邻接表用于表示图形。在这里,对于图中的每个顶点,我们都有一个列表,其中包含该特定顶点有一条边的所有其他顶点。
问题:给定邻接表以及图的顶点和边数,任务是表示有向图的邻接表。
例子:
Input: V = 3, edges[][]= {{0, 1}, {1, 2} {2, 0}}
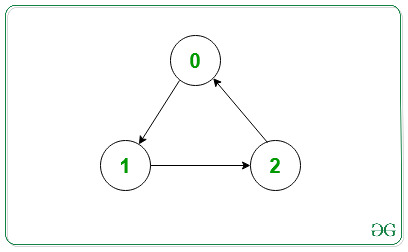
Output: 0 -> 1
1 -> 2
2 -> 0
Explanation:
The output represents the adjacency list for the given graph.
Input: V = 4, edges[][] = {{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {3, 0}}
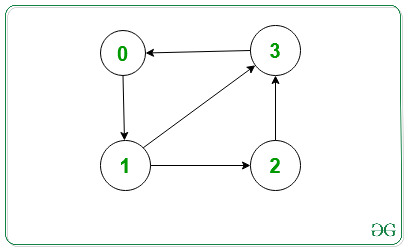
Output: 0 -> 1
1 -> 2 3
2 -> 3
3 -> 0
Explanation:
The output represents the adjacency list for the given graph.
方法(使用STL ):主要思想是将图表示为向量数组,使得每个向量都表示单个顶点的邻接表。使用 STL,代码变得更简单、更容易理解。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to add edges
void addEdge(vector adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
}
// Function to print adjacency list
void adjacencylist(vector adj[], int V)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
cout << i << "->";
for (int& x : adj[i]) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Function to initialize the adjacency list
// of the given graph
void initGraph(int V, int edges[3][2], int noOfEdges)
{
// To represent graph as adjacency list
vector adj[V];
// Traverse edges array and make edges
for (int i = 0; i < noOfEdges; i++) {
// Function call to make an edge
addEdge(adj, edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call to print adjacency list
adjacencylist(adj, V);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given vertices
int V = 3;
// Given edges
int edges[3][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 2 }, { 2, 0 } };
int noOfEdges = 3;
// Function Call
initGraph(V, edges, noOfEdges);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to add edges
static void addEdge(Vector adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].add(v);
}
// Function to print adjacency list
static void adjacencylist(Vector adj[], int V)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
System.out.print(i+ "->");
for (int x : adj[i]) {
System.out.print(x+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Function to initialize the adjacency list
// of the given graph
static void initGraph(int V, int edges[][], int noOfEdges)
{
// To represent graph as adjacency list
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector adj[] = new Vector[3];
for(int i =0;i();
}
// Traverse edges array and make edges
for (int i = 0; i < noOfEdges; i++) {
// Function call to make an edge
addEdge(adj, edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call to print adjacency list
adjacencylist(adj, V);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given vertices
int V = 3;
// Given edges
int edges[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 2 }, { 2, 0 } };
int noOfEdges = 3;
// Function Call
initGraph(V, edges, noOfEdges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
// Function to add edges
static void addEdge(List []adj, int u, int v)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
}
// Function to print adjacency list
static void adjacencylist(List []adj, int V)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
Console.Write(i+ "->");
foreach (int x in adj[i]) {
Console.Write(x+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Function to initialize the adjacency list
// of the given graph
static void initGraph(int V, int [,]edges, int noOfEdges)
{
// To represent graph as adjacency list
List []adj = new List[3];
for(int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++) {
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Traverse edges array and make edges
for (int i = 0; i < noOfEdges; i++) {
// Function call to make an edge
addEdge(adj, edges[i,0], edges[i,1]);
}
// Function Call to print adjacency list
adjacencylist(adj, V);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given vertices
int V = 3;
// Given edges
int [,]edges = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 2 }, { 2, 0 } };
int noOfEdges = 3;
// Function Call
initGraph(V, edges, noOfEdges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar 输出:
0->1
1->2
2->0如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。