齐纳二极管 – 说明、规格、应用、电路符号
半导体材料的电导率值介于导体(例如金属铜)和绝缘体(例如玻璃)之间。它的电阻率随着温度的升高而下降;金属以相反的方式表现。通过将杂质(掺杂)引入晶体结构,可以以有用的方式改变其导电性能。当同一晶体中存在两个不同掺杂的区域时,就会产生一个半导体结。电荷载流子(包括电子、离子和电子空穴)在这些结处的行为是二极管、晶体管和大多数现代电子产品的基础。
半导体的一些例子是硅、锗、砷化镓和元素周期表上所谓的准金属阶梯附近的元素。继硅之后,砷化镓是第二常见的半导体,用于激光二极管、太阳能电池、微波频率集成电路等。硅是制造大多数电子电路的关键元素。这篇文章是关于齐纳二极管的,之前我们先来看看相关的话题。
pn结
A p-n junction is an interface or a boundary between two semiconductor material types, namely the p-type and the n-type, inside a semiconductor.
半导体的 p 侧或正侧具有过量的空穴,而 n 侧或负侧具有过量的电子。在半导体中,pn结是通过掺杂的方法产生的
pn结的形成
- 我们利用独特的半导体材料制造 pn 交叉点,将有一个晶粒限制,通过分散电子和开口来限制电子从一侧到另一侧的发展,因此,我们利用了掺杂的方法。
- 在此模型的帮助下,我们将了解最常见的兴奋剂方式。请允许我们考虑一个微薄的 p 型硅半导体片。
- 如果我们在其中添加适量的五价污染物,一块 p 型硅将变成 n 型硅。该表当前将包含 p 型区域和 n 型区域设置以及这两个区域之间的交叉点。
- 跟踪 pn 交叉点发展的周期有两种——传播和浮动。正如我们可能知道的那样,交叉口不同侧的开口和电子的会聚存在区别,p侧的开口扩散到n侧,n侧的电子扩散到p -边。这些导致交叉路口的分散电流。
Biasing conditions for the p-n Junction Diode
There are two working areas in the p-n intersection diode:
- p-type
- n-type
There are three biasing conditions for p-n intersection diode and this depends on the voltage applied:
- Zero bias: There is no outside voltage applied to the p-n intersection diode.
- Forward bias: The positive terminal of the voltage potential is associated with the p-type while the adverse terminal is associated with the n-type.
- Invert bias: The adverse terminal of the voltage potential is associated with the p-type and the positive is associated with the n-type.
前向偏差
- 当 p 型与电池的正极端子相关联且 n 型与电池的负极端子相关联时,pn 交叉点应该是正向的。在 pn 交叉点为正向一侧的点,pn 交叉点处的基础电场和施加的电场方向相反。
- 当两个电场相加时,合成电场的范围小于隐式电场。这导致阻力较小且更细长的衰竭区域。当施加的电压很大时,耗尽区的阻塞变得不重要。
- 在硅中,电压为 0.6 V 时,耗尽区的对立完全不重要,电流通过它畅通无阻。
反向偏差
- 当 p 型与电池的负极端子相关联并且 n 型与正极侧相关联时,pn 交叉点应该是相反的一侧。
- 对于这种情况,固有电场和外加电场的方式类似。当这两个场相加时,合成电场与底层电场的方式相似,从而形成一个电阻更大、消耗更厚的区域。
- 如果施加的电压增加,消耗区域会变得更电阻和更厚。
齐纳二极管
A Zener diode is a vigorously doped semiconductor gadget that is intended to work the opposite way.
齐纳二极管,也称为击穿二极管,是一种高度掺杂的半导体器件,旨在以相反的方式工作。当齐纳二极管两端的电压反转并且电位达到齐纳电压(拐点电压)时,交叉点分离并且电流以相反的方式流动。这种影响被称为齐纳效应。
齐纳二极管工作在反向偏置
当齐纳二极管是正向的时,它实际上就像一个普通的二极管一样工作。尽管如此,当与反向单侧模式相关时,少量溢出电流会流过二极管。随着相反电压增加到预定击穿电压 (Vz),电流开始流过二极管。电流增加到最大,这是由串联电阻决定的,之后它会平衡并在很宽的施加电压范围内保持稳定。
There are two kinds of breakdowns for a Zener Diode:
- Avalanche Breakdown
- Zener Breakdown
- 齐纳二极管的雪崩击穿:
雪崩击穿发生在普通二极管和齐纳二极管在高反电压下。在向 PN 交叉点施加高值的相反电压时,自由电子获得足够的能量并以高速加速。这些高速运动的自由电子会撞击不同的分子并敲除更多的电子。
由于这种持续的影响,由于二极管中的电流迅速增加,产生了大量的自由电子。电流的这种突然膨胀可能永远抹杀普通二极管,然而,齐纳二极管旨在在洪流滑动击穿下工作,并且可以支持意外的流量尖峰。电流滑动击穿发生在齐纳电压 (Vz) 比 6V 更显着的齐纳二极管中。
- 齐纳二极管中的齐纳击穿:
在施加的逆预置电压接近齐纳电压时,耗尽区域中的电场足以将电子从其价带中拉出。
从耗尽区的固体电场中获得足够能量的价电子从母体分子中释放出来。在齐纳击穿区,电压稍有扩大,就会导致电流快速增加。
雪崩击穿与齐纳击穿:
- 齐纳冲击在高达 5.6 伏的电压中占主导地位,而激流滑动冲击则取代了这一点。
- 它们都是比较影响,区别在于齐纳冲击是量子奇迹,而雪崩击穿冲击是价带中电子的发展,就像在任何电流中一样。
- 雪崩击穿影响同样允许通过二极管的电流比齐纳击穿允许的电流更大。
稳压二极管的电路符号
齐纳二极管的捆绑方式有很多种。一些用于显着程度的力传播,而另一些则包含在表面贴装设计中。最广为人知的齐纳二极管包含在一个小玻璃缩影中。它的一端有一条带,表示二极管的阴极侧。
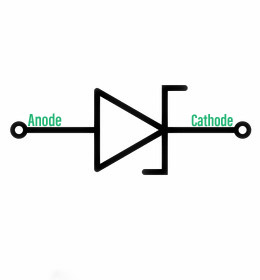
齐纳二极管的象征
VI 齐纳二极管的特性
下面给出的图表显示了齐纳二极管的 VI 质量。

VI特性的图示
The V-I qualities of a Zener diode can be separated into two sections as follows:
- Forward Characteristics of Zener Diode: The primary quadrant in the diagram addresses the forward qualities of a Zener diode. From the diagram, we comprehend that it is practically indistinguishable from the forward attributes of some other p-n intersection diode.
