括号定理用于图的 DFS。它指出深度优先搜索树中的后代有一个有趣的特性。如果v 是 u 的后代,则v的发现时间晚于u 的发现时间。
在图 g = (V, E) 的任何 DFS 遍历中,对于任意两个顶点 u 和 v 正好满足以下条件之一:
- 区间[d[u], f[u]]和[d[v], f[v]]完全不相交,并且u和v都不是深度优先森林中另一个的后代。
- 区间[d[u], f[u]]包含在区间[d[v], f[v]] 内,并且 u 是深度优先树中 v 的后代。
- 区间[d[v], f[v]]完全包含在区间[d[u], f[u]] 内,并且 v 是深度优先树中 u 的后代。
边缘分类:
DFS 遍历可用于对输入图 G=(V, E) 的边进行分类。可以根据深度优先森林定义四种边缘类型:
- 树边:它是在图上应用 DFS 后获得的树中存在的边。
- 前向边:它是一条边 (u, v),使得 v 是后代但不是 DFS 树的一部分。
- Back edge:它是一条边 (u, v),使得 v 是边 u 的祖先,但不是 DFS 树的一部分。后边的存在表示有向图中的循环。
- Cross Edge:它是连接两个节点的边,它们之间没有任何祖先和后代关系。
给定N个顶点和M 个边的图,任务是将 M 个边分类为树边、前向边、后向边和交叉边。
例子:
Input: N = 5, M = 7, arr[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 3, 4 }, { 1, 4 }, { 2, 5 }, { 5, 1 }, { 3, 2 } } }
Output:
{1, 2} -> Tree Edge
{1, 3} -> Tree Edge
{3, 4} -> Tree Edge
{1, 4} -> Forward Edge
{2, 5} -> Tree Edge
{5, 1} -> Backward Edge
{3, 2} -> Cross Edge
Explanation:
1. Green Edges: Tree Edge
2. Blue Edges: Forward Edge
3. Black Edges: Backward Edge
4. Red Edges: Cross Edge
Below is the given graph for the above information:
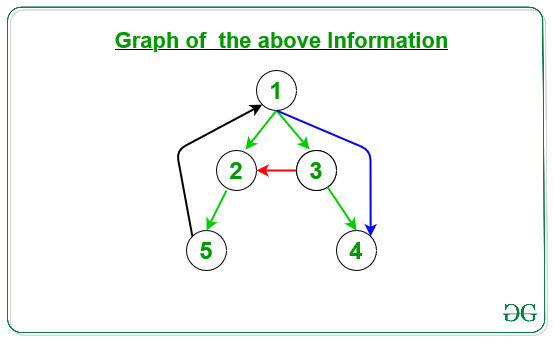
Input: N = 5, M = 4, arr[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 3, 4 }, { 1, 4 } }
Output:
{1, 2} -> Tree Edge
{1, 3} -> Tree Edge
{3, 4} -> Tree Edge
{1, 4} -> Forward Edge
Explanation:
1. Green Edges: Tree Edge
2. Blue Edges: Forward Edge
3. Black Edges: Backward Edge
4. Red Edges: Cross Edge
Below is the given graph for the above information:

方法:
- 在给定的图上使用 DFS 遍历来查找每个节点的发现时间和完成时间以及父节点。
- 通过使用括号定理在以下条件下对给定的边进行分类:
- 树边:对于任意边(U, V) ,如果节点 U 是节点 V 的父节点,则(U, V)是给定图的树边。
- 前向边:对于任何边(U, V) ,如果节点 V 的发现时间和完成时间与节点 U 的发现时间和完成时间完全重叠,则(U, V)是给定图的前向边。
- 后向边:对于任何边(U, V) ,如果节点 U 的发现时间和完成时间与节点 V 的发现时间和完成时间完全重叠,则(U, V)是给定图的后向边。
- 交叉边:对于任意边(U, V) ,如果节点 U 的发现时间和完成时间与节点 V 的发现时间和完成时间不重叠,则(U, V)是给定图的交叉边。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// For recording time
int tim = 0;
// For creating Graph
vector > G;
// For calculating Discovery time
// and finishing time of nodes
vector disc, fin;
// For finding Parent of node
vector Par;
// For storing color of node
vector Color;
// Recursive function for DFS
// to update the
void DFS_Visit(int v)
{
// Make the current nodes as visited
Color[v] = 'G';
// Increment the time
tim = tim + 1;
// Assign the Discovery node of
// node v
disc[v] = tim;
// Traverse the adjacency list of
// vertex v
for (auto& it : G[v]) {
// If the nodes is not visited,
// then mark the parent of the
// current node and call DFS_Visit
// for the current node
if (Color[it] == 'W') {
Par[it] = v;
DFS_Visit(it);
}
}
Color[v] = 'B';
tim = tim + 1;
fin[v] = tim;
}
void DFS(vector >& G)
{
// Initialise Par, disc, fin and
// Color vector to size of graph
Par.resize(G.size());
disc.resize(G.size());
fin.resize(G.size());
Color.resize(G.size());
// Initialise the Par[], Color[],
// disc[], fin[]
for (int i = 1; i < G.size(); i++) {
Color[i] = 'W';
Par[i] = 0;
disc[i] = 0;
fin[i] = 0;
}
// For every vertex if nodes is
// not visited then call DFS_Visit
// to update the discovery and
// finishing time of the node
for (int i = 1; i < G.size(); i++) {
// If color is 'W', then
// node is not visited
if (Color[i] == 'W') {
DFS_Visit(i);
}
}
}
// Function to check whether
// time intervals of x and y overlaps
// or not
bool checkOverlap(int x, int y)
{
// Find the time intervals
int x1 = disc[x], y1 = fin[x];
int x2 = disc[y], y2 = fin[y];
// Complete overlaps
if (x2 > x1 && y1 > y2) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// Function to check which Edges
// (x, y) belongs
string checkEdge(int x, int y)
{
// For Tree Edge
// If x is parent of y, then it
// is Tree Edge
if (Par[y] == x) {
return "Tree Edge";
}
// For Forward Edge
else if (checkOverlap(x, y)) {
return "Forward Edge";
}
// For Backward Edge
else if (checkOverlap(y, x)) {
return "Backward Edge";
}
else {
return "Cross Edge";
}
}
// Function call to find the Tree Edge,
// Back Edge, Forward Edge, and Cross Edge
void solve(int arr[][2], int N, int M)
{
// Create graph of N size
G.resize(N + 1);
// Traverse each edges
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int x = arr[i][0];
int y = arr[i][1];
// Make Directed graph
G[x].push_back(y);
}
// DFS call to calculate discovery
// and finishing time for each node
DFS(G);
// Condition for Tree Edge, Forward
// Edges, Backward Edge and Cross Edge
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int x = arr[i][0];
int y = arr[i][1];
// Function call to check Edges
cout << "{" << x << ", " << y
<< "} -> " << checkEdge(x, y)
<< endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of Nodes
int N = 5;
// Number of Edges
int M = 7;
// Edges for the graph
int arr[M][2]
= { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 1, 4 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 5, 1 },
{ 3, 1 } };
// Function Call
solve(arr, N, M);
return 0;
} {1, 2} -> Tree Edge
{1, 3} -> Tree Edge
{3, 4} -> Tree Edge
{1, 4} -> Forward Edge
{2, 5} -> Tree Edge
{5, 1} -> Backward Edge
{3, 1} -> Backward Edge时间复杂度: O(N),其中 N 是图中节点的总数。
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。