套装类型
当事情安排得井井有条时,它们看起来会更好。在数学中,数字、对象或任何可以分组或可以集体显示的东西都被排列并定义为集合。集合不仅要学习理解数学中的概念,而且要在日常生活中应用它们很重要,因为将属于同一类别的事物安排在一个组中有助于轻松定位事物,并且看起来也很整洁.一个例子是以这种方式将衣服放在外面,例如,袜子将放在一组,而衬衫将放在另一组中,制作这样的套装并将物品放在各自的组中将有助于轻松找到任何衣服。这只是集合如何工作的一个真实示例。让我们详细了解一下集合。
套
定义明确的对象或项目或数据的集合称为集合。对象或数据称为元素。例如,教室里的男孩可以放在一个集合中,从 1 到 100 的所有整数都可以成为一个集合,所有素数都可以称为无限集。用于集合的符号是 {…..}。什么看起来像集合但不能称为集合?基本上,集合不会偏袒,因此,包含对象的任何质量或特征的事物都不能放入集合中。例如,“所有字迹不佳的学生”不能放在一个集合中。
问题:分离出可以放在集合中的集合。
- 公园里的美丽女孩
- 所有偶数
- 所有优秀的篮球运动员
- 能被3整除的自然数
- 从 1 到 10 的数字。
回答:
Anything that tries to define a certain quality or characteristics can not be put in a set. Hence, from the above given Collection of data.
The ones that can be a set,
2. All even numbers
4. The natural numbers divisible by 3.
5. Number from 1 to 10
The ones that cannot be a set,
1. The beautiful girls in the park
3. All the good basketball players.
集合类型
集合是属于同一类别的不同元素的集合,可以看到不同类型的集合。一个集合可能有无数个元素,可能根本没有元素,可能有一些元素,可能只有一个元素,等等。基于所有这些不同的方式,集合被分为不同的类型。
不同类型的集合是:
单例集
单例集是那些只包含 1 个元素的集合。例如,Set A= {1} 是一个单例集,因为它只有一个元素,即 1。Set B= {Reo} 也是一个单例集,因为只有一个元素是名称。同样,所有只包含一个元素的集合称为单例集合。
空集
空集也称为 Null 集或 Void 集。它们是其中没有元素/元素的集合。它们被表示为φ。空集的例子是,
- Set A= {a: a is a number greater than 5 and less than 3}
- Set B= {p: p are the students studying in class 7 and class 8}
有限集
有限集是存在有限数量元素的那些,无论它们增加多少,只要它们本质上是有限的,它们将被称为有限集。
Example:
1. Set A= {a: a is the whole number less than 20}
2. Set B = {a, b, c, d, e}
无限集
无限集是存在无限数量元素的集合,其中元素数量难以确定的情况称为无限集。
Example:
1. Set A= {a: a is an odd number}
2. Set B = {2,4,6,8,10,12,14,…..}
等集
具有相同元素且元素个数相等的两个集合称为相等集合。集合中的元素可以重新排列,也可以重复,但它们仍然是相等的集合。
Example: Set A = {1,2,6,5}
Set B = {2, 1, 5, 6}
In the above example, the elements are 1, 2, 5, 6. Therefore, A= B.
等效集
等效集是其中存在相同数量元素的那些。重要的是要注意,两个集合中的元素可能不同,但存在的元素数量是相等的。例如,如果一个集合中有 6 个元素,而另一个集合也有 6 个元素,则它们是等价集合。
Example: Set A= {2, 3, 5, 7, 11}
Set B = {p, q, r, s, t}
Set A and Set B are equivalent sets.
子集
如果集合 A 中存在的所有元素都属于集合 B,则集合 A 将被称为集合 B 的子集。用于子集的符号是⊆
如果 A 是 B 的子集,则写为 A ⊆ B
Example: Set A= {33, 66, 99}, Set B = {22, 11, 33, 99, 66}
Then, Set A ⊆ Set B
通用套装
通用集是包含其余集合的所有元素的集合。可以说,所有的集合都是全集的子集。全集记为U。
Example: Set A ={a, b, c, d}
Set B= {1,2}
U= {a, b, c, d, e, 1, 2}
示例问题
问题 1: φ 和 {φ}有什么区别。
回答:
- ϕ = this symbol is used to represent the null set, therefore, when only this symbol is given, the set is a Null set or empty set.
- {ϕ}= In this case, the symbol is present inside the brackets used to denote a set and therefore, now the symbol is acting like an element. Hence, this is a Singleton set.
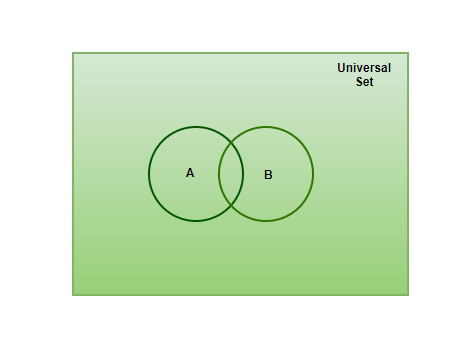
问题 2:在维恩图上表示全集。
回答:
Universal Sets are those that contain all the sets in it. In the below given Venn diagram, Set A and B are given as examples for better understanding of Venn Diagram.
Example: Set A= {1,2,3,4,5}, Set B = {1,2, 5, 0}
U= {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
问题 3:下面给出的集合中哪些是相等的,哪些本质上是等价的?
- 设置 A= {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
- 设置 B= {a, b, c, d, e}
- 设 C= {c: c ∈ N, c 为偶数, c ≤ 10}
- 设置 D = {1, 2, 5, 10}
- 设置 E= {x, y, z}
回答:
Equivalent sets are those which have the equal number of elements, whereas, Equal sets are those which have the equal number of elements present as well as the elements are same in the set.
Equivalent Sets ⇢ Set A, Set B, Set C.
Equal Sets ⇢ Set A, Set C.
问题 4:确定以下给定集合的类型,
- 设置 A= {a: a 是能被 10 整除的数}
- 设置 B = {2, 4, 6}
- 设置 C = {p}
- 设置 D= {n, m, o, p}
- 设 E= φ
回答:
From the knowledge gained above in the article, the above-mentioned sets can easily be identified.
- Set A is an Infinite set.
- Set B is a Finite set
- Set C is a singleton set
- Set D is a Finite set
- Set E is a Null set
问题 5:解释以下哪些集合是集合 P 的子集,
设置 P = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20}
- 设置 A = {a, 1, 0, 2}
- 设置 B ={0, 2, 4}
- 设置 C = {1, 4, 6, 10}
- 设置 D = {2, 20}
- 设置 E ={18, 16, 2, 10}
回答:
- Set A has elements a, 1, which are not present in the Set P. Therefore, set A is not a Subset.
- Set B has elements which are present in set P, Therefore, Set B ⊆ Set P
- Set C has 1 as an extra element. Hence, not a subset of P
- Set D has 2, 20 as element. Therefore, Set D ⊆ Set P
- Set E has all its elements matching the elements of set P. Hence, Set E ⊆ Set P.