用于对 0、1 和 2 的链表进行排序的 C 程序
给定一个由 0、1 和 2 组成的链表,对它进行排序。
例子:
Input: 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0 -> 2 -> 0 -> 1 -> NULL
Output: 0 -> 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 2 -> NULL
Input: 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 0 -> NULL
Output: 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> NULL
来源:微软专访 |设置 1
以下步骤可用于对给定的链表进行排序。
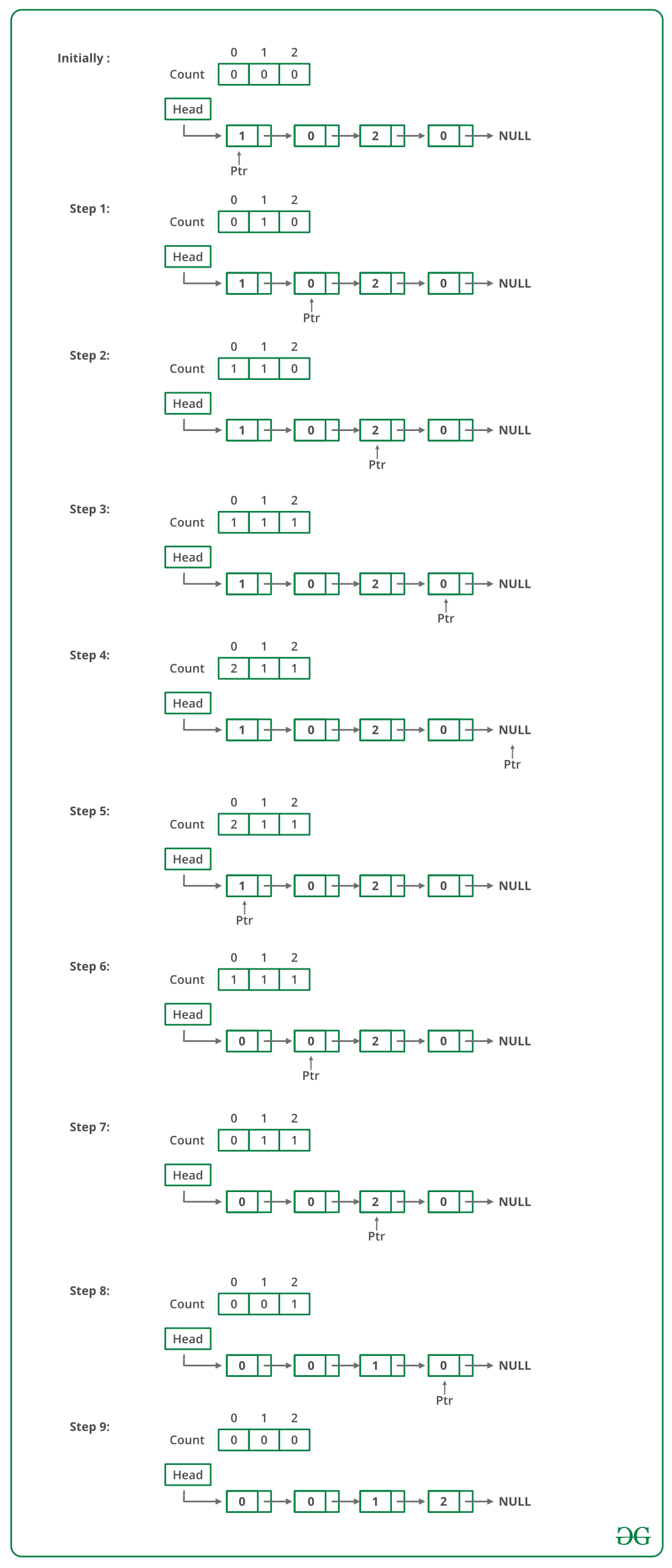
- 遍历列表,统计0、1、2的个数。设计数分别为 n1、n2 和 n3。
- 再次遍历列表,前 n1 个节点用 0 填充,然后 n2 个节点用 1 填充,最后 n3 个节点用 2 填充。
下图是上述方法的试运行:
下面是上述方法的实现:
C
// C Program to sort a linked list
// 0s, 1s or 2s
#include
#include
// Link list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to sort a linked list
// of 0s, 1s and 2s
void sortList(struct Node *head)
{
// Initialize count of '0', '1'
// and '2' as 0
int count[3] = {0, 0, 0};
struct Node *ptr = head;
/* Count total number of '0', '1' and '2'
count[0] will store total number of '0's
count[1] will store total number of '1's
count[2] will store total number of '2's */
while (ptr != NULL)
{
count[ptr->data] += 1;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
int i = 0;
ptr = head;
/* Let say count[0] = n1, count[1] = n2 and
count[2] = n3
now start traversing list from head node,
1) fill the list with 0, till n1 > 0
2) fill the list with 1, till n2 > 0
3) fill the list with 2, till n3 > 0 */
while (ptr != NULL)
{
if (count[i] == 0)
++i;
else
{
ptr->data = i;
--count[i];
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
// Function to push a node
void push (struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to the
// new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Function to print linked list
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf("n");
}
// Driver code
int main(void)
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
push(&head, 0);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 0);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
printf(
"Linked List Before Sorting");
printList(head);
sortList(head);
printf(
"Linked List After Sorting");
printList(head);
return 0;
} 输出:
Linked List Before Sorting
2 1 2 1 1 2 0 1 0
Linked List After Sorting
0 0 1 1 1 1 2 2 2时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是链表中的节点数。
辅助空间: O(1)
请参阅完整的文章对 0s、1s 和 2s 的链表进行排序以获取更多详细信息!