ve 平面的一半),另一个在这条线的这一侧(-ve 平面的一半)。现在,这两个空间称为半空间。
例子:
Let’s consider the same example that we have taken in hyperplane case. So by solving, we got the equation as
x1 + 3x2 + 4 = 0
There may arise 3 cases. Let’s discuss each case with an example.
Case 1:
x1 + 3x2 + 4 = 0 : On the line
Let consider two points (-1,-1). When we put this value on the equation of line we got 0. So we can say that this point is on the hyperplane of the line.
Case 2:
Similarly,
x1 + 3x2 + 4 > 0 : Positive half-space
Consider two points (1,-1). When we put this value on the equation of line we got 2 which is greater than 0. So we can say that this point is on the positive half space.
Case 3:
x1 + 3x2 + 4 < 0 : Negative half-space
Consider two points (1,-2). When we put this value on the equation of line we got -1 which is less than 0. So we can say that this point is on the negative half-space.