给定一个图和图中的一个源顶点,找出从源到给定图中所有顶点的最短路径。
Dijkstra 的算法与 Prim 的最小生成树算法非常相似。与 Prim 的 MST 一样,我们以给定的源作为根生成SPT(最短路径树) 。我们维护两组,一组包含最短路径树中包含的顶点,另一组包含最短路径树中尚未包含的顶点。在算法的每一步,我们都会找到一个顶点,它在另一个集合(尚未包含的集合)中,并且与源的距离最小。
以下是 Dijkstra 算法中使用的详细步骤,用于查找给定图中从单个源顶点到所有其他顶点的最短路径。
算法
1)创建一个集合sptSet (最短路径树集),它跟踪包含在最短路径树中的顶点,即计算并确定其与源的最小距离。最初,这个集合是空的。
2)为输入图中的所有顶点分配一个距离值。将所有距离值初始化为 INFINITE。将源顶点的距离值指定为 0,以便它首先被拾取。
3)虽然sptSet不包括所有顶点
…… a)选择一个在sptSet 中不存在且具有最小距离值的顶点 u。
…… b)包括 u 到sptSet 。
…… c)更新 u 的所有相邻顶点的距离值。要更新距离值,请遍历所有相邻顶点。对于每一个相邻的顶点v,如果u(距源)的距离值和边uv的权重之和小于v的距离值,则更新v的距离值。
让我们通过下面的例子来理解:
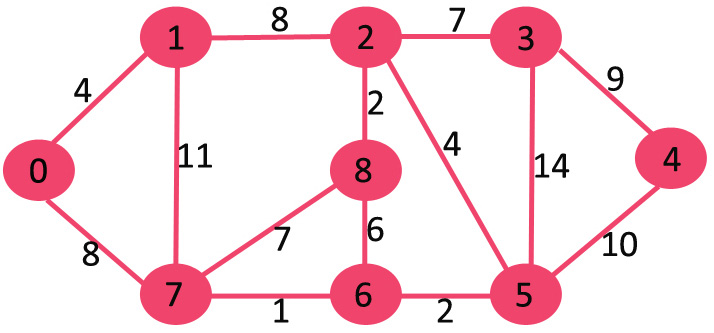
集合sptSet最初是空的,分配给顶点的距离是 {0, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF},其中 INF 表示无限。现在选择具有最小距离值的顶点。顶点 0 被拾取,将其包含在sptSet 中。所以sptSet变为 {0}。将 0 包含到sptSet 后,更新其相邻顶点的距离值。 0 的相邻顶点为 1 和 7。1 和 7 的距离值更新为 4 和 8。以下子图显示了顶点及其距离值,仅显示了具有有限距离值的顶点。 SPT 中包含的顶点以绿色显示。
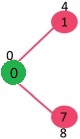
选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 1 被拾取并添加到 sptSet。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1}。更新相邻顶点的距离值为1,顶点2的距离值变为12。
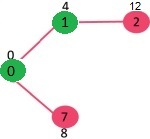
选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 7 被选取。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7}。更新 7 的相邻顶点的距离值。顶点 6 和 8 的距离值变为有限(分别为 15 和 9)。
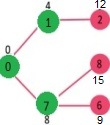
选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在 SPT 中(不在 sptSET 中)的顶点。顶点 6 被选取。所以 sptSet 现在变成了 {0, 1, 7, 6}。更新6的相邻顶点的距离值。更新顶点5和8的距离值。
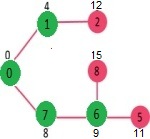
我们重复上述步骤,直到sptSet包含给定图的所有顶点。最后,我们得到以下最短路径树(SPT)。
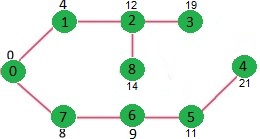
如何实现上述算法?
我们使用布尔数组 sptSet[] 来表示 SPT 中包含的顶点集。如果值 sptSet[v] 为真,则顶点 v 包含在 SPT 中,否则不包含。数组 dist[] 用于存储所有顶点的最短距离值。
C++
// A C++ program for Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm.
// The program is for adjacency matrix representation of the graph
#include
using namespace std;
#include
// Number of vertices in the graph
#define V 9
// A utility function to find the vertex with minimum distance value, from
// the set of vertices not yet included in shortest path tree
int minDistance(int dist[], bool sptSet[])
{
// Initialize min value
int min = INT_MAX, min_index;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (sptSet[v] == false && dist[v] <= min)
min = dist[v], min_index = v;
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print the constructed distance array
void printSolution(int dist[])
{
cout <<"Vertex \t Distance from Source" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
cout << i << " \t\t"< C
// A C++ program for Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm.
