📌 相关文章
- 数据结构和算法选择排序
- 数据结构和算法选择排序(1)
- 数据结构和算法 | 8套(1)
- 数据结构和算法 | 6套(1)
- 数据结构和算法-树(1)
- 数据结构和算法 |组5(1)
- 数据结构与算法(1)
- 数据结构和算法-树
- 数据结构和算法 |组5
- 数据结构和算法 | 6套
- 数据结构与算法
- 数据结构和算法 | 8套
- 数据结构和算法 | 2套
- 数据结构和算法 | 7套
- 数据结构和算法 | 2套(1)
- 数据结构-合并排序算法
- 数据结构-合并排序算法(1)
- 数据结构和算法-快速排序(1)
- 数据结构和算法-快速排序
- python中的数据结构和算法(1)
- 数据结构和算法-数组
- 数据结构和算法-数组(1)
- python代码示例中的数据结构和算法
- 数据结构和算法 |设置 4
- 数据结构和算法 |设置 1
- 数据结构和算法 |设置 3(1)
- 数据结构和算法 |设置 9(1)
- 数据结构和算法 |设置 9
- 数据结构和算法 |设置 3
📜 数据结构和算法-Shell排序
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 10:23:47 🧑 作者: Mango
Shell排序是一种高效的排序算法,它基于插入排序算法。如果较小的值在最右端并且必须移到最左端,则该算法避免了在插入排序的情况下发生大的移位。
该算法对广泛分布的元素使用插入排序,首先对它们进行排序,然后对间距较小的元素进行排序。该间隔称为间隔。该间隔是根据Knuth的公式计算的-
克努斯公式
h = h * 3 + 1
where −
h is interval with initial value 1
该算法对中型数据集非常有效,因为该算法的平均复杂度和最坏情况下的复杂度取决于间隙序列,众所周知的间隙序列为Ο(n),其中n是项数。最坏的情况是空间复杂度为O(n)。
Shell Sort如何工作?
让我们考虑以下示例,以了解壳排序的工作原理。我们采用与先前示例相同的数组。对于我们的示例和易于理解,我们采用4的间隔。为位于4个位置的间隔的所有值创建一个虚拟子列表。这些值是{35,14},{33,19},{42,27}和{10,44}
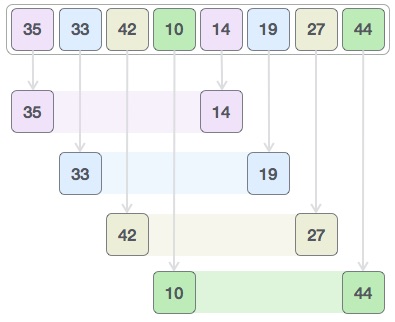
我们比较每个子列表中的值,并在原始数组中交换它们(如果需要)。完成此步骤后,新数组应如下所示:
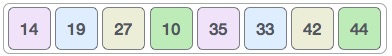
然后,我们取间隔为1,此间隔生成两个子列表-{14,27,35,42},{19,10,33,44}
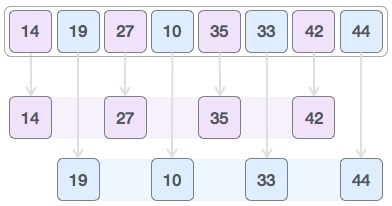
如果需要,我们将比较并交换原始数组中的值。完成此步骤后,数组应如下所示:
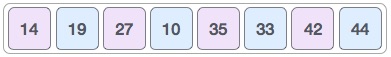
最后,我们使用值1的间隔对数组的其余部分进行排序。Shell sort使用插入排序对数组进行排序。
以下是分步描述-
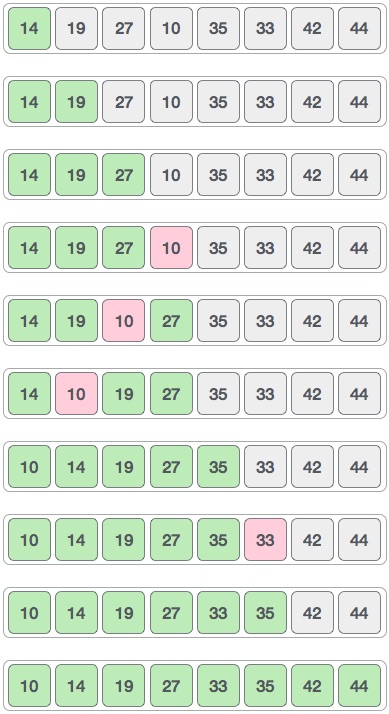
我们看到它只需要四个交换就可以对其余数组进行排序。
算法
以下是外壳排序的算法。
Step 1 − Initialize the value of h
Step 2 − Divide the list into smaller sub-list of equal interval h
Step 3 − Sort these sub-lists using insertion sort
Step 3 − Repeat until complete list is sorted
伪码
以下是用于shell排序的伪代码。
procedure shellSort()
A : array of items
/* calculate interval*/
while interval < A.length /3 do:
interval = interval * 3 + 1
end while
while interval > 0 do:
for outer = interval; outer < A.length; outer ++ do:
/* select value to be inserted */
valueToInsert = A[outer]
inner = outer;
/*shift element towards right*/
while inner > interval -1 && A[inner - interval] >= valueToInsert do:
A[inner] = A[inner - interval]
inner = inner - interval
end while
/* insert the number at hole position */
A[inner] = valueToInsert
end for
/* calculate interval*/
interval = (interval -1) /3;
end while
end procedure
要了解使用C编程语言进行的shell排序实现,请单击此处。