给定一个类型为{ X, Y }的二维数组edge[][]表示树中节点X和Y之间存在一条边,以及一个数组color[]表示第i个节点的颜色值,任务是找到树的根节点,使得同一路径上根节点的所有子节点具有相同的颜色值。如果存在多个解决方案,则打印其中任何一个。否则,打印-1 。
例子:
Input:
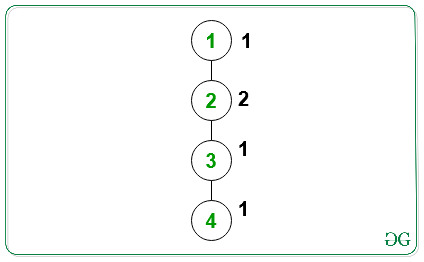
Output: 2
Explanation:

All the child nodes on the path from the root node(= 2) to the leaf node(= 1) have the same value of the color(= 1).
All the child nodes on the path from the root node(= 2) to the leaf node(= 4) have the same value of the color(= 1).
Therefore, the required output is 2.
Input:
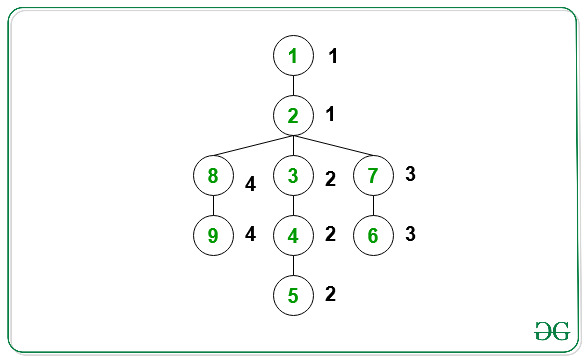
Output: 2
Explanation:
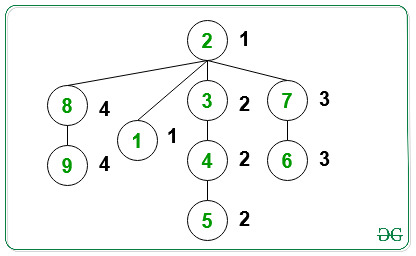
All the child nodes on the path from the root node(=2) to the leaf node(=9) have the same value of the color(= 4).
All the child nodes on the path from the root node(=2) to the leaf node(=1) have the same value of the color(= 1).
All the child nodes on the path from the root node(=2) to the leaf node(=5) have the same value of the color(= 2).
All the child nodes on the path from the root node(=2) to the leaf node(=6) have the same value of the color(= 3).
方法:这个想法是迭代树的所有可能节点。对于每个第i个节点,检查它是否满足根节点的条件或不使用 DFS。如果发现为真,则打印节点。否则,打印-1 。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个变量,比如root ,来存储满足条件的树的根节点。
- 迭代树的所有可能节点。将树的每个第i个节点视为根节点,并使用 DFS 检查从根节点到叶节点的路径上的所有子节点是否具有相同的颜色。如果发现为真,则打印节点。
- 否则,打印-1 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to perform dfs on the tree
bool dfs(int node, int c, vector adj[],
int color[], int visited[])
{
// Mark visited node as true
visited[node] = true;
// If color does not match with
// previous node on the same path
if (color[node] != c) {
return false;
}
// Check if current subtree
// has all same colored nodes
int f = 1;
// Traverse all unvisited neighbors
// node of the tree
for (int j = 0; j < adj[node].size(); j++) {
// Stores neighbors node
// of the tree
int neighbor = adj[node][j];
// If current node is not
// already visited
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
if (dfs(neighbor, c, adj,
color, visited)
== false) {
// Update f
f = 0;
break;
}
}
}
return f;
}
// Function to find the root node of
// the tree such that all child nodes
// on the same path have the same color
void findNode(int edges[][2],
int color[], int n)
{
// Store the adjacency list
vector adj[n + 1];
// Traverse all edges and form
// the adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int a = edges[i][0];
int b = edges[i][1];
adj[a].push_back(b);
adj[b].push_back(a);
}
// Store the root node such that all
// child nodes on the same path have
// the same color
int ans = -1;
// Iterate over all possible
// nodes of the tree
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Check if node i satisfies
// the condition of root node
int f = 1;
// Check if a node has been
// visited or not
int visited[n + 1] = { false };
// Mark visited[i] as true
visited[i] = true;
// Traverse all the neighbors
// of node i
for (int j = 0; j < adj[i].size(); j++) {
// Stores the current neighbor
int neighbor = adj[i][j];
// Perform DFS for current neighbor
if (dfs(neighbor, color[neighbor],
adj, color, visited)
== false) {
// Update f
f = 0;
break;
}
}
if (f == 1) {
ans = i;
break;
}
}
// Print the answer
cout << ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
int color[n + 1] = { -1, 1, 1, 2, 2,
2, 3, 3, 4, 4 };
int edges[][2] = { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 4, 5 },
{ 2, 7 }, { 7, 6 },
{ 2, 8 }, { 8, 9 } };
findNode(edges, color, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to perform dfs on the tree
static boolean dfs(int node, int c, Vector adj[],
int color[], boolean visited[])
{
// Mark visited node as true
visited[node] = true;
// If color does not match with
// previous node on the same path
if (color[node] != c)
{
return false;
}
// Check if current subtree
// has all same colored nodes
boolean f = true;
// Traverse all unvisited neighbors
// node of the tree
for (int j = 0; j < adj[node].size(); j++)
{
// Stores neighbors node
// of the tree
int neighbor = adj[node].get(j);
// If current node is not
// already visited
if (!visited[neighbor])
{
if (dfs(neighbor, c, adj,
color, visited) == false)
{
// Update f
f = false;
break;
}
}
}
return f;
}
// Function to find the root node of
// the tree such that all child nodes
// on the same path have the same color
static void findNode(int edges[][],
int color[], int n)
{
// Store the adjacency list
Vector []adj = new Vector[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
// Traverse all edges and form
// the adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int a = edges[i][0];
int b = edges[i][1];
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
// Store the root node such that all
// child nodes on the same path have
// the same color
int ans = -1;
// Iterate over all possible
// nodes of the tree
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Check if node i satisfies
// the condition of root node
int f = 1;
// Check if a node has been
// visited or not
boolean []visited = new boolean[n + 1];
// Mark visited[i] as true
