给定一个包含N个顶点和M 个边的有向图,任务是找到图中每个顶点的所有依赖关系以及具有最小依赖关系的顶点。
A directed graph (or digraph) is a set of nodes connected by edges, where the edges have a direction associated with them.
For example, an arc (x, y) is considered to be directed from x to y, and the arc (y, x) is the inverted link. Y is a direct successor of x, and x is a direct predecessor of y.
The dependency is the number of connections to different vertices which are dependent on the current vertex.
例子:
Input:

Output:
Vertex 1 dependencies -> 2-> 3
Vertex 2 dependencies -> 3-> 1
Vertex 3 dependencies -> 1-> 2
Node 1 has the minimum number of dependency of 2.
Explanation:
Vertex 1 is dependent on 2 and 3.
Similarly, vertex 2 and 3 on (3, 1) and (1, 2) respectively.
Therefore, the minimum number of dependency among all vertices is 2.
Input:
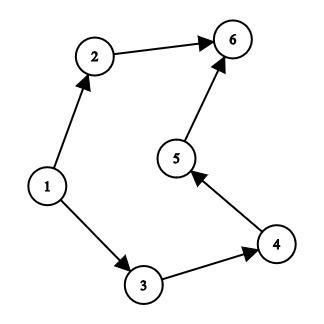
Output:
Vertex 1 dependency -> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5-> 6
Vertex 2 dependency -> 6
Vertex 3 dependency -> 4-> 5-> 6
Vertex 4 dependency -> 5-> 6
Vertex 5 dependency -> 6
Vertex 6 is not dependent on any vertex.
Node 6 has the minimum dependency of 0
Explanation:
Vertex 1 is dependent on (3, 4, 5, 6, 7). Similarly, vertex 2 on (6), vertex 3 on (4, 5, 6), vertex 4 on (5, 6), vertex 5 on (6) and vertex 6 is not dependent on any.
Therefore, the minimum number of dependency among all vertices is 0.
方法:思路是使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来解决这个问题。
- 获取有向图作为输入。
- 对图执行 DFS 并探索图的所有节点。
- 在探索节点的邻居时,将计数加 1,最后返回表示依赖项数量的计数。
- 最后,找到依赖项数最少的节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
CPP
// C++ program to find the
// dependency of each node
#include
using namespace std;
// Defining the graph
class Graph {
// Variable to store the
// number of vertices
int V;
// Adjacency list
list* adjList;
// Initializing the graph
public:
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adjList = new list[V];
}
// Adding edges
void addEdge(int u, int v,
bool bidir = true)
{
adjList[u].push_back(v);
if (bidir) {
adjList[u].push_back(v);
}
}
// Performing DFS on each node
int dfs(int src)
{
// Map is used to mark
// the current node as visited
map visited;
vector dependent;
int count = 0;
stack s;
// Push the current vertex
// to the stack which
// stores the result
s.push(src);
visited[src] = true;
// Traverse through the vertices
// until the stack is empty
while (!s.empty()) {
int n = s.top();
s.pop();
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
for (auto i : adjList[n]) {
// If the vertices are
// not visited
if (!visited[i]) {
dependent.push_back(i + 1);
count++;
// Mark the vertex as
// visited
visited[i] = true;
// Push the current vertex to
// the stack which stores
// the result
s.push(i);
}
}
}
// If the vertex has 0 dependency
if (!count) {
cout << "Vertex " << src + 1
<< " is not dependent on any vertex.\n";
return count;
}
cout << "Vertex " << src + 1 << " dependency ";
for (auto i : dependent) {
cout << "-> " << i;
}
cout << "\n";
return count;
}
};
// Function to find the
// dependency of each node
void operations(int arr[][2],
int n, int m)
{
// Creating a new graph
Graph g(n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
g.addEdge(arr[i][0],
arr[i][1], false);
}
int ans = INT_MAX;
int node = 0;
// Iterating through the graph
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int c = g.dfs(i);
// Finding the node with
// minimum number of
// dependency
if (c < ans) {
ans = c;
node = i + 1;
}
}
cout << "Node " << node
<< "has minimum dependency of "
<< ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n, m;
n = 6, m = 6;
// Defining the edges of the
// graph
int arr[][2] = { { 0, 1 },
{ 0, 2 },
{ 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5 },
{ 3, 4 },
{ 1, 5 } };
operations(arr, n, m);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to find the
# dependency of each node
# Adding edges
def addEdge(u, v, bidir = True):
global adjList
adjList[u].append(v)
if (bidir):
adjList[u].append(v)
# Performing DFS on each node
def dfs(src):
global adjList, V
# Map is used to mark
# the current node as visited
visited = [False for i in range(V+1)]
dependent = []
count = 0
s = []
# Push the current vertex
# to the stack which
# stores the result
s.append(src)
visited[src] = True
# Traverse through the vertices
# until the stack is empty
while (len(s) > 0):
n = s[-1]
del s[-1]
# Recur for all the vertices
# adjacent to this vertex
for i in adjList[n]:
# If the vertices are
# not visited
if (not visited[i]):
dependent.append(i + 1)
count += 1
# Mark the vertex as
# visited
visited[i] = True
# Push the current vertex to
# the stack which stores
# the result
s.append(i)
# If the vertex has 0 dependency
if (not count):
print("Vertex ", src + 1,
" is not dependent on any vertex.")
return count
print("Vertex ",src + 1," dependency ",end="")
for i in dependent:
print("-> ", i, end = "")
print()
return count
# Function to find the
# dependency of each node
def operations(arr, n, m):
# Creating a new graph
global adjList
for i in range(m):
addEdge(arr[i][0], arr[i][1], False)
ans = 10**18
node = 0
# Iterating through the graph
for i in range(n):
c = dfs(i)
# Finding the node with
# minimum number of
# dependency
if (c < ans):
ans = c
node = i + 1
print("Node", node, "has minimum dependency of ", ans)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
V = 6
adjList = [[] for i in range(V+1)]
n, m = 6, 6
# Defining the edges of the
# graph
arr = [ [ 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 2 ],
[ 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5 ],
[ 3, 4 ],
[ 1, 5 ] ]
operations(arr, n, m)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.Vertex 1 dependency -> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5-> 6
Vertex 2 dependency -> 6
Vertex 3 dependency -> 4-> 5-> 6
Vertex 4 dependency -> 5-> 6
Vertex 5 dependency -> 6
Vertex 6 is not dependent on any vertex.
Node 6has minimum dependency of 0如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。