二叉树中从左下到右上的遍历
给定一棵二叉树,任务是打印给定二叉树的从左下到右上的遍历,即级别顺序遍历的级别为左下到右上节点。
例子:
Input: Below is the given Tree:
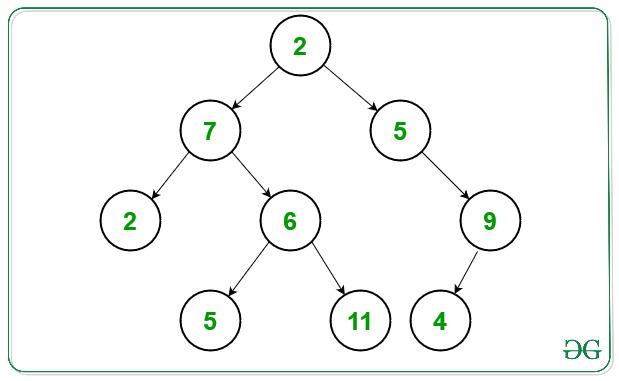
Output: 2 7 2 5 6 5 11 4 9
Explanation:
Level 1: 2 7 2 (going upwards from bottom left to right to root)
Level 2: 5 6 5 (right from each node in layer 1/or bottom left to upwards right in this layer)
Level 3: 11 4 9 (right from each node in layer 2/or bottom left to upwards right in this layer)
Input: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Output: 4 2 1 5 6 3 2
Explanation
Layer 1: 4 2 1 (going upwards from bottom left to right to root)
Layer 2: 5 6 3 (right from each node in layer 1/or bottom left to upwards right in this layer)
Layer 3: 2 (right from each node in layer 2/or bottom left to upwards right in this layer)
方法:这个想法是使用广度优先搜索技术。按照解决此问题所需的步骤:
- 初始化二叉树中的层。它是一个节点列表,从紧邻上一层的最左下角的节点开始,到紧邻上一层的最右上角的节点结束。
- 创建一个堆栈来存储每一层中的所有节点。
- 初始化一个队列以在每一层中维护“根”,层中的根是一个节点,一个节点只能使用左子节点从该节点向下移动。
- 将第一层的根节点(树根)推入队列。
- 定义一个指示符(比如lyr_root )一个预期在层末尾的节点,它是当前层的头,层头是层中的第一个节点。
- 遍历直到队列非空并执行以下操作:
- 从队列前面获取层根
- 如果该层根是新层的层头,则弹出堆栈中的每个元素,即前一层元素的元素,并打印它。
- 从右上到左下遍历层,对于每个元素,如果它有一个右孩子,则检查遍历的节点是否是层头。如果发现为真,则更改预期指示符以指示下一层头部。
- 将右孩子推到队列中的根。
- 将遍历的节点压入栈中。
- 遍历完所有层后,最后一层可能还在栈中,所以我们需要从中弹出每个元素并打印出来。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Node Structures
typedef struct Node {
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
} Node;
// Function to add the new Node in
// the Binary Tree
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* n;
// Create a new Node
n = new Node();
n->data = data;
n->right = NULL;
n->left = NULL;
return n;
}
// Function to traverse the tree in the
// order of bottom left to the upward
// right order
vector
leftBottomTopRightTraversal(Node* root)
{
// Stores the data of the node
vector rr;
// Stores every element in each layer
stack r;
// Stores the roots in the layers
queue roots;
// Push the layer head of the
// first layer
roots.push(root);
// Define the first layer head
// as the tree root
Node* lyr_root = root;
// Traverse all layers
while (!roots.empty()) {
// get current layer root
Node* n = roots.front();
// Pop element from roots
roots.pop();
if (lyr_root == n) {
// Layer root was also
// the layer head
while (!r.empty()) {
rr.push_back(r.top());
// Pop every element
// from the stack
r.pop();
}
}
while (n) {
if (n->right) {
// Current traversed node
// has right child then
// this root is next layer
if (n == lyr_root) {
lyr_root = n->right;
}
// Push the right child
// to layer roots queue
roots.push(n->right);
}
// Push node to the
// layer stack
r.push(n->data);
n = n->left;
}
}
// Insert all remaining elements
// for the traversal
while (!r.empty()) {
// After all of the layer
// roots traversed check the
// final layer in stack
rr.push_back(r.top());
r.pop();
}
// Return the traversal of nodes
return rr;
}
// Function that builds the binary tree
// from the given string
Node* buildBinaryTree(char* t)
{
Node* root = NULL;
// Using queue to build tree
queue q;
int data = 0;
// Stores the status of last
// node to be ignored or not
bool ignore_last = false;
while (*t != '\0') {
int d = *t - '0';
// If the current character
// is a digits then form the
// number of it
if (d >= 0 && d <= 9) {
data *= 10;
data += d;
ignore_last = false;
}
// If the current character
// is N then it is the
// NULL node
else if (*t == 'N') {
data = 0;
q.pop();
ignore_last = true;
}
// If space occured then
// add the number formed
else if (*t == ' ') {
// If last is ignored
if (!ignore_last) {
// If root node is not NULL
if (root) {
Node** p = q.front();
q.pop();
if (p != NULL) {
*p = newNode(data);
q.push(&((*p)->left));
q.push(&((*p)->right));
}
}
// Else create a new
// root node
else {
root = newNode(data);
q.push(&(root->left));
q.push(&(root->right));
}
data = 0;
}
}
// Increment t
t++;
}
// Return the root node of the tree
return root;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given order of nodes
char T[] = "2 7 5 2 6 N 9 N N 5 11 4 N";
// Builds the Binary Tree
Node* root = buildBinaryTree(T);
// Function Call
vector result
= leftBottomTopRightTraversal(root);
// Print the final traversal
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); ++i) {
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
} 2 7 2 5 6 5 11 4 9时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)