visited[i] = true;
// Traverse all the neighbors
// of node i
for (int j = 0; j < adj[i].size(); j++)
{
// Stores the current neighbor
int neighbor = adj[i].get(j);
// Perform DFS for current neighbor
if (dfs(neighbor, color[neighbor],
adj, color, visited) == false)
{
// Update f
f = 0;
break;
}
}
if (f == 1)
{
ans = i;
break;
}
}
// Print the answer
System.out.print(ans);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
int color[] = { -1, 1, 1, 2, 2,
2, 3, 3, 4, 4 };
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 4, 5 },
{ 2, 7 }, { 7, 6 },
{ 2, 8 }, { 8, 9 } };
findNode(edges, color, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python program to implement
# the above approach
from typing import List
# Function to perform dfs on the tree
def dfs(node: int, c: int, adj: List[List[int]],
color: List[int],
visited: List[int]) -> bool:
# Mark visited node as true
visited[node] = True
# If color does not match with
# previous node on the same path
if (color[node] != c):
return False
# Check if current subtree
# has all same colored nodes
f = 1
# Traverse all unvisited neighbors
# node of the tree
for j in range(len(adj[node])):
# Stores neighbors node
# of the tree
neighbor = adj[node][j]
# If current node is not
# already visited
if (not visited[neighbor]):
if not dfs(neighbor, c, adj, color, visited):
# Update f
f = 0
break
return f
# Function to find the root node of
# the tree such that all child nodes
# on the same path have the same color
def findNode(edges: List[List[int]], color: List[int], n: int) -> None:
# Store the adjacency list
adj = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)]
# Traverse all edges and form
# the adjacency list
for i in range(n - 1):
a = edges[i][0]
b = edges[i][1]
adj[a].append(b)
adj[b].append(a)
# Store the root node such that all
# child nodes on the same path have
# the same color
ans = -1
# Iterate over all possible
# nodes of the tree
for i in range(1, n + 1):
# Check if node i satisfies
# the condition of root node
f = 1
# Check if a node has been
# visited or not
visited = [False for _ in range(n + 1)]
# Mark visited[i] as true
visited[i] = True
# Traverse all the neighbors
# of node i
for j in range(len(adj[i])):
# Stores the current neighbor
neighbor = adj[i][j]
# Perform DFS for current neighbor
if not dfs(neighbor, color[neighbor],
adj, color, visited):
# Update f
f = 0
break
if (f == 1):
ans = i
break
# Print the answer
print(ans)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 9
color = [-1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4]
edges = [[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4], [4, 5], [2, 7], [7, 6], [2, 8], [8, 9]]
findNode(edges, color, n)
# This code is contributed by sanjeev2552C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Function to perform dfs on the tree
static bool dfs(int node, int c, List []adj,
int []color, bool []visited)
{
// Mark visited node as true
visited[node] = true;
// If color does not match with
// previous node on the same path
if (color[node] != c)
{
return false;
}
// Check if current subtree
// has all same colored nodes
bool f = true;
// Traverse all unvisited neighbors
// node of the tree
for (int j = 0; j < adj[node].Count; j++)
{
// Stores neighbors node
// of the tree
int neighbor = adj[node][j];
// If current node is not
// already visited
if (!visited[neighbor])
{
if (dfs(neighbor, c, adj,
color, visited) == false)
{
// Update f
f = false;
break;
}
}
}
return f;
}
// Function to find the root node of
// the tree such that all child nodes
// on the same path have the same color
static void findNode(int [,]edges,
int []color, int n)
{
// Store the adjacency list
List []adj = new List[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
// Traverse all edges and form
// the adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int a = edges[i, 0];
int b = edges[i, 1];
adj[a].Add(b);
adj[b].Add(a);
}
// Store the root node such that all
// child nodes on the same path have
// the same color
int ans = -1;
// Iterate over all possible
// nodes of the tree
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Check if node i satisfies
// the condition of root node
int f = 1;
// Check if a node has been
// visited or not
bool []visited = new bool[n + 1];
// Mark visited[i] as true
visited[i] = true;
// Traverse all the neighbors
// of node i
for (int j = 0; j < adj[i].Count; j++)
{
// Stores the current neighbor
int neighbor = adj[i][j];
// Perform DFS for current neighbor
if (dfs(neighbor, color[neighbor],
adj, color, visited) == false)
{
// Update f
f = 0;
break;
}
}
if (f == 1)
{
ans = i;
break;
}
}
// Print the answer
Console.Write(ans);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
int []color = { -1, 1, 1, 2, 2,
2, 3, 3, 4, 4 };
int [,]edges = { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 4, 5 },
{ 2, 7 }, { 7, 6 },
{ 2, 8 }, { 8, 9 } };
findNode(edges, color, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
2时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。