给定 N 叉树中连接重复节点的最大计数
给定一个通用树,使得每个节点都有一个与之关联的值,任务是在树中找到最大数量的具有相同值的连接节点。如果一个节点是另一个节点的子节点,则连接两个节点。
例子:
Input: Tree in the image below
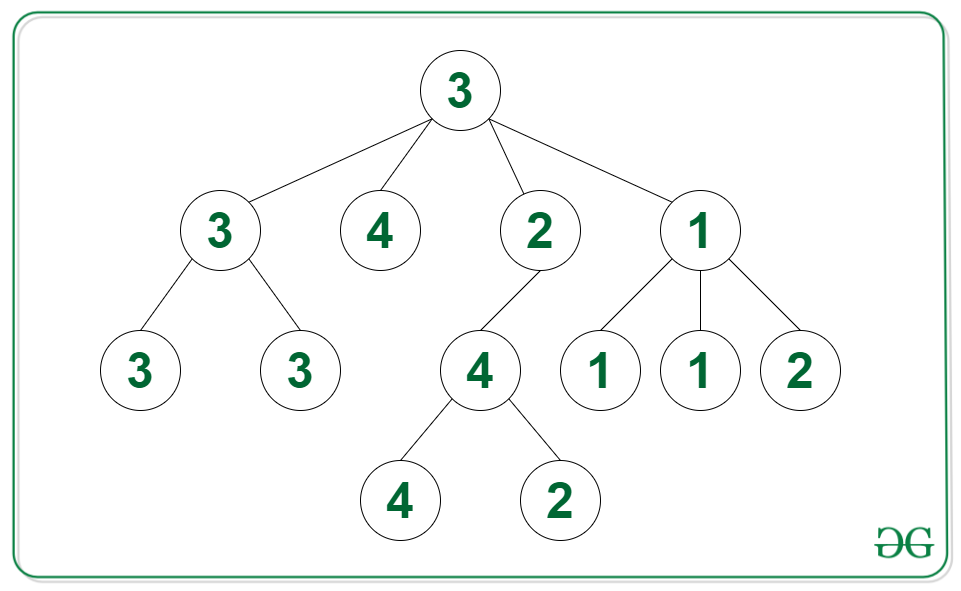
Output: 4
Explanation: The largest group of connected nodes are of the value 3 with number of nodes equal to 4.
Input: Tree in the image below
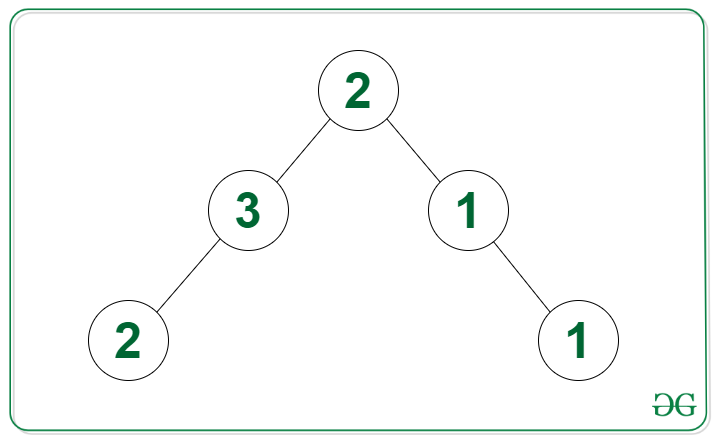
Output: 2
方法:给定的问题可以通过使用后序遍历来解决。这个想法是检查子节点是否与其父节点具有相同的值,并将从子节点返回的答案加 1。可以按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 在 N 叉树上应用后序遍历:
- 如果根没有子节点,则返回 1 给父节点
- 添加从与当前节点值相同的子节点返回的所有答案
- 更新最大连接节点数
- 返回最大连接节点数作为答案
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ code for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
vector children;
int val;
// constructor
Node(int v)
{
val = v;
children = {};
}
};
// Post order traversal function
// to calculate the largest group
// of connected nodes
int postOrder(Node* root, int maxi[])
{
// If the current node has no
// children then return 1
if (root->children.size() == 0)
return 1;
// Initialize a variable sum to
// calculate largest group connected
// to current node with same value
// as current node
int sum = 1;
// Iterate through all neighbors
for (Node* child : root->children) {
// Get the value from children
int nodes = postOrder(child, maxi);
// If child node value is same as
// current node then add the
// returned value to sum
if (child->val == root->val)
sum += nodes;
}
// Update maximum connected
// nodes if sum is greater
maxi[0] = max(maxi[0], sum);
// Return the connected group
// to the current node
return sum;
}
// Function to find the largest
// number of nodes in a tree
int largestGroup(Node* root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Initialize a variable max
// to calculate largest group
int maxi[1];
// Post-order traversal
postOrder(root, maxi);
// Return the answer
return maxi[0];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initialize the tree
Node* three1 = new Node(3);
Node* three2 = new Node(3);
Node* three3 = new Node(3);
Node* three4 = new Node(3);
Node* two1 = new Node(2);
Node* two2 = new Node(2);
Node* two3 = new Node(2);
Node* two4 = new Node(2);
Node* four1 = new Node(4);
Node* four2 = new Node(4);
Node* four3 = new Node(4);
Node* one1 = new Node(1);
Node* one2 = new Node(1);
Node* one3 = new Node(1);
Node* one4 = new Node(1);
three2->children.push_back(two1);
three2->children.push_back(three1);
three2->children.push_back(three3);
four1->children.push_back(four2);
four1->children.push_back(four3);
two2->children.push_back(one1);
two2->children.push_back(one2);
two2->children.push_back(two3);
one3->children.push_back(one4);
one3->children.push_back(two4);
three4->children.push_back(three2);
three4->children.push_back(four1);
three4->children.push_back(two2);
three4->children.push_back(one3);
// Call the function
// and print the result
cout << (largestGroup(three4));
}
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh Java
// Java implementation for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static class Node {
List children;
int val;
// constructor
public Node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
children = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
