作为先决条件的独立图集是没有两个彼此相邻的顶点集。它在定义上与 clique 刚好相反,因此需要了解图的补集才能走得更远。基本上,平面图的概念不是最重要的,但可以参考。因此,我们将使用所有这三个的想法来解决提到的问题。
我们需要在给定的平面图中找到最大的 Clique。集团 任何平面图的顶点是顶点的子集,使得该子集中的任何两个顶点彼此相邻,即顶点集形成一个完整的图,而这个完整的图是给定平面图的子图。换句话说,Maximal Clique 是顶点的最大子集,使得它们在给定图中形成一个完整的子图,并且没有更多的顶点可以添加到该子集中。现在,如果我们熟悉独立集的概念,那么我们可以发现两个概念之间的模糊关系:Clique 和 Independent-set。
因此,如下讨论的关系和差异是齐头并进的:
- 团是无向图或平面图的一组顶点,使得团中每两个不同的顶点是相邻的。
- 独立集是一组顶点,这样没有两个顶点彼此相邻。
- 两个集合的最大值的想法是相同的。
图的 Clique 和独立集的定义直接表明它们之间存在某种互补关系。
假设如果我们补充给定的图,那么根据最大独立集的定义,它将是实图中不相邻的顶点的最大集合(因为我们在补充中找到独立集图形)。因此,给定图的补集的最大独立集只不过是给定图中的最大 Clique。
概念:
所以给定图的最大 Clique 可以认为是给定图的补图中最大的独立集。由于我们有很多方法可以找到给定平面图的最大独立集(尽管它们是 NP 难题),我们可以使用它们中的任何一种来找到团。我们只需要对给定的算法做一个小的改变,因为我们必须输入输入图的补集。
实现:如下图所示:
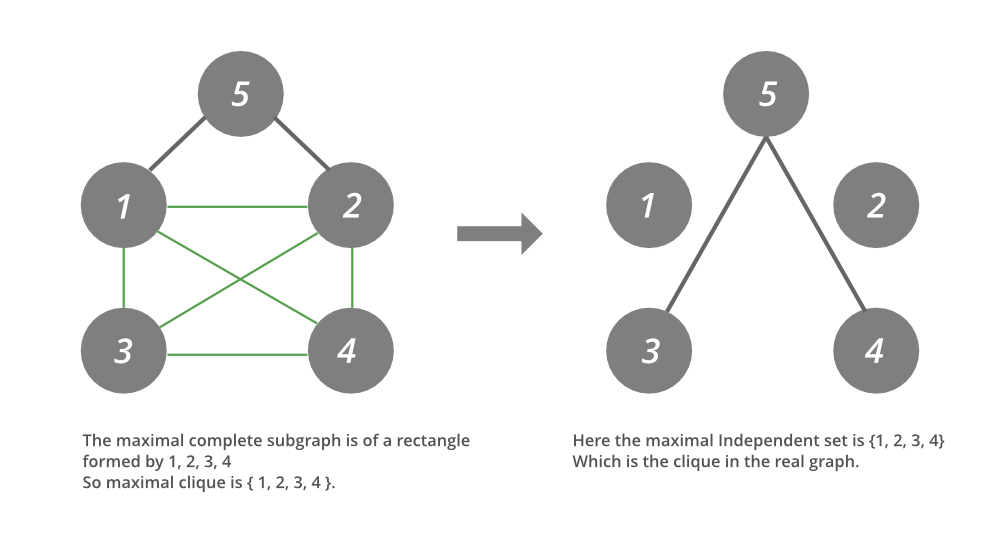
- 现在我们要在上面给出的图中找到最大的集团。 (这是由绿色边组成的子图)
- 下面给出的是上述想法的实现,即找到一个图的补集的独立集,它是该图的 Clique 的间接集合。
Go through if you do not know the idea in order to find the Independent set of graph using different methods
例子
Java
// Java Program to Find Independent Sets in a Graph
// By Graph Coloring
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Importing utility classes from java.util package
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class GFGUTIL {
// Method 1
// To label maximum vertices with 0
// that can be included in the set
public static void
Util(Vector > adjacency_list,
Vector color)
{
int a = 0;
// Condition check
while (a != -1) {
a = remove_all(adjacency_list, color);
if (a != -1)
color.set(a, 0);
}
}
// Method 2
// Tries whether it is possible to remove
// any adjacent vertex of any removed vertex
public static void
Util2(Vector > adjacency_list,
Vector color, int j)
{
int cnt = 0;
// Implementation
// It removes the colored node i.e. uncolor it
// so that some of the adjacent vertices which can
// provide more elements to
// set are colored who were hindered due to the
// previous node.
