散列是一种使用较少的键比较并在最坏情况下以 O(n) 时间和平均情况下 O(1) 时间搜索元素的技术。
- 任务是实现电话簿的所有功能:
- 创建记录
- 显示记录
- 删除记录
- 搜索记录
- 更新记录
以下数据将从客户端获取:
ID, Name, Telephone number方法:
我们正在创建一个哈希表,并插入记录。对于删除、搜索或更新实体,会询问客户端 ID,并根据相等运算符显示或处理详细信息。如果未找到该记录,则会显示相应的消息。
碰撞是散列技术中的主要问题。在开放寻址(封闭散列)中,所有冲突都在主要区域(即包含所有家庭地址的区域)中解决。
当发生冲突时,使用线性探测在主要区域地址中搜索开放或未占用的元素。
在哈希表中插入实体的步骤:
1 .如果位置为空,则直接插入实体。
2 .如果映射的位置被占用,则继续探测直到找到一个空槽。找到空槽后,插入实体。
- 创建记录:此方法从用户那里获取详细信息,如 ID、姓名和电话号码,并在哈希表中创建新记录。
- 显示记录:创建此函数是为了显示日记的所有记录。
- 删除记录:此方法获取要删除的记录的键。然后,它在哈希表中搜索记录 id 是否与键匹配。然后,该记录被删除。
- 搜索记录:该方法获取要搜索的记录的关键字。然后,它遍历哈希表,如果记录 id 与键匹配,则显示记录详细信息。
- 更新记录:此方法获取要搜索的记录的键。然后,它遍历哈希表,如果记录 id 与键匹配,则显示记录详细信息。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Class to store contact
// details
class node {
string name;
long int tel;
int id;
public:
node()
{
tel = 0;
id = 0;
}
friend class hashing;
};
class hashing {
// Maximum size of
// directory is 100
node data[100];
string n;
long int t;
int i, index;
public:
hashing()
{
i = 0;
t = 0;
}
// This method takes details
// from the user like ID,
// Name and Telephone number
// and create new record in
// the hashtable.
void create_record(int size)
{
// Enter ID
i = 4;
// Enter Name
n = "XYZ Gupta";
// Enter telephone number
t = 23451234;
cout << "\nEnter id :";
cout << " \t\t\t"
<< i;
cout << "\nEnter name :";
cout << " \t\t\t " << n;
cout
<< "\nEnter telephone";
cout << " number :\t"
<< t;
index = i % size;
// Inserting record using linear
// probing in case of collision
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
if (data[index].id == 0) {
data[index].id = i;
data[index].name = n;
data[index].tel = t;
break;
}
else
index
= (index + 1) % size;
}
}
// This method takes the key of
// the record to be searched.
// Then, it traverses the hash
// table, if record id matches
// with the key it displays the
// record detail.
void search_record(int size)
{
int index1, key, flag = 0;
key = 4;
cout << "\nEnter record";
cout << " id to search : "
<< key;
index1 = key % size;
// Traversing the directory
// linearly inorder to search
// record detail
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[index1].id == key) {
flag = 1;
cout << "\nRecord found:";
cout << "\n\tID ";
cout << "\tNAME ";
cout << "\t\tTELEPHONE ";
cout << "\n\t"
<< data[index1].id
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].name
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].tel;
break;
}
else
index1
= (index1 + 1) % size;
}
if (flag == 0)
cout << "\nRecord";
cout << " not found";
}
// This method takes the key
// of the record to be deleted.
// Then, it searches in hash
// table if record id matches
// with the key. Then, that
// record is deleted.
void delete_record(int size)
{
int index1, key, flag = 0;
key = 4;
cout << "\nEnter record";
cout << " id to delete : "
<< key << "\n ";
index1 = key % size;
// Traversing the directory
// linearly inorder to delete
// the record detail
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[index1].id
== key) {
flag = 1;
data[index1].id = 0;
data[index1].name = " ";
data[index1].tel = 0;
cout << "\nRecord";
cout << " deleted";
cout << " successfully";
break;
}
else
index1
= (index1 + 1) % size;
}
if (flag == 0)
cout << "\nRecord";
cout << " not found";
}
// This method takes the key
// of the record to be searched.
// Then, it traverses the hash table,
// if record id matches with the
// key then it displays the record
// detail.
void update_record(int size)
{
int index1, key, flag = 0;
key = 4;
cout << "\nEnter record";
cout << " id to update : "
<< key;
index1 = key % size;
// Traversing the directory
// linearly inorder to search
// record detail
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[index1].id
== key) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
else
index1
= (index1 + 1) % size;
}
// If the record is found
// the details are updated
if (flag == 1) {
n = "XYZ Agarwal";
t = 23413421;
data[index1].name = n;
data[index1].tel = t;
cout << "\nEnter";
cout << " name: \t\t\t"
<< n;
cout << "\nEnter";
cout << " telephone number: \t"
<< t;
cout << "\nDetails updated: ";
cout << "\n\tID \tNAME";
cout << " \t\tTELEPHONE ";
cout << "\n\t"
<< data[index1].id
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].name
<< " \t"
<< data[index1].tel;
}
}
// This function is created to
// display all the record of
// the diary.
void display_record(int size)
{
cout << "\n\tID \tNAME";
cout << " \t\tTELEPHONE ";
// Displaying the details of
// all records of the directory.
for (int a = 0; a < size; a++) {
if (data[a].id != 0) {
cout << "\n\t"
<< data[a].id
<< " \t"
<< data[a].name
<< " \t"
<< data[a].tel;
}
}
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
// size of directory
int size;
// creating object of hashing
// class
hashing s;
size = 20;
// Creating a record in
// directory
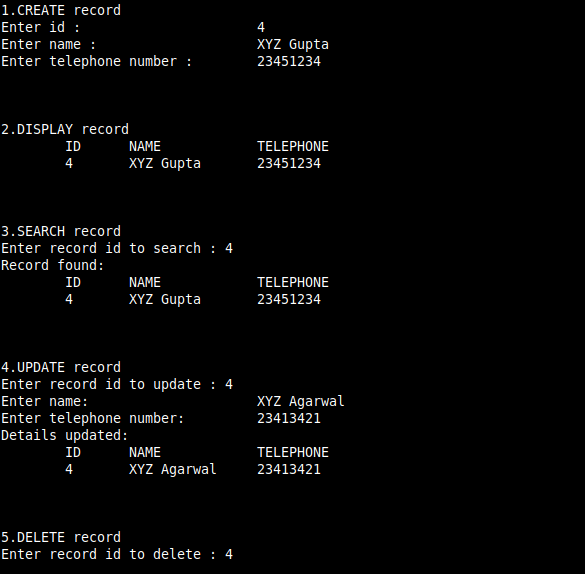
cout << "\n1.CREATE record ";
s.create_record(size);
// Display available
// record details
cout << "\n\n\n\n2.DISPLAY";
cout << " record ";
s.display_record(size);
// Searching a record detail
// in the directory
cout << "\n\n\n\n3.SEARCH";
cout << " record";
s.search_record(size);
// Updating the existing
// details of a record
cout << "\n\n\n\n4.UPDATE";
cout << " record ";
s.update_record(size);
// Removing specified
// existing record
// from dictionary
cout << "\n\n\n\n5.DELETE";
cout << " record ";
s.delete_record(size);
return 0;
} 输出:

如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。