- 机械系统建模
- 机械系统建模(1)
- 电气安全教程
- 电气安全教程(1)
- 讨论电气安全
- 讨论电气安全(1)
- 电气安全-有用的资源
- 电气安全-有用的资源(1)
- 电气安全-测试认证
- 电气安全-电缆
- 电气安全-电缆(1)
- 使用 Word2Vec 嵌入从给定单词中查找单词类比
- 使用 Word2Vec 嵌入从给定单词中查找单词类比(1)
- Bajaj 电气面试经验(1)
- Bajaj 电气面试经验
- 电气安全-印度标准
- 电气安全-印度标准(1)
- 电气安全-接地
- 电气安全-接地(1)
- 电气安全-电源系统
- 电气安全-电源系统(1)
- 电气安全-粘接
- 电气安全-粘接(1)
- 电气安全-安全设备类型
- 电气安全-安全设备类型(1)
- 电气安全-短路保护(1)
- 电气安全-短路保护
- 施耐德电气 E&A 面试经历
- 施耐德电气 E&A 面试经历(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-25 05:12:29 🧑 作者: Mango
如果满足以下两个条件,则认为两个系统彼此相似。
- 这两个系统在物理上是不同的
- 这两个系统的微分方程建模相同
电气系统和机械系统是两个物理上不同的系统。平移机械系统的电气类比有两种类型。这些是力电压类比和力电流类比。
力电压类比
在力电压类比中,将平移机械系统的数学方程与电气系统的网格方程进行比较。
如图所示,请考虑以下平移机械系统。
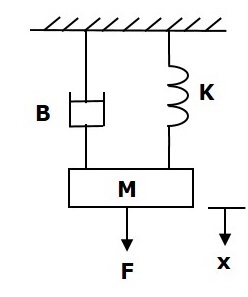
该系统的力平衡方程为
$$ F = F_m + F_b + F_k $$
$ \ Rightarrow F = M \ frac {\ text {d} ^ 2x} {\ text {d} t ^ 2} + B \ frac {\ text {d} x} {\ text {d} t} + Kx $ (式1)
如图所示,考虑以下电气系统。该电路由电阻器,电感器和电容器组成。所有这些电气元件串联连接。施加到该电路的输入电压为$ V $伏,流经电路的电流为$ i $安培。
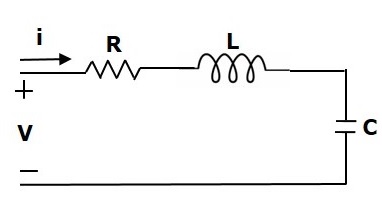
该电路的网格方程为
$ V = Ri + L \ frac {\ text {d} i} {\ text {d} t} + \ frac {1} {c} \ int idt $ (等式2)
用公式2中的$ i = \ frac {\ text {d} q} {\ text {d} t} $代替。
$$ V = R \ frac {\ text {d} q} {\ text {d} t} + L \ frac {\ text {d} ^ 2q} {\ text {d} t ^ 2} + \ frac { q} {C} $$
$ \ Rightarrow V = L \ frac {\ text {d} ^ 2q} {\ text {d} t ^ 2} + R \ frac {\ text {d} q} {\ text {d} t} + \ left (\ frac {1} {c} \ right)q $ (等式3)
通过比较方程式1和方程式3,我们将获得平移机械系统和电气系统的相似量。下表显示了这些类似的数量。
| Translational Mechanical System | Electrical System |
|---|---|
| Force(F) | Voltage(V) |
| Mass(M) | Inductance(L) |
| Frictional Coefficient(B) | Resistance(R) |
| Spring Constant(K) | Reciprocal of Capacitance $(\frac{1}{c})$ |
| Displacement(x) | Charge(q) |
| Velocity(v) | Current(i) |
类似地,存在旋转机械系统的转矩电压类比。现在让我们讨论这个类比。
转矩电压模拟
在这种类比中,将旋转机械系统的数学方程与电气系统的网格方程进行比较。
旋转机械系统如下图所示。
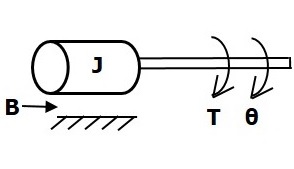
扭矩平衡方程为
$$ T = T_j + T_b + T_k $$
$ \ Rightarrow T = J \ frac {\ text {d} ^ 2 \ theta} {\ text {d} t ^ 2} + B \ frac {\ text {d} \ theta} {\ text {d} t} + k \ theta $ (公式4)
