有限递归和无限递归的例子
函数直接或间接调用自身的过程称为递归,对应的函数称为递归函数。
使用递归,可以很容易地解决某些问题。此类问题的示例有河内塔 (TOH)、中序/前序/后序树遍历、DFS 等。
递归类型:
递归可以进一步分为两种,取决于它们何时终止:
- 有限递归
- 无限递归
有限递归:
当递归在有限次数的递归调用后终止时,就会发生有限递归。递归仅在满足基本条件时终止。
例子:
下面是一个演示有限递归的实现。
C++
// C++ program to demsonstrate Finite Recursion
#include
using namespace std;
// Recursive function
void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// When this condition is met,
// the recursion terminates
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
cout << N << " ";
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
class GFG{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// When this condition is met,
// the recursion terminates
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
System.out.println(N + " ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by abhinavjain194Python3
# Python program to demsonstrate Finite Recursion
# Recursive function
def Geek( N):
# Base condition
# When this condition is met,
# the recursion terminates
if (N == 0):
return
# Pr the current value of N
print( N, end =" " )
# Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1)
# Driver code
# Initial value of N
N = 5
# Call the recursive function
Geek(N)
# this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// When this condition is met,
// the recursion terminates
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
Console.Write(N + " ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N - 1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by target_2.Javascript
C++
// C++ program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
#include
using namespace std;
// Recursive function
void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
cout << N << " ";
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
System.out.print( N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110Python3
# Python3 to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
# Recursive function
def Geek(N):
# Base condition
# This condition is never met here
if (N == 0):
return
# Print the current value of N
print(N, end = " " )
# Call itself recursively
Geek(N)
# Driver code
# Initial value of N
N = 5
# Call the recursive function
Geek(N)
# This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110C#
// C# program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
using System;
class GFG
{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
Console.Write( N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110Javascript
输出
5 4 3 2 1 上述递归函数的递归树如下所示。
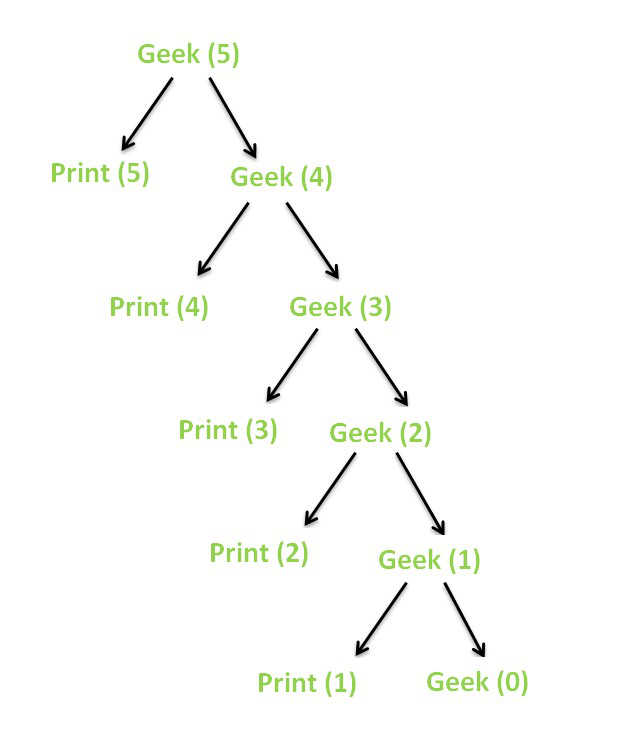
递归树
当N的值变为0 时,由于基本条件,递归终止。
无限递归:
当递归在有限次数的递归调用后没有终止时,就会发生无限递归。由于永远不满足基本条件,递归无限进行。
例子:
下面是一个演示无限递归的实现。
C++
// C++ program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
#include
using namespace std;
// Recursive function
void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
cout << N << " ";
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
System.out.print( N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
蟒蛇3
# Python3 to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
# Recursive function
def Geek(N):
# Base condition
# This condition is never met here
if (N == 0):
return
# Print the current value of N
print(N, end = " " )
# Call itself recursively
Geek(N)
# Driver code
# Initial value of N
N = 5
# Call the recursive function
Geek(N)
# This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C#
// C# program to demsonstrate Infinite Recursion
using System;
class GFG
{
// Recursive function
static void Geek(int N)
{
// Base condition
// This condition is never met here
if (N == 0)
return;
// Print the current value of N
Console.Write( N +" ");
// Call itself recursively
Geek(N);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initial value of N
int N = 5;
// Call the recursive function
Geek(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Javascript
上述递归函数的递归树如下所示。
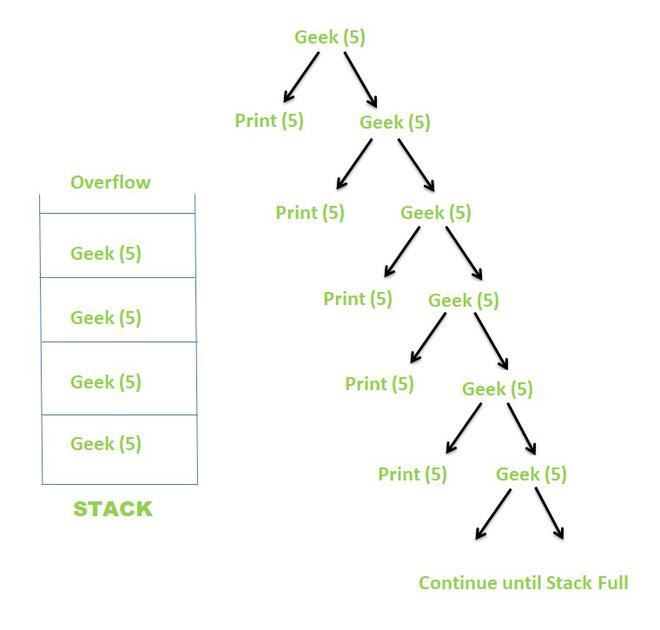
递归树
由于N的值永远不会变为0 ,因此递归永远不会终止。相反,递归继续进行,直到隐式堆栈变满,从而导致堆栈溢出。一些编译器直接将输出作为 Segmentation Fault (Core Dumped) 给出,而其他编译器可能会异常终止某些值,然后显示 Segmentation fault。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。