给定一个包含正元素和负元素的数组arr[] ,任务是计算总和为完全平方数的所有子数组。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {2, 3, -5, 6, -7, 4};
Output: 5
Explanation:
Subarrays {2, 3, -5}, {-5, 6}, {3, -5, 6}, {3, -5, 6, -7, 4} and {4} with sum is 0, 1, 4, 1 and 4 respectively have perfect square sum.
Input: arr[] = {3, -6, 4, -2, 7};
Output: 3
Explanation: {3, -6, 4}, {4}, {4, -2, 7} are the subarrays with perfect square sum.
天真的方法:
一个简单的解决方案是生成所有可能的子数组。在遍历时,跟踪子数组和。保持总和为完美平方的所有子数组的计数。
有效的解决方案:想法是使用前缀和数组来解决给定的问题。
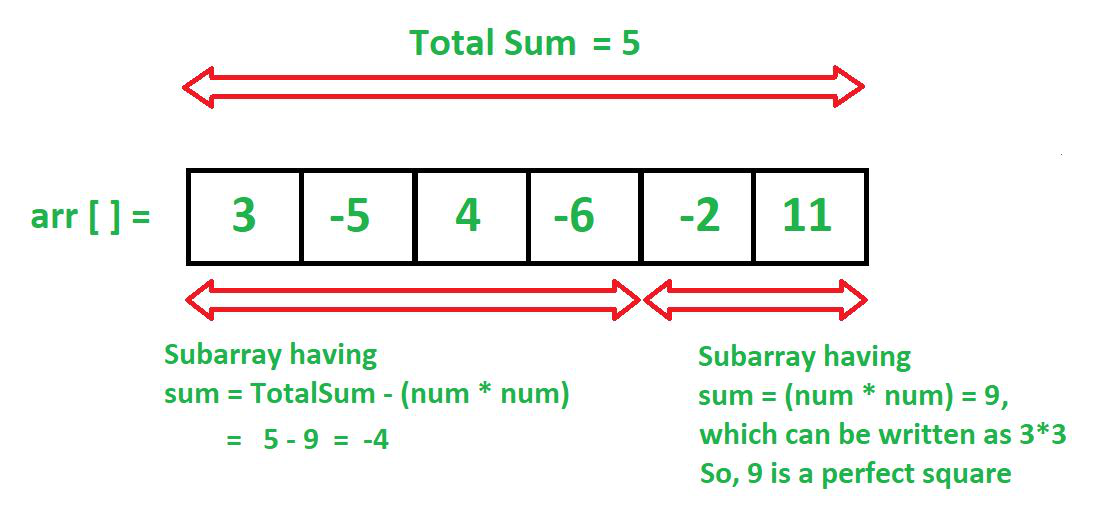
- 创建一个prefixSum 数组并存储它的前缀和。
- 遍历prefixSum 数组并确定它的最小值,即( prefixMin )。
- 现在,创建一个无序映射,可用于存储当前 prefixSum 的频率,同时遍历prefixSum 数组。
- 用值 1 初始化映射的第 0 个键索引,因为 0 是一个完美的正方形。
- 使用嵌套循环遍历prefixSum 数组。
- 对于每个 prefixSum 元素,嵌套循环将查找mapKey = (prefixSum[i] – j*j) (如果在地图索引中可用) 。
- 如果(prefixSum[i] – j*j)在地图中已经可用,我们用(prefixSum[i] – j*j)的索引值更新我们的计数器。
- 这个想法是用所有的平方 (j*j) 检查当前的 prefixSum 值,直到差异达到prefixMin 。
- 现在,在外循环的每次迭代中,将带有当前 prefixSum索引的映射增加 1。
- 基本概念是我们继续从(prefixSum[i] – j*j ) 搜索,因为如果数组的一部分是(prefixSum[i] – j*j ) ,那么数组的另一部分将是(j *j)即一个完美的平方和。
- 您可以在上图中看到 totalSum 实际上是用于此目的的 prefixSum。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ code for the above approach.
#include
using namespace std;
#define lli long long int
// Function to find count of subarrays
// whose sum is a perfect square.
lli countSubarrays(int arr[],
int n)
{
// to search for index with
// (current prefix sum - j*j)
unordered_map mp;
// storing the prefix sum
int prefixSum[n];
// used to track the minimum
// value in prefixSum
int prefixMin = 0;
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
prefixMin = min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[0]);
// Calculating the prefixSum
// and tracking the prefixMin
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1]
+ arr[i];
// below statement is used if
// array contains
// negative numbers
prefixMin = min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[i]);
}
// counts the no of subarrays
// with perfect square sum
lli countSubs = 0;
// as 0 is a perfect square,
// so we initialize 0th
// index-key with value 1
mp[0] = 1;
// Here we count the perfect
// square subarray sum by
// searching if there is a
// prefix with
// sum = (current prefixSum - (sq*sq))
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0;
prefixSum[i] - j * j >= prefixMin;
j++) {
if (mp.find(prefixSum[i] - j * j)
!= mp.end())
// increasing our subarray count
countSubs += mp[prefixSum[i]
- j * j];
}
// increasing the current prefixSum
// index value in map by 1 to count
// the other perfect squares while
// traversing further
mp[prefixSum[i]]++;
}
return countSubs;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, -5,
6, -7, 4 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
lli ans = countSubarrays(arr, n);
// printing the result
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Java
// Java code for
// the above approach.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find count of
// subarrays whose sum is
// a perfect square.
