先决条件–图、生成树、不相交集(联合 – 查找)。
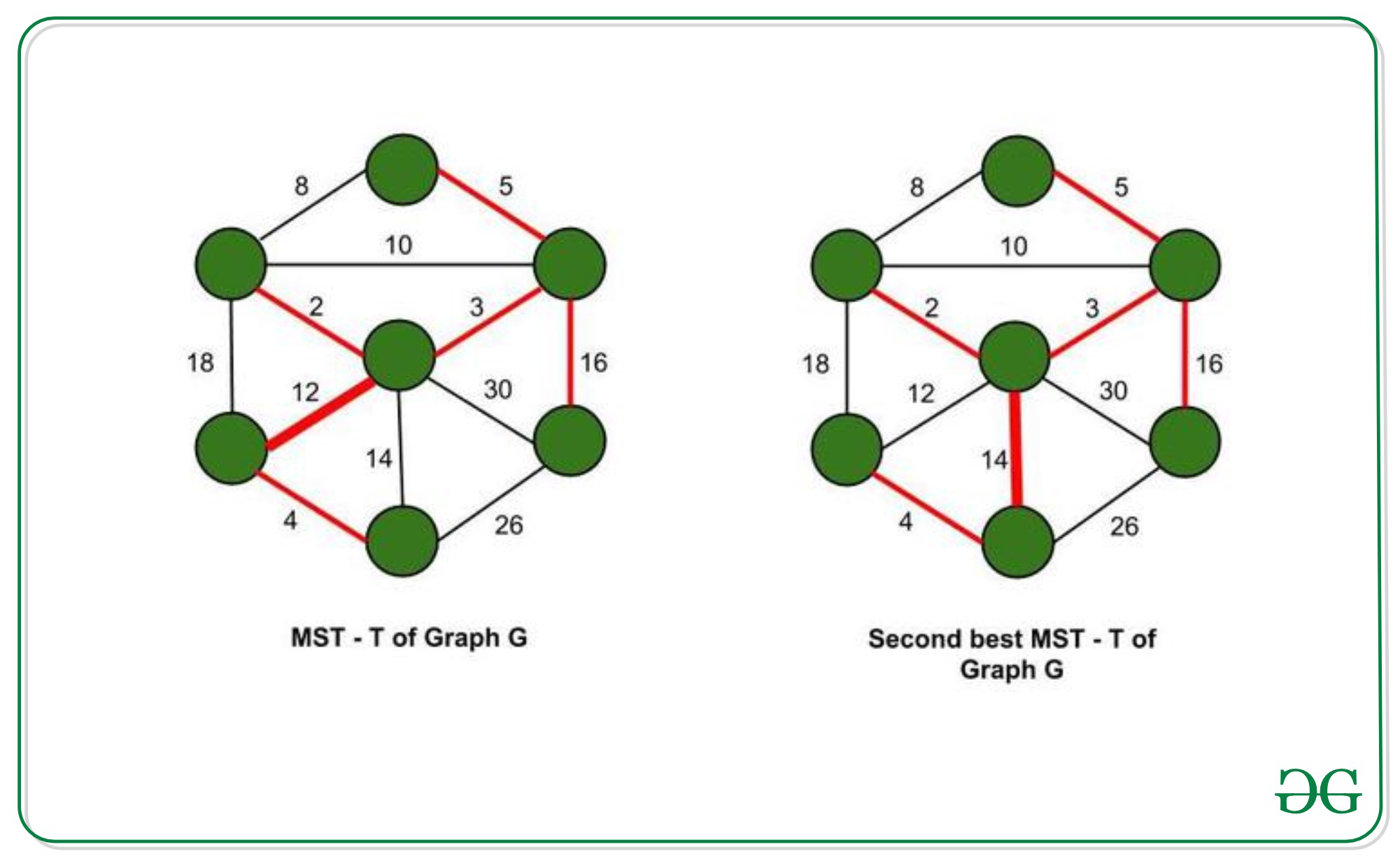
A minimum spanning tree (MST) T, for a given graph G, spans over all vertices of a given graph and has minimum weight sum of all edges, out of all the possible spanning trees.
Second best MST, T’, is a spanning tree with the second minimum weight sum of all edges, out of all spanning trees of graph G.
