求前 10 个偶数的平均值
偶数是能被 2 整除的数。将这个数分成相等的组后,没有余数。偶数被认为是 2 的倍数。因此,所有偶数都可以配对成组,没有任何项目不配对。除以 2 时,返回的余数为 0。
偶数的性质
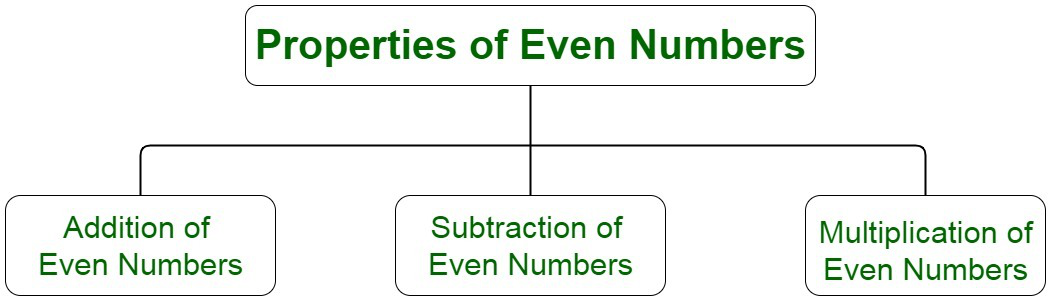
偶数的一些基本性质如下:
偶数的加法:
- 两个偶数之和为偶数。例如,数字 2 和 4 的和是 6。
- 偶数和奇数之和是奇数。例如,数字 2 和 5 的和是 7。
- 两个奇数之和是偶数。例如,数字 3 和 5 的和是 8。
偶数减法:
- 两个偶数之差也是偶数。然而,结果可能是正面的,也可能是负面的。例如,两个数字 4 和 2 之间的差是 2。
- 偶数和奇数之间的差异是奇数。例如,15 和 4 的差 = 15-4 = 11。
偶数的乘法:
- 两个偶数相乘是偶数。例如,数字 2 和 4 的乘积是 8。
- 两个奇数相乘是奇数。例如,数字 3 和 5 的乘积是 15。
- 偶数和奇数相乘是偶数。例如,数字 2 和 3 的乘积是 6。
意思是
平均值是统计概念之一,用于计算给定整数集的平均值或中心值。它提供有关数据集中趋势的信息。数据的集中趋势是一种统计度量,它使用单个值来收集有关整个数据分布集的信息。它提供了整个数据集的描述。平均值等于所有观测值之和与观测值总数之和。平均值也称为算术平均值或平均值。让我们假设一个数据集由 X = x 1 , x 2 ,..., x n给出。平均值用 x̄ 表示,它是给定 n 个值的平均值。
According to the definition, we have,
X̄ = (Sum of values ÷ Number of values)
X̄ = (x1+x2+x3+….+xn) / n
Some of the examples of mean in our real life are:
- Mean of marks scored by students in a test.
- Mean of runs scored by a cricketer in a one day match.
计算平均值
可以通过计算数字的平均值来计算数据集的平均值。在负数的情况下,计算数据值的总和,然后除以负整数的个数。
例如,如果我们有四个随机整数值,例如 -2,0,4,5 ,我们可以通过计算这些数字的平均值来计算均值,由下式给出,
平均值 = 总和 / 此类值的数量
总和 = -2 + 0 + 4 + 5
= 7
并且,值的数量 = 4
平均 = 7/4 = 3
因此,这些值的平均值等于 7/4。
前 10 个偶数的平均值是多少?
Natural numbers are counting numbers beginning from 1.
The first 10 even natural numbers, therefore begin with 2.
Hence, we have the first 10 natural numbers to be 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20.
Sum of numbers = 2 + 4… + 20 = 110
Now, we have,
Mean = Sum of numbers / Count of numbers
Substituting the values, we get,
Mean = 110 / 10 = 11
Therefore, the required mean of the first 10 even natural numbers is equivalent to 11.
类似问题
问题1:前10个偶数自然数的计算如何形成AP?
回答:
Sum (S) = (a+l) n/2
where a is the first term in the series, l is the last term of the series and n is the number of terms.
Substituting the values, we get,
a = 2, l = 20, n = 10 we get,
S = (2+20) 10/2
We obtain,
S = 5 × (22)
= 110
问题2:4个偶数的平均值是6。其中两个是2和4。剩下的两个是3x和x+2。计算第三个和第四个数字。
回答:
Sum of numbers = 2 + 4 + 3x + x+2 = 2x + 8
Mean = (4x + 8)/4
6 = 2x + 4
2 = 2x
x = 1
问题 3:计算前 50 个偶数的平均值。
回答:
Since, we have, first 50 even natural numbers are 2,4,6,………,98,100.
Now, we have,
Mean = Sum of observation / Number of observations
Sum of observation = 2+4+6……+98+100 = 2(1+2+3……+50)
We know,
Sum of n natural number = n(n+1) /2
On substituting the values, we get,
So, (1+2+3……+50) = 50 × 51/2
Sum = 2 × 50 × (51 / 2)
= 50 × 51
Total no. of such observation = 50
Therefore,
Mean = 50 × (51 / 50)
= 51