给定一个由 N 个顶点和一个数组Edges[][]组成的有向加权图,每行代表由一条边和该边的权重连接的两个顶点,任务是从一个给定源顶点src到给定目标顶点dst ,最多由K 个中间顶点组成。如果不存在这样的路径,则打印-1 。
例子:
Input: N = 3, Edges[][] = {{0, 1, 100}, {1, 2, 100}, {0, 2, 500}}, src = 0, dst = 2, K = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
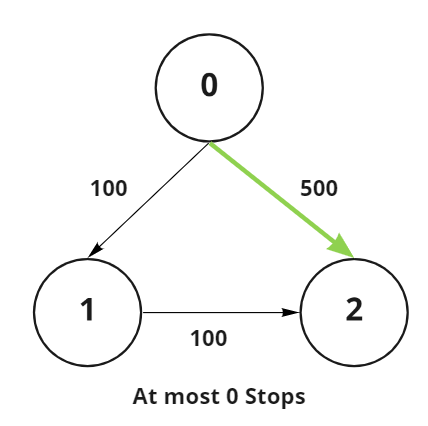
Path 0 → 2: The path with maximum weight and at most 0 intermediate nodes is of weight 500.
Input: N = 3, Edges[][] = {{0, 1, 100}, {1, 2, 100}, {0, 2, 500}}, src = 0, dst = 2, K = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
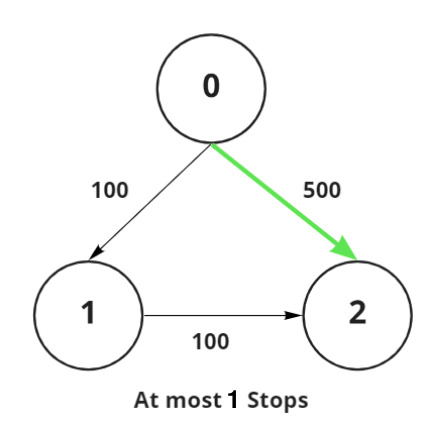
Path 0 → 2: The path with maximum weight and at most 1 intermediate node is of weight 500.
方法:给定的问题可以通过使用 BFS(广度优先搜索)遍历来解决。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化变量,比如ans ,以存储源节点和目标节点之间的最大距离,最多有 K 个中间节点。
- 使用边初始化图的邻接表。
- 初始化一个空队列并将源顶点推入其中。初始化一个变量,比如lvl ,以存储 src和dst之间存在的节点数。
- 当队列不为空且lvl小于K + 2 时,执行以下步骤:
- 将队列的大小存储在一个变量中,比如S 。
- 迭代范围[1, S]并执行以下步骤:
- 弹出队列的前端元素并将其存储在一个变量中,比如T 。
- 如果T是dst顶点,则将ans的值更新为ans和当前距离T.second 的最大值。
- 遍历当前弹出节点的所有邻居,并检查其邻居的距离是否大于当前距离。如果发现为真,则将其推入队列并更新其距离。
- 将 lvl的值增加1 。
- 完成上述步骤后,打印ans的值作为结果的最大距离。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the longest distance
// from source to destination with at
// most K intermediate nodes
int findShortestPath(
int n, vector >& edges,
int src, int dst, int K)
{
// Initialize the adjacency list
vector > > adjlist(
n, vector >());
// Initialize a queue to perform BFS
queue > q;
unordered_map mp;
// Store the maximum distance of
// every node from source vertex
int ans = INT_MIN;
// Initialize adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
auto edge = edges[i];
adjlist[edge[0]].push_back(
make_pair(edge[1], edge[2]));
}
// Push the first element into queue
q.push({ src, 0 });
int level = 0;
// Iterate until the queue becomes empty
// and the number of nodes between src
// and dst vertex is at most to K
while (!q.empty() && level < K + 2) {
// Current size of the queue
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
// Extract the front
// element of the queue
auto pr = q.front();
// Pop the front element
// of the queue
q.pop();
// If the dst vertex is reached
if (pr.first == dst)
ans = max(ans, pr.second);
// Traverse the adjacent nodes
for (auto pr2 : adjlist[pr.first]) {
// If the distance is greater
// than the current distance
if (mp.find(pr2.first)
== mp.end()
|| mp[pr2.first]
> pr.second
+ pr2.second) {
// Push it into the queue
q.push({ pr2.first,
pr.second
+ pr2.second });
mp[pr2.first] = pr.second
+ pr2.second;
}
}
}
// Increment the level by 1
level++;
}
// Finally, return the maximum distance
return ans != INT_MIN ? ans : -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 3, src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1;
vector > edges
= { { 0, 1, 100 },
{ 1, 2, 100 },
{ 0, 2, 500 } };
cout << findShortestPath(n, edges,
src, dst, k);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
from collections import deque
# Function to find the longest distance
# from source to destination with at
# most K intermediate nodes
def findShortestPath(n, edges, src, dst, K):
# Initialize the adjacency list
adjlist = [[] for i in range(n)]
# Initialize a queue to perform BFS
q = deque()
mp = {}
# Store the maximum distance of
# every node from source vertex
ans = -10**9
# Initialize adjacency list
for i in range(len(edges)):
edge = edges[i]
adjlist[edge[0]].append([edge[1],
edge[2]])
# Push the first element into queue
q.append([src, 0])
level = 0
# Iterate until the queue becomes empty
# and the number of nodes between src
# and dst vertex is at most to K
while (len(q) > 0 and level < K + 2):
# Current size of the queue
sz = len(q)
for i in range(sz):
# Extract the front
# element of the queue
pr = q.popleft()
# Pop the front element
# of the queue
# q.pop()
# If the dst vertex is reached
if (pr[0] == dst):
ans = max(ans, pr[1])
# Traverse the adjacent nodes
for pr2 in adjlist[pr[0]]:
# If the distance is greater
# than the current distance
if ((pr2[0] not in mp) or
mp[pr2[0]] > pr[1] + pr2[1]):
# Push it into the queue
q.append([pr2[0], pr[1] + pr2[1]])
mp[pr2[0]] = pr[1] + pr2[1]
# Increment the level by 1
level += 1
# Finally, return the maximum distance
return ans if ans != -10**9 else -1
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n, src, dst, k = 3, 0, 2, 1
edges= [ [ 0, 1, 100 ],
[ 1, 2, 100 ],
[ 0, 2, 500 ] ]
print(findShortestPath(n, edges,src, dst, k))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29输出:
500时间复杂度: O(N + E)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。