T 和 T’ 仅在一个边替换上有所不同。因此,我们应该找到一条不在 T 中的边 e new并将其替换为 T 中的一条边(比如 e old ),使得 T’ = T union {e new } – {e old } 是一棵生成树和权重差异of (e new – e old ) 是最小值(e new , e old是图 G 中的边)。
使用克鲁斯卡尔算法——
- 使用 Kruskal 算法找到图 G 的 MST T。从中删除一条边并用另一条边替换以获得 T’。
- 在 O(ElogE) 时间(E-no.of 边)中对边进行排序,并在 O(E) 时间内使用 Kruskal 算法找到 MST(MST 中的边数 = V-1,其中 V = 图中的顶点数G)。
- 对于 MST 中的每条边,暂时将其从边列表中排除(这样我们就无法选择它)。
- 然后,尝试使用剩余的边在 O(E) 中找到 MST。 (无需再次排序)
- 对 MST 中的所有边重复上述操作,并取最好的一条。 (具有第二个最小权重总和)。因此,我们获得了 T’——第二好的 MST。
- 总时间复杂度 – O(ElogE + E +VE) = O(VE)
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// second best MST
#include
using namespace std;
// used to implement union-find algorithm
int parent[100005];
// to keep track of edges in MST
vector present;
// to keep track of number of edges
// in spanning trees other than the MST
int edg;
// a structure to represent a
// weighted edge in graph
struct edge {
int src, dest, weight;
} edges[100005];
// array edges is of type edge.
// Compare two edges according
// to their weights.
// Used in sort() for sorting
// an array of edges
bool cmp(edge x, edge y)
{
return x.weight < y.weight;
}
// initialising the array -
// each vertex is its own parent
// initially
void initialise(int n)
{
// 1-indexed
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Implementing the union-find algorithm
int find(int x)
{
if (parent[x] == x)
return x;
return parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
// Function to find the union
// for the Minimum spanning Tree
int union1(int i, int sum)
{
int x, y;
x = find(edges[i].src);
y = find(edges[i].dest);
if (x != y) {
// parent of x = y (LCA) -
// both are edge connected
parent[x] = y;
// keeping track of edges in MST
present.push_back(i);
// finding sum of weights
// of edges in MST
sum += edges[i].weight;
}
return sum;
}
// Function to find the second
// best minimum spanning Tree
int union2(int i, int sum)
{
int x, y;
x = find(edges[i].src);
y = find(edges[i].dest);
if (x != y) {
// parent of x = y (LCA) -
// both are edge connected
parent[x] = y;
// sum of weights of edges
// in spanning tree
sum += edges[i].weight;
edg++;
}
return sum;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// V-> Number of vertices,
// E-> Number of edges
int V, E;
V = 5;
E = 8;
// initialising the array to
// be used for union-find
initialise(V);
// src, dest and weights can
// also be taken from user as
// input the following vectors
// represent - source[0],
// destination[0] are connected
// by an edge with
// weight[0]
vector source = { 1, 3, 2, 3,
2, 5, 1, 3 };
vector destination = { 3, 4, 4,
2, 5, 4, 2, 5 };
vector weights = { 75, 51, 19,
95, 42, 31, 9, 66 };
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
edges[i].src = source[i];
edges[i].dest = destination[i];
edges[i].weight = weights[i];
}
// sorting the array of edges
// based on edge weights
sort(edges, edges + E, cmp);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
sum = union1(i, sum);
}
// printing the cost of MST
cout << "MST: " << sum << "\n";
// initialising cost of second best MST
int sec_best_mst = INT_MAX;
// setting the sum to zero again.
sum = 0;
int j;
for (j = 0; j < present.size(); j++) {
initialise(V);
edg = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
// excluding one edge of
// MST at a time
// and forming spanning tree
// with remaining
// edges
if (i == present[j])
continue;
sum = union2(i, sum);
}
// checking if number of edges = V-1 or not
// since number of edges in a spanning tree of
// graph with V vertices is (V-1)
if (edg != V - 1) {
sum = 0;
continue;
}
// storing the minimum sum
// in sec_best_mst
if (sec_best_mst > sum)
sec_best_mst = sum;
sum = 0;
}
// printing the cost of second best MST
cout << "Second Best MST: "
<< sec_best_mst << "\n";
return 0;
} 输出
MST: 110
Second Best MST: 121
时间复杂度 – O(VE) 其中 V – 输入图中的顶点数,E – 输入图中的边数。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。