- Reverse Characteristics of Zener Diode: At the point when an opposite voltage is applied to a Zener voltage, at first a little converse immersion current Io streams across the diode. This current is because of thermally created minority transporters. As the opposite voltage is expanded, at a specific worth of converse voltage, the converse current increments definitely and forcefully. This means that the breakdown has happened. We call this voltage breakdown voltage or Zener voltage and it is signified by Vz.
齐纳二极管规格:
齐纳二极管的一些常用细节如下:
- 齐纳/击穿电压——齐纳或相反的击穿电压从 2.4 V 到 200 V,有时它可以达到 1 kV,而表面贴装设备的最大击穿电压为 47 V。
- 电流 Iz (max) –评估齐纳电压 (Vz – 200μA 至 200 A) 时的最大电流
- 电流 Iz (min) –二极管击穿所需的基本电流值。
- 额定力——它表示齐纳二极管可以分散的最极端的力。它是由二极管的电压和流过它的电流的结果给出的。
- 温度稳定性 – 5 V 左右的二极管具有最佳安全性
- 电压容差 –通常为 ±5%
- 齐纳电阻 (Rz) –它是齐纳二极管显示的保护。
齐纳二极管的应用
以下是齐纳二极管的用途:
1)齐纳二极管作为电压调节器:齐纳二极管用作分流电压控制器,用于管理小负载上的电压。齐纳二极管的击穿电压将在很宽的电流范围内保持稳定。齐纳二极管与堆相关联,使其具有开关倾向,当齐纳二极管超过拐点电压时,堆两端的电压将变得一致。
2)齐纳二极管过压保护:当信息电压高于齐纳断路电压时,电阻两端的电压下降导致短路。这可以通过使用齐纳二极管来避免。
3) 限幅电路中的齐纳二极管:齐纳二极管用于通过限制交流波形的一个或两个半模式的可能部分来调整交流波形切割电路。
示例问题
问题一:什么是稳压二极管?
回答:
A Zener Diode, otherwise called a breakdown diode, is an intensely doped semiconductor gadget that is intended to work the converse way. At the point when the voltage across the terminals of a Zener diode is turned around and the potential arrives at the Zener Voltage (knee voltage), the intersection separates and the current streams the opposite way. This impact is known as the Zener Effect.
问题 2:什么是反向偏置条件?
回答:
At the point when the p-type is associated with the adverse terminal of the battery and the n-type is associated with the positive side then the p-n intersection is supposed to be converse one-sided. For this situation, the inherent electric field and the applied electric field are a similar way. At the point when the two fields are added, the resultant electric field is a similar way as the underlying electric field making a more resistive, thicker consumption district. The consumption locale turns out to be more resistive and thicker if the applied voltage increases.
问题3:齐纳二极管的雪崩击穿是什么?
回答:
Avalanche breakdown happens both in ordinary diode and Zener Diode at high opposite voltage. At the point when a high worth of opposite voltage is applied to the PN intersection, the free electrons acquire adequate energy and speed up at high speeds. These free electrons moving at high speed impacts different molecules and knocks off more electrons. Because of this consistent impact, an enormous number of free electrons are produced because of electric flow in the diode quickly increments. This abrupt expansion in electric flow may forever obliterate the ordinary diode, nonetheless, a Zener diode is intended to work under torrential slide breakdown and can support the unexpected spike of flow. Torrential slide breakdown happens in Zener diodes with Zener voltage (Vz) more prominent than 6V.
问题4:稳压二极管和普通二极管有什么区别?
回答:
The principle contrast between a Zener diode and an ordinary diode lies in the entry of current. An ordinary diode permits current to stream just one way while Zener diode permits current to stream in the two ways.
问题5:稳压二极管有哪些应用?
回答:
Following are the applications of Zener diode:
1) Zener diode as a voltage regulator
2) Zener diode in over-voltage protection
3) Zener diode in clipping circuits
问题 6:齐纳二极管如何在反向偏置条件下工作?
回答:
A Zener diode works actually like an ordinary diode when it is forward-one-sided. Notwithstanding, when associated backward one-sided mode, a little spillage current moves through the diode. As the opposite voltage increments to the foreordained breakdown voltage (Vz), current beginnings coursing through the diode. The current increments to a greatest, which is dictated by the series resistor, after which it balances out and stays steady over a wide scope of applied voltage.