给定一个由六边形的 6 条边的长度组成的数组S[] ,任务是计算可以由给定的六边形组成的单位长度的等边三角形的数量。
例子:
Input: S = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
Output: 6
Explanation:
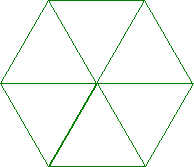
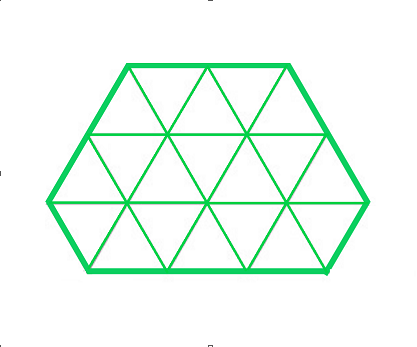
Input: S = {2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2}
Output: 19
Explanation:
方法:需要进行以下观察来解决给定的问题:
- 考虑一个边长为“X”的等边三角形。通过绘制平行于其边的线,它被分成单位长度的较小三角形。
- 下面是三个这样的等边三角形的图像:
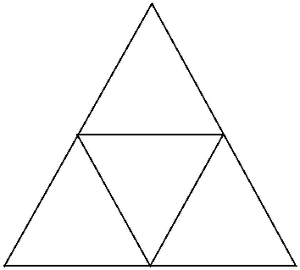
示例 1:X = 2
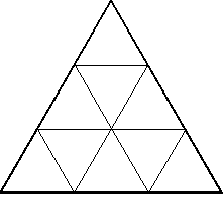
示例 2:X = 3
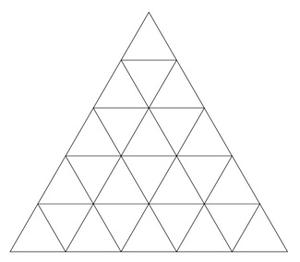
示例 3:X = 5
- 在上述三个例子中的每一个中,单位长度等边三角形可能的数量是:
- X = 2: 4 equilateral triangles of 1 unit length side.
- X = 3: 9 equilateral triangles of 1 unit length side.
- X = 5: 25 equilateral triangles of 1 unit length side.
- 通过观察,很明显,对于边长为X的等边三角形, X 2 个单位长度的等边三角形是可能的。
- 将此观察扩展到六边形,在等边三角形内内切六边形,如下所示:
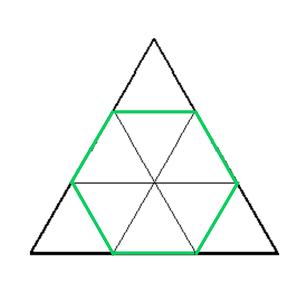
由边 X = 3 的等边三角形内接而成的正六边形内部有 6 个小三角形。
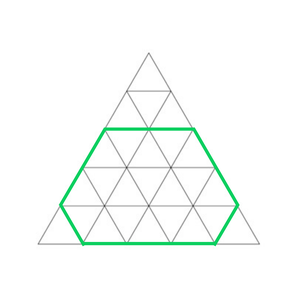
从边 X = 5 的等边三角形内接的不规则六边形,里面有 19 个小三角形。
- 可以观察到,通过从较大的三角形中去除一定数量的小三角形,可以找到给定尺寸的六边形。
对于具有六个边 S 1 、S 2 、S 3 、S 4 、S 5 、S 6的六边形,计算单位长度三角形数量的公式可以概括为:
Number of triangles that can be formed = ( S1 + S2 + S3 )2 – S12 – S32 – S52
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate the
// the number of Triangles possible
int calculateTriangles(int sides[])
{
double count = pow(sides[0] + sides[1] +
sides[2], 2);
count -= pow(sides[0], 2);
count -= pow(sides[2], 2);
count -= pow(sides[4], 2);
return (int)(count);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Regular Hexagon
int sides[] = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 };
cout << (calculateTriangles(sides)) << endl;
// Irregular Hexagon
int sides1[] = { 2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2 };
cout << (calculateTriangles(sides1)) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate the
// the number of Triangles possible
static int calculateTriangles(int sides[])
{
double count = Math.pow(sides[0] + sides[1] +
sides[2], 2);
count -= Math.pow(sides[0], 2);
count -= Math.pow(sides[2], 2);
count -= Math.pow(sides[4], 2);
return (int)(count);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Regular Hexagon
int sides[] = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 };
System.out.print((calculateTriangles(sides)) + "\n");
// Irregular Hexagon
int sides1[] = { 2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2 };
System.out.print((calculateTriangles(sides1)) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubeyPython3
# Python3 Program to implement
# the above approach
# Function to calculate the
# the number of Triangles possible
def calculateTriangles(sides):
count = pow( sides[0] + sides[1] + sides[2], 2)
count -= pow( sides[0], 2)
count -= pow( sides[2], 2)
count -= pow( sides[4], 2)
return int(count)
# Driver Code
# Regular Hexagon
sides = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
print(calculateTriangles(sides))
# Irregular Hexagon
sides = [2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2]
print(calculateTriangles(sides))C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate the
// the number of Triangles possible
static int calculateTriangles(int []sides)
{
double count = Math.Pow(sides[0] + sides[1] +
sides[2], 2);
count -= Math.Pow(sides[0], 2);
count -= Math.Pow(sides[2], 2);
count -= Math.Pow(sides[4], 2);
return (int)(count);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Regular Hexagon
int []sides = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 };
Console.Write((calculateTriangles(sides)) + "\n");
// Irregular Hexagon
int []sides1 = { 2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2 };
Console.Write((calculateTriangles(sides1)) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubeyJavascript
输出:
6
19时间复杂度: O(1)
辅助空间: O(1)