圆是距特定点固定距离的点的集合。固定点称为圆的中心,固定距离称为圆的半径。我们在现实生活中遇到了许多圆形的物体。例如,汽车的轮子,手镯,电话的拨号盘等。在钟表中,其指针也以圆形的方式反复移动。钟针尖所追踪的路径称为圆。
让我们简单地看一下与圆有关的一些术语:
- 圆弧:两点之间的一个圆称为圆弧。
- 和弦:如果在圆上取两个点I和J,则线段IJ称为圆的和弦。
- 周长:整个圆的长度称为周长。
- 线段:弦和其弧线之间的区域称为圆形区域的段,或简称为圆形的段。
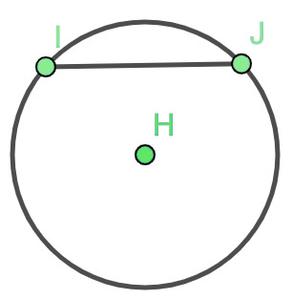
弦在点处的对角
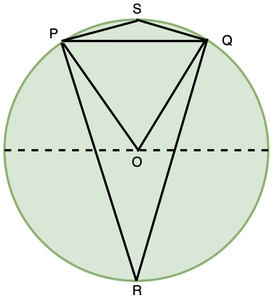
在PQ上方的图中和弦。 R和S是圆上的两个点。 ∠PRQ称为点R上弦PQ对角。类似地,弦对S上以及圆O的中心对角。让我们研究在这些点上弦PQ对角之间的关系。
定理1:圆的相等弦在中心对角相等。
证明:
We are given two chords KL and JI. We need to prove that ∠KHL = ∠JHI.
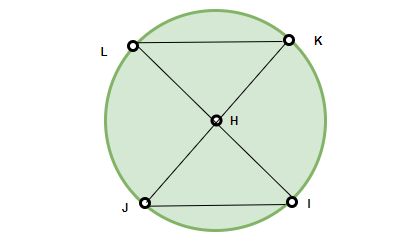
In triangles KHL and JHI,
HL = HJ
HI = HK
and we are given that KL = JI.
So, both the triangles are congruent. Thus, both of these angles are equal. Hence, proved.
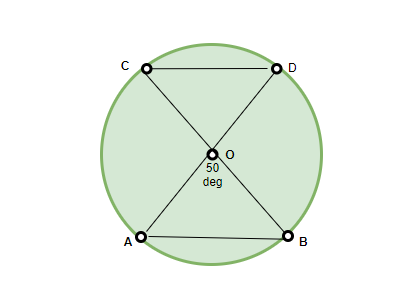
问题:如果下图中的∠AOB= 50°,只要和弦AB和CD相等,∠COD所成的角度将是多少。
回答:
According to the theorem mentioned above, the angles ∠AOB and ∠COD are equal, since they are equal chords subtending equal angles at the centre. Therefore, ∠COD = 50°.
Note: The converse of this theorem “If the angles subtended by two chords at the centre are equal, then the two chords are equal” is also true and can be proved similarly by the properties of triangles.
从中心垂直到和弦

定理:通过圆心将弦二等分的线垂直于弦
证明:
Let PQ be the chord of a circle and OM be the line from the centre that bisects the chord. Here, M is the mid point of the chord, and we have to prove that ∠OMQ = 90°.
In triangles ΔOPM and ΔOQM.
PM = MQ (perpendicular bisects the chord)
OP = OQ (radius of the circle)
OM = OM (common side of both the triangles)
So, both these triangles are congruent. This gives, angles ∠OMQ and ∠OMP as 90°
Note: The converse of this theorem “The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord” is also true.
圆弧对角
如果一个圆的两个和弦相等,则它们的对应弧相等;反之,如果两个圆和弦相等,则它们的对应弦相等。
类似于和弦的情况,相等的弧线在中心也呈相等的角度。
定理:圆弧在中心处所成的角度是圆的其余部分在任何点处所成的角度的两倍。
证明:
Let’s consider three cases,
- Arc PQ is major arc.
- Arc PQ is minor arc.
- Arc PQ is semi-circle.

Let’s join AO and extend it to B.
In all three cases, ∠BOQ = ∠OAQ + ∠OQA. (Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles).
Also in triangle ΔOAQ,
OA = OQ (Radii of Circle)
Therefore, ∠ OAQ = ∠ OQA
this gives, ∠ BOQ = 2∠OAQ
∠ BOP = 2∠OAP
from (1) and (2), ∠ BOP + ∠ BOQ = 2(∠ OAP + ∠ OAQ)
∠POQ = 2 ∠PAQ
For the case (iii), where PQ is the major arc, (3) is replaced by
Reflex angle POQ = 2∠PAQ
问题:∠ABC的价值是什么?
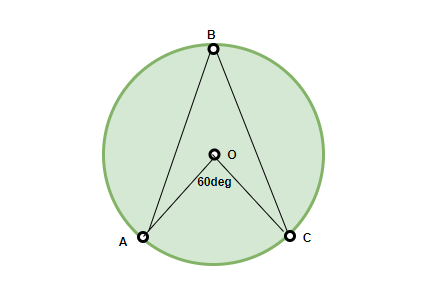
回答:
According to the theorem, ∠AOC = 2 ∠ABC
Therefore, ∠ABC = 60°/2 = 30°
其他一些属性:
- 圆的同一段中的角度相等。
- 如果连接两个点的线段在包含该线段的线的同一侧上的其他两个点对角相等,则这四个点位于一个圆上(即它们是同心的)。
循环四边形
如果四边形的所有四个顶点都位于一个圆上,则称该四边形为循环。
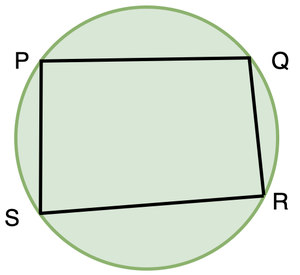
它们也称为内接四边形。
定理:循环四边形的任意一对相反的角度之和为180º。
证明:
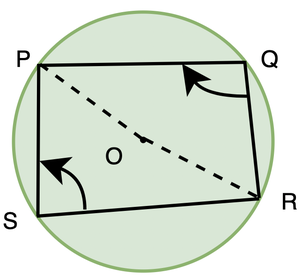
Considering arc PQR, ∠POR = 2 ∠PSR,
Similarly, considering PSR, reflex ∠POR = 2∠PQR
We know, ∠POR + relfex ∠POR = 360°.
⇒ 2 ∠PSR + 2∠PQR = 360°
⇒ 2(∠PSR + ∠PQR) = 360°
⇒ ∠PSR + ∠PQR = 180°
Thus, sum of opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral is 180°.
问题:在下图中,BC是圆的直径,ED是与圆的半径相等的弦。延伸时的BE和CD在F点相交。证明∠BFC= 60°。
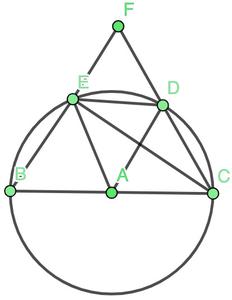
解决方案:
In the figure, join AE, AD and EC. Triangle AED is an equilateral triangle.
Therefore, ∠EAD = 60o. Now, ∠ECD becomes 30o.
We know that ∠BEC = 90o.
So, by the property of exterior angles of triangle,
∠BEC = ∠ECD + ∠BFC,
90o = 30o + ∠BFC
⇒60o = ∠BFC
Hence, Proved.