通过比较方程式4和方程式3,我们将得到旋转机械系统和电气系统的相似量。下表显示了这些类似的数量。
| Rotational Mechanical System | Electrical System |
|---|---|
| Torque(T) | Voltage(V) |
| Moment of Inertia(J) | Inductance(L) |
| Rotational friction coefficient(B) | Resistance(R) |
| Torsional spring constant(K) | Reciprocal of Capacitance $(\frac{1}{c})$ |
| Angular Displacement(θ) | Charge(q) |
| Angular Velocity(ω) | Current(i) |
力电流类比
在力流模拟中,将平移机械系统的数学方程与电气系统的节点方程进行比较。
如图所示,考虑以下电气系统。该电路由电流源,电阻器,电感器和电容器组成。所有这些电气元件都并联连接。
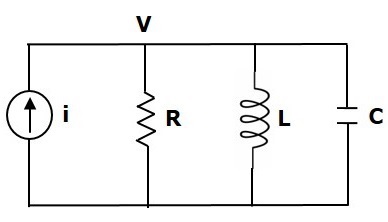
节点方程为
$ i = \ frac {V} {R} + \ frac {1} {L} \ int Vdt + C \ frac {\ text {d} V} {\ text {d} t} $ (等式5)
用公式5中的$ V = \ frac {\ text {d} \ Psi} {\ text {d} t} $代替。
$$ i = \ frac {1} {R} \ frac {\ text {d} \ Psi} {\ text {d} t} + \ left(\ frac {1} {L} \ right)\ Psi + C \ frac {\ text {d} ^ 2 \ Psi} {\ text {d} t ^ 2} $$
$ \ Rightarrow i = C \ frac {\ text {d} ^ 2 \ Psi} {\ text {d} t ^ 2} + \ left(\ frac {1} {R} \ right)\ frac {\ text { d} \ Psi} {\ text {d} t} + \ left(\ frac {1} {L} \ right)\ Psi $ (等式6)
通过比较方程式1和方程式6,我们将获得平移机械系统和电气系统的相似量。下表显示了这些类似的数量。
| Translational Mechanical System | Electrical System |
|---|---|
| Force(F) | Current(i) |
| Mass(M) | Capacitance(C) |
| Frictional coefficient(B) | Reciprocal of Resistance$(\frac{1}{R})$ |
| Spring constant(K) | Reciprocal of Inductance$(\frac{1}{L})$ |
| Displacement(x) | Magnetic Flux(ψ) |
| Velocity(v) | Voltage(V) |
类似地,存在用于旋转机械系统的转矩电流类比。现在让我们讨论这个类比。
转矩电流模拟
以此类推,将旋转机械系统的数学方程与电气系统的节点网格方程进行比较。
通过比较方程式4和方程式6,我们将得到旋转机械系统和电气系统的相似量。下表显示了这些类似的数量。
| Rotational Mechanical System | Electrical System |
|---|---|
| Torque(T) | Current(i) |
| Moment of inertia(J) | Capacitance(C) |
| Rotational friction coefficient(B) | Reciprocal of Resistance$(\frac{1}{R})$ |
| Torsional spring constant(K) | Reciprocal of Inductance$(\frac{1}{L})$ |
| Angular displacement(θ) | Magnetic flux(ψ) |
| Angular velocity(ω) | Voltage(V) |
在本章中,我们讨论了机械系统的电气类比。这些类比有助于研究和分析类比电气系统中的机械系统等非电气系统。