在软件行业,手动测试和自动化测试之间存在明显的区别。手动测试用于确保软件代码按预期执行并且需要时间和精力。大多数手动测试包括检查日志文件、外部服务和数据库是否有错误。以不同的方式,自动化测试是自动化的,其中某些软件/代码像用户一样执行测试。因为自动化测试是使用自动化工具完成的,所以探索测试花费更少的时间和更多的测试脚本,同时增加了测试的整体范围。
在 Golang 中,包测试负责不同类型的测试,可能是性能测试、并行测试、功能测试或所有这些的任何可能组合。
测试包为 Golang 代码的自动化测试提供支持。要运行任何测试函数使用“ go test ”命令,它会自动执行任何形式为TestXxx(*testing.T) 的函数,其中 Xxx 不得以任何小写字母开头。
测试函数语法:
func TestXxx(*testing.T)
在 Golang 中编写测试套件的步骤:
- 创建一个名称以 _test.go 结尾的文件
- 通过 import “testing” 命令导入包测试
- 编写形式为func TestXxx(*testing.T)的测试函数,它使用Error、Fail或相关方法中的任何一种来表示失败。
- 将文件放在任何包中。
- 运行命令 go test
注意:测试文件将被排除在包构建中,并且只会在 go test 命令上执行。
例子:
文件:main.go
Go
package main
// function which return "geeks"
func ReturnGeeks() string{
return "geeks";
}
// main function of package
func main() {
ReturnHello()
}Go
package main
import (
"testing"
)
// test function
func TestReturnGeeks(t *testing.T) {
actualString := ReturnGeeks()
expectedString := "geeks"
if actualString != expectedString{
t.Errorf("Expected String(%s) is not same as"+
" actual string (%s)", expectedString,actualString)
}
}测试文件:pkg_test.go
去
package main
import (
"testing"
)
// test function
func TestReturnGeeks(t *testing.T) {
actualString := ReturnGeeks()
expectedString := "geeks"
if actualString != expectedString{
t.Errorf("Expected String(%s) is not same as"+
" actual string (%s)", expectedString,actualString)
}
}
输出:
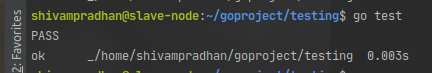
运行测试用例后的屏幕