// Function to find the largest
// number of nodes in a tree
public static int largestGroup(Node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Initialize a variable max
// to calculate largest group
int[] max = new int[1];
// Post-order traversal
postOrder(root, max);
// Return the answer
return max[0];
}
// Post order traversal function
// to calculate the largest group
// of connected nodes
public static int postOrder(
Node root, int[] max)
{
// If the current node has no
// children then return 1
if (root.children.size() == 0)
return 1;
// Initialize a variable sum to
// calculate largest group connected
// to current node with same value
// as current node
int sum = 1;
// Iterate through all neighbors
for (Node child : root.children) {
// Get the value from children
int nodes = postOrder(child, max);
// If child node value is same as
// current node then add the
// returned value to sum
if (child.val == root.val)
sum += nodes;
}
// Update maximum connected
// nodes if sum is greater
max[0] = Math.max(max[0], sum);
// Return the connected group
// to the current node
return sum;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize the tree
Node three1 = new Node(3);
Node three2 = new Node(3);
Node three3 = new Node(3);
Node three4 = new Node(3);
Node two1 = new Node(2);
Node two2 = new Node(2);
Node two3 = new Node(2);
Node two4 = new Node(2);
Node four1 = new Node(4);
Node four2 = new Node(4);
Node four3 = new Node(4);
Node one1 = new Node(1);
Node one2 = new Node(1);
Node one3 = new Node(1);
Node one4 = new Node(1);
three2.children.add(two1);
three2.children.add(three1);
three2.children.add(three3);
four1.children.add(four2);
four1.children.add(four3);
two2.children.add(one1);
two2.children.add(one2);
two2.children.add(two3);
one3.children.add(one4);
one3.children.add(two4);
three4.children.add(three2);
three4.children.add(four1);
three4.children.add(two2);
three4.children.add(one3);
// Call the function
// and print the result
System.out.println(
largestGroup(three4));
}
} Python3
# Python code for the above approach
class Node:
# constructor
def __init__(self, v):
self.val = v;
self.children = [];
# Post order traversal function
# to calculate the largest group
# of connected nodes
def postOrder(root, maxi):
# If the current node has no
# children then return 1
if (len(root.children) == 0):
return 1;
# Initialize a variable sum to
# calculate largest group connected
# to current node with same value
# as current node
sum = 1;
# Iterate through all neighbors
for child in root.children:
# Get the value from children
nodes = postOrder(child, maxi);
# If child node value is same as
# current node then add the
# returned value to sum
if (child.val == root.val):
sum += nodes;
# Update maximum connected
# nodes if sum is greater
maxi[0] = max(maxi[0], sum);
# Return the connected group
# to the current node
return sum;
# Function to find the largest
# number of nodes in a tree
def largestGroup(root):
# Base case
if (root == None):
return 0;
# Initialize a variable max
# to calculate largest group
maxi = [0];
# Post-order traversal
postOrder(root, maxi);
# Return the answer
return maxi[0];
# Driver code
# Initialize the tree
three1 = Node(3);
