给定一个由N 个正整数组成的数组weights[] ,其中weights[i]表示第i个节点的权重,任务是构造一个 N 叉树,使得没有两个直接连接的节点具有相同的权重。如果可以制作这样的树,请在边缘打印“是” 。否则,打印“否” 。
例子:
Input: weights[] = {1 2 1 2 5}
Output:
Yes
1 2
1 4
1 5
2 3
Explanation:
Index: 1 2 3 4 5
Weight : 1 2 1 2 5
The constructed Tree is shown in the following diagram:
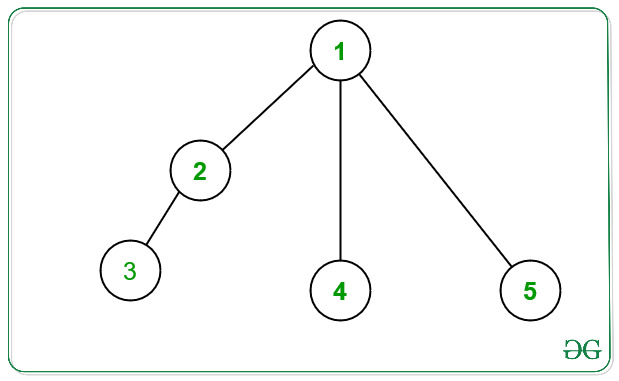
Input: weights[] = {1 1 1}
Output: No
Explanation: Since all weights are already same, no such tree can be constructed.
方法:解决这个问题的思路是首先检查是否所有节点都分配了相同的权重。如果发现为真,则无法构建所需的树。否则,可以构造这样的树。因此遍历数组weights[]并检查所有值是否相同。如果发现是真的,则打印“否” 。否则,打印“Yes”并使用以下步骤构建一棵树:
- 采取任何节点,并使其根节点。
- 现在,将权重不等于根的所有其他节点连接到根节点。现在剩下的节点是值等于根节点的节点。
- 选择根节点的任意子节点和所有其余节点连接到它们。因此,相同权重的节点之间不存在直接边。
- 要检查尚未包含哪些节点,请使用辅助数组visited[]跟踪访问过的节点。如果一个节点被访问,则将一个节点与其连接,但不要将被访问节点与另一个节点连接,因为将未访问节点与访问节点连接是可能的,但反之则不然。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
// Keep track of visited nodes
int visited[N];
// Function to construct a tree such
// that there are no two adjacent
// nodes with the same weight
void construct_tree(int weights[], int n)
{
int minimum = *min_element(weights, weights + n);
int maximum = *max_element(weights, weights + n);
// If minimum and maximum
// elements are equal, i.e.
// array contains one distinct element
if (minimum == maximum) {
// Tree cannot be constructed
cout << "No";
return;
}
// Otherwise
else {
// Tree can be constructed
cout << "Yes" << endl;
}
// Find the edges below
// Choose weights[0] as root
int root = weights[0];
// First Node is visited
visited[1] = 1;
// Traverse the array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// If current element has the
// same weight as root and if
// the node is visited, then
// do not make an edge
// Otherwise, make an edge
if (weights[i] != root
&& visited[i + 1] == 0) {
cout << 1 << " "
<< i + 1 << " "
<< endl;
// Mark this node as visited
visited[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
// Find a weight not same as the
// root & make edges with that node
int notroot = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (weights[i] != root) {
notroot = i + 1;
break;
}
}
// Join non-roots with remaining nodes
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Check if current node's weight
// is same as root node's weight
// and if it is not visited or not
if (weights[i] == root
&& visited[i + 1] == 0) {
cout << notroot << " "
<< i + 1 << endl;
visited[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int weights[] = { 1, 2, 1, 2, 5 };
int N = sizeof(weights) / sizeof(weights[0]);
// Function Call
construct_tree(weights, N);
} Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int N = 100000 + 5;
// Keep track of visited nodes
static int visited[] = new int[N];
// Function to construct a tree such
// that there are no two adjacent
// nodes with the same weight
static void construct_tree(int weights[], int n)
{
int minimum = Arrays.stream(weights).min().getAsInt();
int maximum = Arrays.stream(weights).max().getAsInt();
// If minimum and maximum
// elements are equal, i.e.