// The program is for adjacency matrix representation of the graph
#include
#include
#include
// Number of vertices in the graph
#define V 9
// A utility function to find the vertex with minimum distance value, from
// the set of vertices not yet included in shortest path tree
int minDistance(int dist[], bool sptSet[])
{
// Initialize min value
int min = INT_MAX, min_index;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (sptSet[v] == false && dist[v] <= min)
min = dist[v], min_index = v;
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print the constructed distance array
void printSolution(int dist[])
{
printf("Vertex \t\t Distance from Source\n");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}
// Function that implements Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm
// for a graph represented using adjacency matrix representation
void dijkstra(int graph[V][V], int src)
{
int dist[V]; // The output array. dist[i] will hold the shortest
// distance from src to i
bool sptSet[V]; // sptSet[i] will be true if vertex i is included in shortest
// path tree or shortest distance from src to i is finalized
// Initialize all distances as INFINITE and stpSet[] as false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INT_MAX, sptSet[i] = false;
// Distance of source vertex from itself is always 0
dist[src] = 0;
// Find shortest path for all vertices
for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {
// Pick the minimum distance vertex from the set of vertices not
// yet processed. u is always equal to src in the first iteration.
int u = minDistance(dist, sptSet);
// Mark the picked vertex as processed
sptSet[u] = true;
// Update dist value of the adjacent vertices of the picked vertex.
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
// Update dist[v] only if is not in sptSet, there is an edge from
// u to v, and total weight of path from src to v through u is
// smaller than current value of dist[v]
if (!sptSet[v] && graph[u][v] && dist[u] != INT_MAX
&& dist[u] + graph[u][v] < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + graph[u][v];
}
// print the constructed distance array
printSolution(dist);
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Let us create the example graph discussed above */
int graph[V][V] = { { 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0 },
{ 4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0 },
{ 0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6 },
{ 8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0 } };
dijkstra(graph, 0);
return 0;
} Java
// A Java program for Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm.
// The program is for adjacency matrix representation of the graph
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class ShortestPath {
// A utility function to find the vertex with minimum distance value,
// from the set of vertices not yet included in shortest path tree
static final int V = 9;
int minDistance(int dist[], Boolean sptSet[])
{
// Initialize min value
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, min_index = -1;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (sptSet[v] == false && dist[v] <= min) {
min = dist[v];
min_index = v;
}
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print the constructed distance array
void printSolution(int dist[])
{
System.out.println("Vertex \t\t Distance from Source");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
System.out.println(i + " \t\t " + dist[i]);
}
// Function that implements Dijkstra's single source shortest path
// algorithm for a graph represented using adjacency matrix
// representation
void dijkstra(int graph[][], int src)
{
int dist[] = new int[V]; // The output array. dist[i] will hold
// the shortest distance from src to i
// sptSet[i] will true if vertex i is included in shortest
// path tree or shortest distance from src to i is finalized
Boolean sptSet[] = new Boolean[V];
// Initialize all distances as INFINITE and stpSet[] as false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
sptSet[i] = false;
}
// Distance of source vertex from itself is always 0
dist[src] = 0;
// Find shortest path for all vertices
for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {
// Pick the minimum distance vertex from the set of vertices
// not yet processed. u is always equal to src in first
// iteration.
int u = minDistance(dist, sptSet);
// Mark the picked vertex as processed
sptSet[u] = true;
// Update dist value of the adjacent vertices of the
// picked vertex.
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
// Update dist[v] only if is not in sptSet, there is an
// edge from u to v, and total weight of path from src to
// v through u is smaller than current value of dist[v]
if (!sptSet[v] && graph[u][v] != 0 && dist[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + graph[u][v] < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + graph[u][v];
}
// print the constructed distance array
printSolution(dist);
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the example graph discussed above */
int graph[][] = new int[][] { { 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0 },
{ 4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0 },
{ 0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6 },
{ 8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0 } };
ShortestPath t = new ShortestPath();
t.dijkstra(graph, 0);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash HasijaPython
# Python program for Dijkstra's single
# source shortest path algorithm. The program is
# for adjacency matrix representation of the graph
# Library for INT_MAX
import sys
class Graph():
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices
self.graph = [[0 for column in range(vertices)]
for row in range(vertices)]
def printSolution(self, dist):
print "Vertex \tDistance from Source"
for node in range(self.V):
print node, "\t", dist[node]
# A utility function to find the vertex with
# minimum distance value, from the set of vertices
# not yet included in shortest path tree
def minDistance(self, dist, sptSet):
# Initialize minimum distance for next node
min = sys.maxint
# Search not nearest vertex not in the
# shortest path tree
for v in range(self.V):
if dist[v] < min and sptSet[v] == False:
min = dist[v]
min_index = v
return min_index
# Function that implements Dijkstra's single source
# shortest path algorithm for a graph represented
# using adjacency matrix representation
def dijkstra(self, src):
dist = [sys.maxint] * self.V
dist[src] = 0
sptSet = [False] * self.V
for cout in range(self.V):
