在本文中,我们将讨论抽象和具体数据结构或类型之间的区别。
抽象数据类型(ADT):
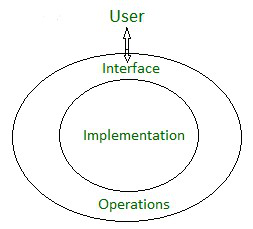
它是一种对象类型(或类),其行为由一组值和一组操作定义。用户使用抽象数据类型指定的操作与界面交互。它提供了一个独立于它的实现的概念的高级使用。他们将数据结构和操作打包在一起,隐藏了内部细节。
例子 –
使用具有私有数据和公共函数的类来表示记录。
public class date
{
private int day;
private string month;
private int year;
};
public void increment ()
{
return day;
}具体数据类型(CDT):
具体数据类型与抽象数据类型相反。它是一种专门的面向解决方案的数据类型,表示定义良好的单一解决方案域概念。一个具体的数据类型很少能在其原始用途之外重用,但可以嵌入或与其他数据类型组合以形成更大的数据类型。它们是相对简单概念的直接实现。它不隐藏任何东西。
例子 –
使用带有公共数据且没有函数的结构来表示记录
struct date
{
int day;
string month;
int year;
};类和对象的区别:
对象和类之间有很多区别。下面给出了对象和类之间的一些区别:
| S. No. |
Abstract Data Types or structure (ADT) |
Concrete Data Types or structure (CDT) |
| 1 | Abstract Data Types or structures describe the data and the operations to manipulate and change it. | Concrete data types or structures provide how these operations are actually implemented. |
| 2 | Most of the program becomes independent of the abstract data types representation, so it can be improved without breaking the program. | Which is not possible in Concrete Data Types or structure (CDT) |
| 3 | It’s easier for each part of a program to use an implementation of its data types and that will be more efficient. | It is not so efficient compared to ADT. |
| 4 | Implementation of a high level concept | Implementation of a simple concept |
| 5 | It is usable beyond its original use. | It is rarely reusable beyond its original use. |
| 6 | It hides the internal details. | It doesn’t hide anything. |
| 7 | It uses class. | It uses structure. |
| 8 | Examples- lists, sets, stacks. | Examples-Arrays, linked lists, trees, graphs. |