- Android UI 布局(1)
- Android-UI布局(1)
- Android UI 设计中的布局
- Android UI 设计中的布局(1)
- android 包含布局 (1)
- Android中的绝对布局示例
- android 包含布局 - 任何代码示例
- 移动Angular UI-布局
- 移动Angular UI-布局(1)
- Python| Kivy 中的布局(多个布局)中的布局(1)
- Python| Kivy 中的布局(多个布局)中的布局
- Android中的相对布局(1)
- Android中的相对布局
- HTML 布局布局技术(1)
- HTML 布局布局技术
- Android 中的 Flexbox 布局(1)
- Android 中的 Flexbox 布局
- HTML-布局(1)
- HTML-布局
- HTML |布局(1)
- HTML布局
- HTML布局(1)
- HTML |布局
- HTML |布局
- CSS-布局(1)
- CSS-布局
- Kotlin 中的 Android 表格布局(1)
- Kotlin 中的 Android 表格布局
- Kotlin 中的 Android 框架布局(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-05 04:55:03 🧑 作者: Mango
用户界面的基本构建块是一个View对象,该View对象是从View类创建的,并且在屏幕上占据一个矩形区域,并负责绘图和事件处理。 View是窗口小部件的基类,窗口小部件用于创建交互式UI组件,例如按钮,文本字段等。
ViewGroup是View的子类,并提供不可见的容器,用于容纳其他View或其他ViewGroup并定义其布局属性。
在第三层,我们有不同的布局,它们是ViewGroup类的子类,典型的布局定义了Android用户界面的视觉结构,可以在运行时使用View / ViewGroup对象创建,也可以使用简单的XML文件main_layout声明布局。 .xml ,位于项目的res / layout文件夹中。
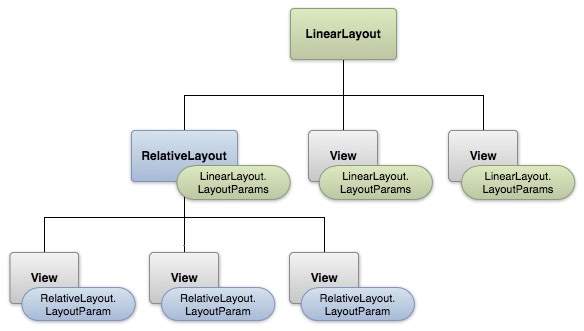
布局参数
本教程更多关于基于XML文件中定义的布局创建GUI。布局可以包含任何类型的小部件,例如按钮,标签,文本框等。以下是具有LinearLayout的XML文件的简单示例-
创建布局后,您可以在Activity.onCreate()回调实现中从应用程序代码中加载布局资源,如下所示-
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
Android布局类型
Android提供了许多版式,您几乎可以在所有Android应用程序中使用它们来提供不同的视图,外观和感觉。
| Sr.No | Layout & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Linear Layout
LinearLayout is a view group that aligns all children in a single direction, vertically or horizontally. |
| 2 |
Relative Layout
RelativeLayout is a view group that displays child views in relative positions. |
| 3 |
Table Layout
TableLayout is a view that groups views into rows and columns. |
| 4 |
Absolute Layout
AbsoluteLayout enables you to specify the exact location of its children. |
| 5 |
Frame Layout
The FrameLayout is a placeholder on screen that you can use to display a single view. |
| 6 |
List View
ListView is a view group that displays a list of scrollable items. |
| 7 |
Grid View
GridView is a ViewGroup that displays items in a two-dimensional, scrollable grid. |
布局属性
每个布局都有一组属性,这些属性定义该布局的视觉属性。在所有布局中,只有很少的公共属性,而其他属性是该布局所特有的。以下是常见属性,这些属性将应用于所有布局:
| Sr.No | Attribute & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
android:id This is the ID which uniquely identifies the view. |
| 2 |
android:layout_width This is the width of the layout. |
| 3 |
android:layout_height This is the height of the layout |
| 4 |
android:layout_marginTop This is the extra space on the top side of the layout. |
| 5 |
android:layout_marginBottom This is the extra space on the bottom side of the layout. |
| 6 |
android:layout_marginLeft This is the extra space on the left side of the layout. |
| 7 |
android:layout_marginRight This is the extra space on the right side of the layout. |
| 8 |
android:layout_gravity This specifies how child Views are positioned. |
| 9 |
android:layout_weight This specifies how much of the extra space in the layout should be allocated to the View. |
| 10 |
android:layout_x This specifies the x-coordinate of the layout. |
| 11 |
android:layout_y This specifies the y-coordinate of the layout. |
| 12 |
android:layout_width This is the width of the layout. |
| 13 |
android:paddingLeft This is the left padding filled for the layout. |
| 14 |
android:paddingRight This is the right padding filled for the layout. |
| 15 |
android:paddingTop This is the top padding filled for the layout. |
| 16 |
android:paddingBottom This is the bottom padding filled for the layout. |
此处的宽度和高度是布局/视图的尺寸,可以根据dp(与密度无关的像素),sp(与比例无关的像素),pt(为1/72英寸的点),px(像素),毫米(毫米),最后以英寸为单位。
您可以通过精确的测量来指定宽度和高度,但是更常见的是,您将使用以下常量之一来设置宽度或高度-
-
android:layout_width = wrap_content告诉您将视图调整为其内容所需的尺寸。
-
android:layout_width = fill_parent告诉您视图变得与其父视图一样大。
重力属性在定位视图对象中起着重要作用,它可以采用以下一个或多个(用“ |”分隔)以下常量值。
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| top | 0x30 | Push object to the top of its container, not changing its size. |
| bottom | 0x50 | Push object to the bottom of its container, not changing its size. |
| left | 0x03 | Push object to the left of its container, not changing its size. |
| right | 0x05 | Push object to the right of its container, not changing its size. |
| center_vertical | 0x10 | Place object in the vertical center of its container, not changing its size. |
| fill_vertical | 0x70 | Grow the vertical size of the object if needed so it completely fills its container. |
| center_horizontal | 0x01 | Place object in the horizontal center of its container, not changing its size. |
| fill_horizontal | 0x07 | Grow the horizontal size of the object if needed so it completely fills its container. |
| center | 0x11 | Place the object in the center of its container in both the vertical and horizontal axis, not changing its size. |
| fill | 0x77 | Grow the horizontal and vertical size of the object if needed so it completely fills its container. |
| clip_vertical | 0x80 | Additional option that can be set to have the top and/or bottom edges of the child clipped to its container’s bounds. The clip will be based on the vertical gravity: a top gravity will clip the bottom edge, a bottom gravity will clip the top edge, and neither will clip both edges. |
| clip_horizontal | 0x08 | Additional option that can be set to have the left and/or right edges of the child clipped to its container’s bounds. The clip will be based on the horizontal gravity: a left gravity will clip the right edge, a right gravity will clip the left edge, and neither will clip both edges. |
| start | 0x00800003 | Push object to the beginning of its container, not changing its size. |
| end | 0x00800005 | Push object to the end of its container, not changing its size. |
查看识别
视图对象可能具有分配给它的唯一ID,该ID将在树中唯一标识视图。 XML标记内的ID的语法是-
android:id="@+id/my_button"
以下是@和+符号的简要说明-
-
字符串开头的符号(@)表示XML解析器应解析并扩展ID字符串的其余部分,并将其标识为ID资源。
-
加号(+)表示这是必须创建并添加到我们资源中的新资源名称。要创建视图对象的实例并从布局中捕获它,请使用以下命令:
Button myButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.my_button);