three2 = Node(3);
three3 = Node(3);
three4 = Node(3);
two1 = Node(2);
two2 = Node(2);
two3 = Node(2);
two4 = Node(2);
four1 = Node(4);
four2 = Node(4);
four3 = Node(4);
one1 = Node(1);
one2 = Node(1);
one3 = Node(1);
one4 = Node(1);
three2.children.append(two1);
three2.children.append(three1);
three2.children.append(three3);
four1.children.append(four2);
four1.children.append(four3);
two2.children.append(one1);
two2.children.append(one2);
two2.children.append(two3);
one3.children.append(one4);
one3.children.append(two4);
three4.children.append(three2);
three4.children.append(four1);
three4.children.append(two2);
three4.children.append(one3);
# Call the function
# and print the result
print((largestGroup(three4)));
# This code is contributed by gfgkingC#
// C# implementation for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Class representing a Node of an N-ary tree
public class Node
{
public int val;
public List children;
// Constructor to create a Node
public Node(int vall)
{
val = vall;
children = new List();
}
}
class GFG {
// Function to find the largest
// number of nodes in a tree
public static int largestGroup(Node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Initialize a variable max
// to calculate largest group
int[] max = new int[1];
// Post-order traversal
postOrder(root, max);
// Return the answer
return max[0];
}
// Post order traversal function
// to calculate the largest group
// of connected nodes
public static int postOrder(
Node root, int[] max)
{
// If the current node has no
// children then return 1
if (root.children.Count == 0)
return 1;
// Initialize a variable sum to
// calculate largest group connected
// to current node with same value
// as current node
int sum = 1;
// Iterate through all neighbors
foreach (Node child in root.children) {
// Get the value from children
int nodes = postOrder(child, max);
// If child node value is same as
// current node then Add the
// returned value to sum
if (child.val == root.val)
sum += nodes;
}
// Update maximum connected
// nodes if sum is greater
max[0] = Math.Max(max[0], sum);
// Return the connected group
// to the current node
return sum;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main (){
// Initialize the tree
Node three1 = new Node(3);
Node three2 = new Node(3);
Node three3 = new Node(3);
Node three4 = new Node(3);
Node two1 = new Node(2);
Node two2 = new Node(2);
Node two3 = new Node(2);
Node two4 = new Node(2);
Node four1 = new Node(4);
Node four2 = new Node(4);
Node four3 = new Node(4);
Node one1 = new Node(1);
Node one2 = new Node(1);
Node one3 = new Node(1);
Node one4 = new Node(1);
three2.children.Add(two1);
three2.children.Add(three1);
three2.children.Add(three3);
four1.children.Add(four2);
four1.children.Add(four3);
two2.children.Add(one1);
two2.children.Add(one2);
two2.children.Add(two3);
one3.children.Add(one4);
one3.children.Add(two4);
three4.children.Add(three2);
three4.children.Add(four1);
three4.children.Add(two2);
three4.children.Add(one3);
// Call the function
// and print the result
Console.WriteLine(
largestGroup(three4));
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Shubham Singh Javascript
输出:
4时间复杂度: O(N),其中 N 是树中的节点数
辅助空间: O(H),H是树的高度