Vector tmp_color = new Vector();
for (int g = 0; g < color.size(); ++g)
tmp_color.add(color.get(g));
for (int i = 0; i < color.size(); ++i) {
if (tmp_color.get(i) == 1) {
int sum = 0;
int idx = -1;
for (int g = 0;
g < adjacency_list.get(i).size(); ++g)
if (tmp_color.get(
adjacency_list.get(i).get(g))
== 0) {
idx = g;
sum++;
}
if (sum == 1
&& color.get(
adjacency_list.get(i).get(idx))
== 0) {
tmp_color.set(
adjacency_list.get(i).get(idx), 1);
tmp_color.set(i, 0);
Util(adjacency_list, tmp_color);
++cnt;
}
if (cnt > j)
break;
}
}
for (int g = 0; g < color.size(); ++g)
color.set(g, tmp_color.get(g));
}
// Method 3
// Returning the number of vertices
// that can't be included in the set
public static int Util3(Vector color)
{
int cnt = 0;
// Checking the condition when the vertices cannot
// be included.
for (int i = 0; i < color.size(); i++)
if (color.get(i) == 1)
++cnt;
return cnt;
}
// Method 4
// This method return all the elements which can be
// removed.
public static int
remove_all(Vector > adjacency_list,
Vector color)
{
int a = -1, max = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < color.size(); ++i) {
if (color.get(i) == 1
&& can_remove(adjacency_list.get(i), color)
== 1) {
Vector tmp_color
= new Vector();
for (int j = 0; j < color.size(); ++j)
tmp_color.add(color.get(j));
tmp_color.set(i, 0);
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < tmp_color.size(); ++j)
if (tmp_color.get(j) == 1
&& can_remove(adjacency_list.get(j),
tmp_color)
== 1)
++sum;
if (sum > max) {
max = sum;
a = i;
}
}
}
// Index of the vertex
return a;
}
// Method 5
// To check whether a vertex can be removed or not
public static int can_remove(Vector adj_list,
Vector color)
{
int check = 1;
// condition checking for removal
for (int i = 0; i < adj_list.size(); ++i)
// cannot be removed if this condition happens
if (color.get(adj_list.get(i)) == 0)
check = 0;
return check;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Graph input alongside forming it's adjacency List
// Display message for better readibility
System.out.println(
"The number of vertices in the graph is taken as 5");
// Custom input is taken here
int n = 5;
// Creating a vector object for adjacency matrix.
Vector > adjacency_matrix
= new Vector >(n, (n));
// Input matrix is
// 01111
// 10111
// 11010
// 11100
// 11000
// Complement graph's matrix of the given input
// graph 00000 00000 00001 00001 00110
// Nested for loops for iterations
// creating the adjacency matrix of the input graph
// As shown above
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Vector adj = new Vector(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if ((i == 2 && j == 4) || (i == 3 && j == 4)
|| (i == 4 && j == 2)
|| (i == 4 && j == 3))
adj.add(1);
else
adj.add(0);
adjacency_matrix.add(adj);
}
// Creating a vector object for adjacency list
Vector > adjacency_list
= new Vector >();
// Nested for loops for creating the adjacency list
// of graph given
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Vector adj_list
= new Vector();
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (adjacency_matrix.get(i).get(j) == 1)
adj_list.add(j);
}
adjacency_list.add(adj_list);
}
// Display messsage only for
// taking the minimum size of the set required.
System.out.println(
"The maximal independent set's size to be find is 4");
// Declaring and initializing variable with
// least size of the set required
// can be set to full size too.
int x = 4;
// Complement of the size
int y = n - x;
int found = 0;
c // variable to check if answer is found
int size
= 0;
int min = n + 1;
// Creating a set found vector to
// store all the possible set
Vector > set_found
= new Vector >();
// Display message
System.out.println("Searching for the set");
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// If set is found
if (found == 1)
// Hault the further execution of Program
break;
// graph coloring method is used.
