先决条件:图形及其表示
在本文中,在给定的邻接表表示中讨论了添加和删除边。
向量已用于使用邻接表表示来实现图。它用于存储所有顶点的邻接表。顶点编号用作此向量中的索引。
例子:
Below is a graph and its adjacency list representation:
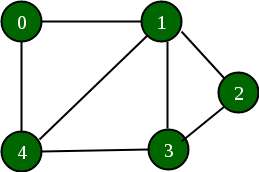

If the edge between 1 and 4 has to be removed, then the above graph and the adjacency list transforms to:

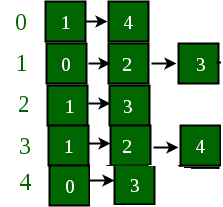
方法:想法是将图表示为向量数组,使得每个向量都表示顶点的邻接表。
- 添加边:添加边是通过在彼此列表中插入由该边连接的两个顶点来完成的。例如,如果必须添加(u, v)之间的边,则u存储在v 的向量列表中,而v存储在u 的向量列表中。 (推回)
- 删除一条边:要删除(u, v)之间的边,会遍历u 的邻接表,直到找到v并将其从中删除。对v .(erase) 执行相同的操作
下面是该方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function to add an edge in an
// undirected graph.
void addEdge(vector adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
// A utility function to delete an edge in an
// undirected graph.
void delEdge(vector adj[], int u, int v)
{
// Traversing through the first vector list
// and removing the second element from it
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++) {
if (adj[u][i] == v) {
adj[u].erase(adj[u].begin() + i);
break;
}
}
// Traversing through the second vector list
// and removing the first element from it
for (int i = 0; i < adj[v].size(); i++) {
if (adj[v][i] == u) {
adj[v].erase(adj[v].begin() + i);
break;
}
}
}
// A utility function to print the adjacency list
// representation of graph
void printGraph(vector adj[], int V)
{
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
cout << "vertex " << v << " ";
for (auto x : adj[v])
cout << "-> " << x;
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int V = 5;
vector adj[V];
// Adding edge as shown in the example figure
addEdge(adj, 0, 1);
addEdge(adj, 0, 4);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
// Printing adjacency matrix
printGraph(adj, V);
// Deleting edge (1, 4)
// as shown in the example figure
delEdge(adj, 1, 4);
// Printing adjacency matrix
printGraph(adj, V);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A utility function to add an edge in an
// undirected graph.
static void addEdge(Vector adj[],
int u, int v)
{
adj[u].add(v);
adj[v].add(u);
}
// A utility function to delete an edge in an
// undirected graph.
static void delEdge(Vector adj[],
int u, int v)
{
// Traversing through the first vector list
// and removing the second element from it
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].size(); i++)
{
if (adj[u].get(i) == v)
{
adj[u].remove(i);
break;
}
}
// Traversing through the second vector list
// and removing the first element from it
for (int i = 0; i < adj[v].size(); i++)
{
if (adj[v].get(i) == u)
{
adj[v].remove(i);
break;
}
}
}
// A utility function to print the adjacency list
// representation of graph
static void printGraph(Vector adj[], int V)
{
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
System.out.print("vertex " + v+ " ");
for (Integer x : adj[v])
System.out.print("-> " + x);
System.out.printf("\n");
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int V = 5;
Vector []adj = new Vector[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
// Adding edge as shown in the example figure
addEdge(adj, 0, 1);
addEdge(adj, 0, 4);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
// Printing adjacency matrix
printGraph(adj, V);
// Deleting edge (1, 4)
// as shown in the example figure
delEdge(adj, 1, 4);
// Printing adjacency matrix
printGraph(adj, V);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
# A utility function to add an edge in an
# undirected graph.
def addEdge(adj, u, v):
adj[u].append(v);
adj[v].append(u);
# A utility function to delete an edge in an
# undirected graph.
def delEdge(adj, u, v):
# Traversing through the first vector list
# and removing the second element from it
for i in range(len(adj[u])):
if (adj[u][i] == v):
adj[u].pop(i);
break;
# Traversing through the second vector list
# and removing the first element from it
for i in range(len(adj[v])):
if (adj[v][i] == u):
adj[v].pop(i);
break;
# A utility function to pr the adjacency list
# representation of graph
def prGraph(adj, V):
for v in range(V):
print("vertex " + str(v), end = ' ')
for x in adj[v]:
print("-> " + str(x), end = '')
print()
print()
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
V = 5;
adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
# Adding edge as shown in the example figure
addEdge(adj, 0, 1);
addEdge(adj, 0, 4);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
# Pring adjacency matrix
prGraph(adj, V);
# Deleting edge (1, 4)
# as shown in the example figure
delEdge(adj, 1, 4);
# Pring adjacency matrix
prGraph(adj, V);
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// A utility function to add an edge in an
// undirected graph.
static void addEdge(List []adj,
int u, int v)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
// A utility function to delete an edge in an
// undirected graph.
static void delEdge(List []adj,
int u, int v)
{
// Traversing through the first vector list
// and removing the second element from it
for (int i = 0; i < adj[u].Count; i++)
{
if (adj[u][i] == v)
{
adj[u].RemoveAt(i);
break;
}
}
// Traversing through the second vector list
// and removing the first element from it
for (int i = 0; i < adj[v].Count; i++)
{
if (adj[v][i] == u)
{
adj[v].RemoveAt(i);
break;
}
}
}
// A utility function to print the adjacency list
// representation of graph
static void printGraph(List []adj, int V)
{
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
Console.Write("vertex " + v + " ");
foreach (int x in adj[v])
Console.Write("-> " + x);
Console.Write("\n");
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int V = 5;
List []adj = new List[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
// Adding edge as shown in the example figure
addEdge(adj, 0, 1);
addEdge(adj, 0, 4);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
// Printing adjacency matrix
printGraph(adj, V);
// Deleting edge (1, 4)
// as shown in the example figure
delEdge(adj, 1, 4);
// Printing adjacency matrix
printGraph(adj, V);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
vertex 0 -> 1-> 4
vertex 1 -> 0-> 2-> 3-> 4
vertex 2 -> 1-> 3
vertex 3 -> 1-> 2-> 4
vertex 4 -> 0-> 1-> 3
vertex 0 -> 1-> 4
vertex 1 -> 0-> 2-> 3
vertex 2 -> 1-> 3
vertex 3 -> 1-> 2-> 4
vertex 4 -> 0-> 3如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。