static long countSubarrays(int arr[],
int n)
{
// To search for index with
// (current prefix sum - j*j)
HashMap mp = new HashMap();
// Storing the prefix sum
int []prefixSum = new int[n];
// Used to track the minimum
// value in prefixSum
int prefixMin = 0;
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
prefixMin = Math.min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[0]);
// Calculating the prefixSum
// and tracking the prefixMin
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + arr[i];
// Below statement is used if
// array contains
// negative numbers
prefixMin = Math.min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[i]);
}
// Counts the no of subarrays
// with perfect square sum
long countSubs = 0;
// As 0 is a perfect square,
// so we initialize 0th
// index-key with value 1
mp.put(0, 1);
// Here we count the perfect
// square subarray sum by
// searching if there is a
// prefix with
// sum = (current prefixSum - (sq*sq))
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0;
prefixSum[i] - j *
j >= prefixMin; j++)
{
if (mp.containsKey(prefixSum[i] - j * j))
// Increasing our subarray count
countSubs += mp.get(prefixSum[i] -
j * j);
}
// Increasing the current prefixSum
// index value in map by 1 to count
// the other perfect squares while
// traversing further
if(mp.containsKey(prefixSum[i]))
{
mp.put(prefixSum[i],
mp.get(prefixSum[i]) + 1);
}
else
{
mp.put(prefixSum[i], 1);
}
}
return countSubs;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {2, 3, -5,
6, -7, 4};
int n = arr.length;
long ans = countSubarrays(arr, n);
// Printing the result
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Python3
# Python3 code for the above approach.
from collections import defaultdict
# Function to find count of subarrays
# whose sum is a perfect square.
def countSubarrays(arr, n):
# To search for index with
# (current prefix sum - j*j)
mp = defaultdict(lambda:0)
# Storing the prefix sum
prefixSum = [0] * n
# Used to track the minimum
# value in prefixSum
prefixMin = 0
prefixSum[0] = arr[0]
prefixMin = min(prefixMin, prefixSum[0])
# Calculating the prefixSum
# and tracking the prefixMin
for i in range(1, n):
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + arr[i]
# Below statement is used if
# array contains negative numbers
prefixMin = min(prefixMin, prefixSum[i])
# Counts the no of subarrays
# with perfect square sum
countSubs = 0
# As 0 is a perfect square,
# so we initialize 0th
# index-key with value 1
mp[0] = 1
# Here we count the perfect
# square subarray sum by
# searching if there is a
# prefix with
# sum = (current prefixSum - (sq*sq))
for i in range(n):
j = 0
while prefixSum[i] - j * j >= prefixMin:
if prefixSum[i] - j * j in mp:
# Increasing our subarray count
countSubs += mp[prefixSum[i] - j * j]
j += 1
# Increasing the current prefixSum
# index value in map by 1 to count
# the other perfect squares while
# traversing further
mp[prefixSum[i]] += 1
return countSubs
# Driver code
arr = [ 2, 3, -5, 6, -7, 4 ]
n = len(arr)
ans = countSubarrays(arr, n)
# Printing the result
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by Shivam SinghC#
// C# code for
// the above approach.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to find count of
// subarrays whose sum is
// a perfect square.
static long countSubarrays(int []arr,
int n)
{
// To search for index with
// (current prefix sum - j*j)
Dictionary mp =
new Dictionary();
// Storing the prefix sum
int []prefixSum = new int[n];
// Used to track the minimum
// value in prefixSum
int prefixMin = 0;
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
prefixMin = Math.Min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[0]);
// Calculating the prefixSum
// and tracking the prefixMin
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] +
arr[i];
// Below statement is used if
// array contains
// negative numbers
prefixMin = Math.Min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[i]);
}
// Counts the no of subarrays
// with perfect square sum
long countSubs = 0;
// As 0 is a perfect square,
// so we initialize 0th
// index-key with value 1
mp.Add(0, 1);
// Here we count the perfect
// square subarray sum by
// searching if there is a
// prefix with
// sum = (current prefixSum -
// (sq*sq))
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; prefixSum[i] - j *
j >= prefixMin; j++)
{
if (mp.ContainsKey(prefixSum[i] -
j * j))
// Increasing our subarray count
countSubs += mp[prefixSum[i] -
j * j];
}
// Increasing the current prefixSum
// index value in map by 1 to count
// the other perfect squares while
// traversing further
if(mp.ContainsKey(prefixSum[i]))
{
mp[prefixSum[i]]++;
}
else
{
mp.Add(prefixSum[i], 1);
}
}
return countSubs;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = {2, 3, -5,
6, -7, 4};
int n = arr.Length;
long ans = countSubarrays(arr, n);
// Printing the result
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 Javascript
输出:
5时间复杂度: O(N * sqrt(K))
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。