# Pick the minimum distance vertex from
# the set of vertices not yet processed.
# u is always equal to src in first iteration
u = self.minDistance(dist, sptSet)
# Put the minimum distance vertex in the
# shortest path tree
sptSet[u] = True
# Update dist value of the adjacent vertices
# of the picked vertex only if the current
# distance is greater than new distance and
# the vertex in not in the shortest path tree
for v in range(self.V):
if self.graph[u][v] > 0 and sptSet[v] == False and \
dist[v] > dist[u] + self.graph[u][v]:
dist[v] = dist[u] + self.graph[u][v]
self.printSolution(dist)
# Driver program
g = Graph(9)
g.graph = [[0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0],
[4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0],
[0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6],
[8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7],
[0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0]
];
g.dijkstra(0);
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu MehtaC#
// A C# program for Dijkstra's single
// source shortest path algorithm.
// The program is for adjacency matrix
// representation of the graph
using System;
class GFG {
// A utility function to find the
// vertex with minimum distance
// value, from the set of vertices
// not yet included in shortest
// path tree
static int V = 9;
int minDistance(int[] dist,
bool[] sptSet)
{
// Initialize min value
int min = int.MaxValue, min_index = -1;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (sptSet[v] == false && dist[v] <= min) {
min = dist[v];
min_index = v;
}
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print
// the constructed distance array
void printSolution(int[] dist)
{
Console.Write("Vertex \t\t Distance "
+ "from Source\n");
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
Console.Write(i + " \t\t " + dist[i] + "\n");
}
// Function that implements Dijkstra's
// single source shortest path algorithm
// for a graph represented using adjacency
// matrix representation
void dijkstra(int[, ] graph, int src)
{
int[] dist = new int[V]; // The output array. dist[i]
// will hold the shortest
// distance from src to i
// sptSet[i] will true if vertex
// i is included in shortest path
// tree or shortest distance from
// src to i is finalized
bool[] sptSet = new bool[V];
// Initialize all distances as
// INFINITE and stpSet[] as false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
dist[i] = int.MaxValue;
sptSet[i] = false;
}
// Distance of source vertex
// from itself is always 0
dist[src] = 0;
// Find shortest path for all vertices
for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {
// Pick the minimum distance vertex
// from the set of vertices not yet
// processed. u is always equal to
// src in first iteration.
int u = minDistance(dist, sptSet);
// Mark the picked vertex as processed
sptSet[u] = true;
// Update dist value of the adjacent
// vertices of the picked vertex.
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
// Update dist[v] only if is not in
// sptSet, there is an edge from u
// to v, and total weight of path
// from src to v through u is smaller
// than current value of dist[v]
if (!sptSet[v] && graph[u, v] != 0 && dist[u] != int.MaxValue && dist[u] + graph[u, v] < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + graph[u, v];
}
// print the constructed distance array
printSolution(dist);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
/* Let us create the example
graph discussed above */
int[, ] graph = new int[, ] { { 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0 },
{ 4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0 },
{ 0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6 },
{ 8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0 } };
GFG t = new GFG();
t.dijkstra(graph, 0);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ChitraNayalJavascript
输出:
Vertex Distance from Source
0 0
1 4
2 12
3 19
4 21
5 11
6 9
7 8
8 14笔记:
1)代码计算最短距离但不计算路径信息。我们可以创建一个父数组,在距离更新时更新父数组(如 prim 的实现),并使用它来显示从源到不同顶点的最短路径。
2)该代码用于无向图,同样的 Dijkstra函数也可用于有向图。
3)代码找到从源到所有顶点的最短距离。如果我们只对从源到单个目标的最短距离感兴趣,我们可以在选择的最小距离顶点等于目标时中断 for 循环(算法的步骤 3.a)。
4) 实现的时间复杂度为 O(V^2)。如果使用邻接表表示输入图,则可以在二叉堆的帮助下将其简化为 O(E log V)。请参见
Dijkstra’s Algorithm for Adjacency List Representation 了解更多细节。
5) Dijkstra 算法不适用于具有负权重循环的图。它可能会为具有负边的图提供正确的结果,但您必须允许一个顶点可以多次访问,并且该版本将失去其快速时间复杂度。对于具有负权重边和环的图,可以使用 Bellman-Ford 算法,我们很快将在单独的帖子中讨论它。
Dijkstra 的邻接表表示算法
在 Dijkstra 的最短路径算法中打印路径
Dijkstra 的最短路径算法使用 STL 中的集合
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。