// Color vector to have the state of all the
// vertices initially
Vector color = new Vector(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
color.add(1);
// Starting by putting the ith node in set
color.set(i, 0);
// Then finding all the nodes to be pushed
GFGUTIL.Util(adjacency_list, color);
// Finding the number of those which cannot be
// pushed in set
size = GFGUTIL.Util3(color);
if (size < min)
min = size;
// If the number of elements in set
// are more or equal
if (size <= y) {
// Print and display the size
System.out.println(
"Independent set of size " + (n - size)
+ "found");
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (color.get(j) == 0)
System.out.print(j + 1 + " ");
System.out.println();
set_found.add(color);
// Set flag to 1
found = 1;
// Hault the further execution of Program
break;
}
// If sufficient nodes are not found then
// we call util2 function
for (int j = 0; j < x; ++j)
GFGUTIL.Util2(adjacency_list, color, j);
// Getting the posssible size from util2
size = GFGUTIL.Util3(color);
if (size < min)
min = size;
// Printing what's found of which size and
// contents
System.out.println("Independent set of size "
+ (n - size) + "found");
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (color.get(j) == 0)
System.out.print(j + 1 + " ");
System.out.println();
set_found.add(color);
// If found then set the falg to 1 and hault
if (size <= y) {
found = 1;
break;
}
}
int r = set_found.size();
// Now searching pairwise and
// repeating same procedure as above discussed
// But using the idea discussed above in the
// article.
for (int a = 0; a < r; ++a) {
if (found == 1)
break;
for (int b = a + 1; b < r; ++b) {
if (found == 1)
break;
Vector color
= new Vector(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
color.add(1);
for (int c = 0; c < n; ++c)
if (set_found.get(a).get(c) == 0
&& set_found.get(b).get(c) == 0)
color.set(c, 0);
GFGUTIL.Util(adjacency_list, color);
size = GFGUTIL.Util3(color);
if (size < min)
min = size;
if (size <= y) {
System.out.println(
"Independent set of size"
+ (n - size));
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (color.get(j) == 0)
System.out.print(j + 1 + " ");
System.out.println();
found = 1;
break;
}
for (int j = 0; j < y; ++j)
GFGUTIL.Util2(adjacency_list, color, j);
size = GFGUTIL.Util3(color);
if (size < min)
min = size;
System.out.println(
"Independent set of size " + (n - size)
+ "found");
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (color.get(j) == 0)
System.out.print(j + 1 + " ");
System.out.println();
if (size <= y) {
found = 1;
break;
}
}
}
// If it is found
if (found == 1)
// Display command
System.out.println(
"Found set of " + (n - size)
+ " size whose elements are displayed above as a clique for the input graph");
// Not found
else
// Display command
System.out.println(
"Found set of " + (n - size)
+ " size whose elements are displayed above as a clique for the input graph");
}
} The number of vertices in the graph is taken as 5
The maximal independent set's size to be find is 4
Searching for the set
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Found set of 4 size whose elements are displayed above as a clique for the input graph输出说明:
正如我们所看到的,输出告诉我们所取的顶点数是 5,在找到大小为 4 的独立集合后,它返回一组顶点,它们一起形成了互补图中的独立集合,因为我们已经讨论过该独立的互补集合是原始图中的派系,因此这些集合是原始图中的派系。
Note: If we will mention the full size of graph (i.e. 5 in above eg), Then the output is shown below:
The number of vertices in the graph is taken as 5
The maximal independent set's size to be find is 5
Searching for the set
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Independent set of size 4found
1 2 3 4
Found set of 4 size whose elements are displayed above as a clique for the input graph输出说明:
为了找到最大集团集,只需提及图形的原始大小(即此处为 5)。如果找到任何此类大小的独立集合,则将其返回到输出,否则返回最接近的最大值。因此,我们总能找到具有这个想法的最大集团图集。因此,我们可以看到上述想法有效,并且我们能够找到给定图的最大团。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。