// array contains one distinct element
if (minimum == maximum)
{
// Tree cannot be constructed
System.out.println("No");
return;
}
// Otherwise
else
{
// Tree can be constructed
System.out.println("Yes");
}
// Find the edges below
// Choose weights[0] as root
int root = weights[0];
// First Node is visited
visited[1] = 1;
// Traverse the array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// If current element has the
// same weight as root and if
// the node is visited, then
// do not make an edge
// Otherwise, make an edge
if (weights[i] != root &&
visited[i + 1] == 0)
{
System.out.println(1 + " " +
(i + 1) + " ");
// Mark this node as visited
visited[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
// Find a weight not same as the
// root & make edges with that node
int notroot = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (weights[i] != root)
{
notroot = i + 1;
break;
}
}
// Join non-roots with remaining nodes
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Check if current node's weight
// is same as root node's weight
// and if it is not visited or not
if (weights[i] == root &&
visited[i + 1] == 0)
{
System.out.println(notroot + " " +
(i + 1));
visited[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int weights[] = { 1, 2, 1, 2, 5 };
int N = weights.length;
// Function Call
construct_tree(weights, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62Python3
# Python3 program to implement
# the above approach
N = 10**5 + 5
#Keep track of visited nodes
visited=[0]*N
#Function to construct a tree such
#that there are no two adjacent
#nodes with the same weight
def construct_tree(weights, n):
minimum = min(weights)
maximum = max(weights)
#If minimum and maximum
#elements are equal, i.e.
#array contains one distinct element
if (minimum == maximum):
#Tree cannot be constructed
print("No")
return
#Otherwise
else:
print("Yes")
#Find the edges below
#Choose weights[0] as root
root = weights[0]
#First Node is visited
visited[1] = 1
#Traverse the array
for i in range(n):
#If current element has the
#same weight as root and if
#the node is visited, then
#do not make an edge
#Otherwise, make an edge
if (weights[i] != root
and visited[i + 1] == 0):
print(1,i+1)
#Mark this node as visited
visited[i + 1] = 1
#Find a weight not same as the
#root & make edges with that node
notroot = 0
for i in range(n):
if (weights[i] != root):
notroot = i + 1
break
#Join non-roots with remaining nodes
for i in range(n):
#Check if current node's weight
#is same as root node's weight
#and if it is not visited or not
if (weights[i] == root
and visited[i + 1] == 0):
print(notroot,i + 1)
visited[i + 1] = 1
#Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
weights=[1, 2, 1, 2, 5]
N = len(weights)
#Function Call
construct_tree(weights, N)C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Linq;
class GFG{
static int N = 100000 + 5;
// Keep track of visited nodes
static int[] visited = new int[N];
// Function to construct a tree such
// that there are no two adjacent
// nodes with the same weight
static void construct_tree(int[] weights, int n)
{
int minimum = weights.Min();
int maximum = weights.Max();
// If minimum and maximum
// elements are equal, i.e.
// array contains one distinct element
if (minimum == maximum)
{
// Tree cannot be constructed
Console.WriteLine("No");
return;
}
// Otherwise
else
{
// Tree can be constructed
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
}
// Find the edges below
// Choose weights[0] as root
int root = weights[0];
// First Node is visited
visited[1] = 1;
// Traverse the array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// If current element has the
// same weight as root and if
// the node is visited, then
// do not make an edge
// Otherwise, make an edge
if (weights[i] != root &&
visited[i + 1] == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(1 + " " + (i + 1) + " ");
// Mark this node as visited
visited[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
// Find a weight not same as the
// root & make edges with that node
int notroot = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (weights[i] != root)
{
notroot = i + 1;
break;
}
}
// Join non-roots with remaining nodes
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Check if current node's weight
// is same as root node's weight
// and if it is not visited or not
if (weights[i] == root &&
visited[i + 1] == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(notroot + " " +
(i + 1));
visited[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] weights = { 1, 2, 1, 2, 5 };
int N = weights.Length;
// Function Call
construct_tree(weights, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.Javascript
输出:
Yes
1 2
1 4
1 5
2 3时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。